ASTM D7811-13(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Bow and Skew Using a Measuring Tool
Standard Test Method for Bow and Skew Using a Measuring Tool
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method provides a standard procedure for obtaining data for research and development, quality control, acceptance and rejection under specifications, and for special purposes.
5.2 The data obtained by this test method is applicable to the material under the conditions of this particular test and is not necessarily the same as obtained under other environments in use.
5.3 This test method is considered satisfactory for acceptance testing of commercial shipments.
5.4 If there are differences of practical significance between reported test results for two laboratories (or more), comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical assistance. As a minimum, the test samples to be used are as homogeneous as possible, are drawn from the material from which the disparate test results were obtained, and are randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. Other fabrics with established test values may be used for this purpose. The test results from the two laboratories should be compared using a statistical test for unpaired data, at a probability level chosen prior to the testing series. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected, or future test results must be adjusted in consideration of the known bias.
5.5 Bow or skew can be induced during fabric manufacturing, dyeing, tentering, finishing, or other operations where a potential exists for uneven distribution of tensions across the fabric width. Bow and skew are more visually displeasing in colored, patterned fabrics such as plaids and horizontal stripes rather than in solid colors because the contrast makes the distortion more prominent. These defects may cause sewing problems in such fabrics and draping problems in finished products. Wavy or sharp breaks in the bow line are more detrimental to the appearance of small specimens of a sewn assembly.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is used to determine the bow and skew of woven and knitted fabrics over a fixed distance, using a measuring tool.
1.2 This test method is useful when a small specimen or cut parts need to be evaluated for bow and skew, provided a warp or fill, or both, reference line is available, to aid in aligning the tool.
1.3 Test Method D3882 may be used when measuring bow and skew in fabric in rolls. However, results obtained with D3882 may not be comparable with results obtained by this test method.
1.4 There is no known ISO equivalent standard.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7811 − 13 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Method for
Bow and Skew Using a Measuring Tool
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7811; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D3882 Test Method for Bow and Skew in Woven and
Knitted Fabrics
1.1 This test method is used to determine the bow and skew
D3990 Terminology Relating to Fabric Defects
of woven and knitted fabrics over a fixed distance, using a
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
measuring tool.
ASTM Test Methods
1.2 This test method is useful when a small specimen or cut
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
parts need to be evaluated for bow and skew, provided a warp
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
or fill, or both, reference line is available, to aid in aligning the
tool.
3. Terminology
1.3 Test Method D3882 may be used when measuring bow
3.1 For all terminology related to fabric defect terms, refer
and skew in fabric in rolls. However, results obtained with
to Terminology D3990.
D3882maynotbecomparablewithresultsobtainedbythistest
3.1.1 Thefollowingtermsarerelevanttothisstandard:bow,
method.
double bow, double hooked bow, double reverse bow, hooked
bow, knitted fabric, skew, standard atmosphere for testing
1.4 There is no known ISO equivalent standard.
textiles.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.2 For all other terminology related to textiles, refer to
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
Terminology D123.
standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Summary of Test Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 A straightedge is placed across the fabric between two
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health and environmental practices and deter- points at which a marked filling yarn, knitted course, desig-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. nated printed line, or designated design meets the two selvages
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor- or edges. The greatest distance between the straightedge and
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- the marked filling line, knitted course, designated printed line,
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the or designated design is measured parallel to the selvage.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
5. Significance and Use
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 This test method provides a standard procedure for
obtaining data for research and development, quality control,
2. Referenced Documents
acceptance and rejection under specifications, and for special
2.1 ASTM Standards: purposes.
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
5.2 Thedataobtainedbythistestmethodisapplicabletothe
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
material under the conditions of this particular test and is not
necessarily the same as obtained under other environments in
use.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
5.3 This test method is considered satisfactory for accep-
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.60 on Fabric Physical Test
Methods B.
tance testing of commercial shipments.
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2022.PublishedJuly2022.Originallyapproved
5.4 If there are differences of practical significance between
in 2013. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D7811-13(2017). DOI:
10.1520/D7811-13R22.
reported test results for two laboratories (or more), compara-
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
tive tests should be performed to determine if there is a
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
statistical bias between them, using competent statistical assis-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. tance. As a minimum, the test samples to be used are as
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7811 − 13 (2022)
homogeneous as possible, are drawn from the material from 6.4 Flat Surface, of sufficient area to lay the test specimen.
which the disparate test results were obtained, and are ran-
6.5 Fabric Inspection Table (Optional) with suffıcient
domlyassignedinequalnumberstoeachlaboratoryfortesting.
lighting, for fabric on rolls or bolts.
Other fabrics with established test values may be used for this
purpose. The test results from the two laboratories should be
7. Interferences
compared using a statistical test for unpaired data, at a
7.1 None identified.
probability level chosen prior to the testing series. If a bias is
found, either its cause must be found and corrected, or future
8. Sampling
test results must be adjusted in consideration of the known
8.1 When testing fabric in rolls, consider rolls to be the
bias.
primarysamplingunitsandselectatleastthreeareasfromeach
5.5 Bow or skew can be induced during fabric
roll for testing, excluding the first and last fifth of the roll.
manufacturing, dyeing, tentering, finishing, or other operations
Select areas for testing at random, and no closer to one another
where a potential exists for uneven distribution of tensions
than one fifth of the length of the roll.
across the fabric width. Bow and skew are more visually
8.2 Forcutpartsofsufficientsizefortesting(i.e.atleast400
displeasing in colored, patterned fabrics such as plaids and
mm in length), consider each part a test specimen, and test at
horizontal stripes rather than in solid colors because the
least three randomly chosen specimens.
contrast makes the distortion more prominent. These defects
may cause sewing problems in such fabrics and draping
9. Calibration and Standardization
problemsinfinishedproducts.Wavyorsharpbreaksinthebow
9.1 Bow and Skew Measurement Tool Calibration:
line are more detrimental to the appearance of small specimens
of a sewn assembly.
9.2 Bow Skew Measurement Tool is to be verified to Fig. 3
dimensions by using scale or rule traceable to NIST or
6. Apparatus
equivalent national standard.
6.1 Millimeter Rule, graduated in 1 mm ( ⁄16-in.) divisions.
10. Conditioning
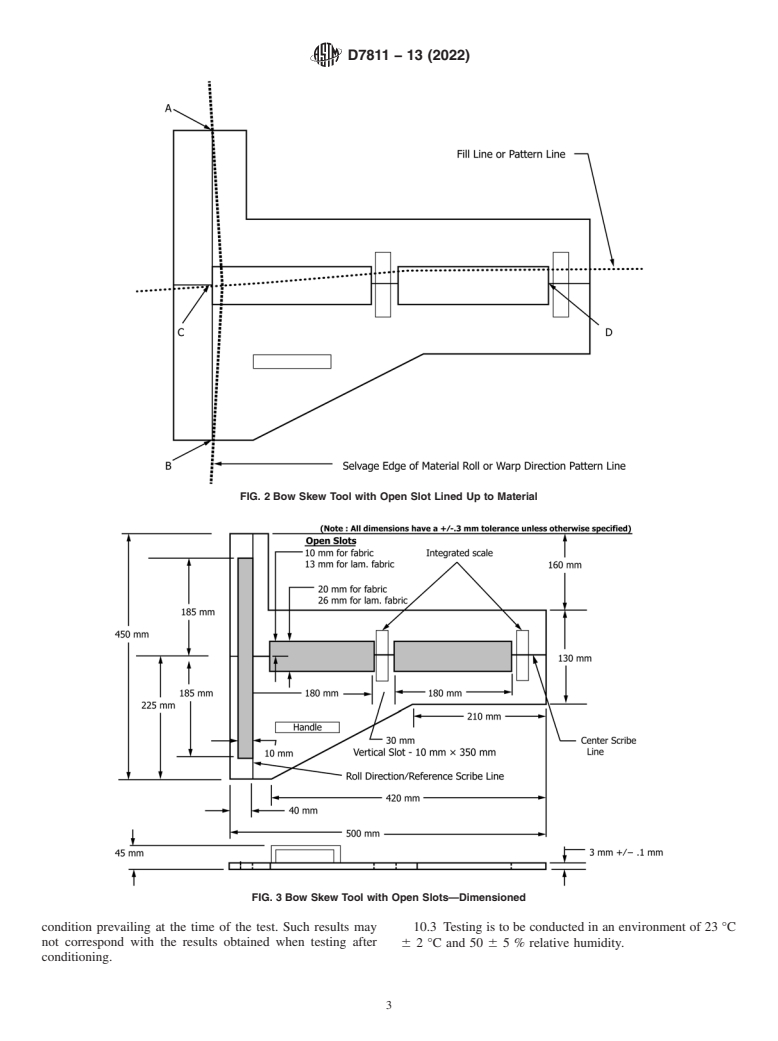
6.2 Test Fixture—See Fig. 1 and Fig. 3. This tool, hereafter
referred to as “bow and skew measurement tool” is to be used 10.1 Condition the test specimens to moisture equilibrium
for each measurement. for testing in the standard atmosphere for testing textiles in
6.2.1 Fig. 3 is a dimensioned drawing of bow and skew accordance with Practice D1776 or, if applicable, in the
measurement tool. specified atmosphere in which the testing is to be performed.
6.3 Bow Skew Measurement Tool Construction: 10.2 When full rolls or bolts of fabric cannot be properly
6.3.1 Transparent material such as polycarbonate. conditioned in a reasonable time with available facilities,
perform the test without conditioning and report the actual
6.3.2 Thickness 3 mm to 5 mm.
FIG. 1 Bow Skew Tool with Open Slot
D7811 − 13 (2022)
FIG. 2 Bow Skew Tool with Open Slot Lined Up to Material
FIG. 3 Bow Skew Tool with Open Slots—Dimensioned
condition prevailing at the time of the test. Such results may 10.3 Testing is to be conducted in an environment of 23 °C
not correspond with the results obtained when testing after 6 2 °C and 50 6 5 % relative humidity.
conditioning.
D7811 − 13 (2022)
FIG. 4 Photograph of Test Tool (Typical)
10.4 Condition test specimens for 24 h in an environment of 11.7 Record the measurement. The scale on the Bow and
23 °C 6 2 °C and 50 6 5 % relative humidity. Skew Measurement Tool has 1 mm increments grouped in
sections of 5 mm each totaling 620 mm from Line CD.
10.5 If test specimens are conditioned for less than 24 h, or
11.8 Move the Bow and Skew Measurement Tool to the
under different conditions, note and report the alternative
times/conditions used. right so that point C is now located where point D was
previously(LineCDis400mmwhichisthedimensionthatthe
10.6 If the test specimen is tested in an environment other
Bow or Skew is to be measured over).
than the environment outlined in 10.3, note actual environmen-
11.9 Line up point C on the same fill line or pattern that was
tal conditions at the time of testing.
chosen in step 11.3.
11. Procedure A—Using the Tool on Rolled Goods
11.10 PositiontheBowandSkewMeasurementToolsothat
11.1 Start by positioning the Bow and Skew Measurement
Line AB is now located over a warp line or pattern instead of
Tool (reference Fig. 1 and Fig. 2) to the far left side of the
selvage edge (use method in step 11.2) if warp line or pattern
unrolled material.
is not straight.
11.2 Line up line AB on the Bow and Skew Measurement
11.11 Recheck that Line CD is on the correct fill line or
Tool to the selvage edge of the material (selvage may curve
pattern and recheck that Line AB is still on a warp line or
away from LineAB – match pointsA& B to edge as shown in
pattern – repeat 11.9 and 11.10 as
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.