ASTM D7270-07
(Guide)Standard Guide for Environmental and Performance Verification of Factory-Applied Liquid Coatings
Standard Guide for Environmental and Performance Verification of Factory-Applied Liquid Coatings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The primary objective of this verification guide is to determine the “air pollution-prevention potential” (possible reduction in VOC or HAP emissions) of factory-applied liquid coatings.
The overall objective of this guide is to verify the above pollution-prevention characteristics and basic performance characteristics of liquid coating technologies. Use of this guide can increase acceptance of more environmentally friendly technologies for product finishing with an accompanying reduction in emissions to the atmosphere. The specific objectives of this guide are to (1) quantify the VOC and HAP content of liquid coatings and (2) verify the basic quality and durability performance of these coatings.
The primary criteria for verification of liquid coatings will be:
3.3.1 Confirm that use of the coating will significantly reduce VOC and HAP content or emissions (or both) during application or cure, or both.
3.3.2 Confirm that the coating can provide an acceptable finish (appearance, hardness, flexibility, etc.) for the intended end use.
The test results from this guide can provide to potential users the best data available to determine whether the coating will provide a pollution-prevention benefit while meeting the finish quality requirements for its intended use. This guide intends to supply end users with unbiased technical data to assist them in this decision-making process.
The quantitative air pollution-prevention potential depends on a multitude of factors; therefore, the liquid coatings are to be applied in accordance with the coating vendor’s instructions and the resulting verification data reflect only the specific conditions of the test. To quantify the environmental benefit (air pollution-prevention potential), a test to quantify the VOC or HAP emissions from the new liquid coatings will be conducted and compared to data for existing coatings typically used in the target industry.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides a generic testing procedure to verify the air pollution-prevention characteristics and basic properties of liquid coatings applied to metal, plastic, wood, or composite substrates in a factory/manufacturing environment. Thus it may be used to evaluate these liquid coatings to verify their volatile organic compound (VOC) and organic hazardous air pollutant (HAP) content as well as basic performance properties.
1.2 This guide is adapted from a procedure used by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to establish third party verification of the physical properties and performance of coatings that have potential to reduce air emissions. The data from the verification testing is available on the internet at the EPAs Environmental Technology Verification (ETV) Program website (http://www.epa.gov/etv/centers/center6.html) under the "P2 Innovative Coatings and Coating Equipment Pilot."
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7270 −07
StandardGuide for
Environmental and Performance Verification of Factory-
Applied Liquid Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7270; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D522 Test Methods for Mandrel Bend Test of Attached
Organic Coatings
1.1 Thisguideprovidesagenerictestingproceduretoverify
D523 Test Method for Specular Gloss
the air pollution-prevention characteristics and basic properties
D1729 Practice for Visual Appraisal of Colors and Color
of liquid coatings applied to metal, plastic, wood, or composite
Differences of Diffusely-Illuminated Opaque Materials
substrates in a factory/manufacturing environment. Thus it
D1735 Practice for Testing Water Resistance of Coatings
may be used to evaluate these liquid coatings to verify their
Using Water Fog Apparatus
volatile organic compound (VOC) and organic hazardous air
pollutant (HAP) content as well as basic performance proper- D2244 Practice for Calculation of Color Tolerances and
ties.
Color Differences from Instrumentally Measured Color
Coordinates
1.2 This guide is adapted from a procedure used by the US
D2369 Test Method for Volatile Content of Coatings
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to establish third
D2794 Test Method for Resistance of Organic Coatings to
partyverificationofthephysicalpropertiesandperformanceof
the Effects of Rapid Deformation (Impact)
coatings that have potential to reduce air emissions. The data
from the verification testing is available on the internet at the D3359 Test Methods for Measuring Adhesion by Tape Test
EPA’s Environmental Technology Verification (ETV) Program D3363 Test Method for Film Hardness by Pencil Test
website (http://www.epa.gov/etv/centers/center6.html) under
D3792 Test Method forWater Content of Coatings by Direct
the “P2 Innovative Coatings and Coating Equipment Pilot.”
Injection Into a Gas Chromatograph
D3960 PracticeforDeterminingVolatileOrganicCompound
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
(VOC) Content of Paints and Related Coatings
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
D4017 Test Method for Water in Paints and Paint Materials
only.
by Karl Fischer Method
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D4060 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Organic
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Coatings by the Taber Abraser
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
D4457 Test Method for Determination of Dichloromethane
priate safety and health practices and to determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. and 1,1,1-Trichloroethane in Paints and Coatings by
Direct Injection into a Gas Chromatograph
2. Referenced Documents
D5402 Practice for Assessing the Solvent Resistance of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Organic Coatings Using Solvent Rubs
B117 Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus
D5767 Test Methods for Instrumental Measurement of
B499 Test Method for Measurement of Coating Thicknesses
Distinctness-of-Image Gloss of Coating Surfaces
by the Magnetic Method: Nonmagnetic Coatings on
D6133 Test Method for Acetone, p-Chlorobenzotrifluoride,
Magnetic Basis Metals
Methyl Acetate or t-Butyl Acetate Content of Solvent-
borne and Waterborne Paints, Coatings, Resins, and Raw
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Materials by Direct Injection Into a Gas Chromatograph
Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
D6438 Test Method for Acetone, Methyl Acetate, and
Subcommittee D01.55 on Factory Applied Coatings on Preformed Products.
Parachlorobenzotrifluoride Content of Paints, and Coat-
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2007. Published March 2007. DOI: 10.1520/
D7270-07. ings by Solid Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatogra-
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
phy
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
D6695 Practice for Xenon-Arc Exposures of Paint and
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. Related Coatings
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D7270−07
D6886 Test Method for Determination of the Individual commercial equipment. The coating application equipment in
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) inAir-Dry Coatings the test facility should be available for the pilot-scale testing
by Gas Chromatography performed in this guide (for example, surface pretreatment,
powder coating, electrocoating, wet spray, and conventional
2.2 EPA Methods
forced-air and infrared ovens, as applicable). Layouts of an
EPAMethod 24 Surface Coatings (Determination ofVolatile
example of an approved test facility are shown in Appendix
Matter Content, Water Content, Density, Volume Solids,
X1,Figs.X1.1andX1.2,respectively.Examplesofthevarious
and Weight Solids of Surface Coatings)
EPAMethod 311 HAPS in Paints and Coatings (Analysis of testing laboratories and their representative equipment hold-
ings that are relevant to the approved test facility verification
Hazardous Air Pollutant Compounds in Paints and Coat-
ings by Direct Injection Into a Gas Chromatograph) projects are listed in Table X1.1.
4.2 A test plan, referred to as a Testing and Quality
3. Significance and Use
AssuranceProtocol(T/QAP),willbeestablishedtoprovidethe
3.1 The primary objective of this verification guide is to
testing details that are dependent upon the specific liquid
determine the “air pollution-prevention potential” (possible
coating being tested. Some general guidelines and procedures
reduction in VOC or HAPemissions) of factory-applied liquid
can be applied to each T/QAP. These include:
coatings.
4.2.1 A detailed description of each part of the test will be
provided. The selection of tests to be performed, test details,
3.2 The overall objective of this guide is to verify the above
pollution-prevention characteristics and basic performance evaluation methods and acceptance criteria are defined by the
end use requirements of the coating. These details should be
characteristics of liquid coating technologies. Use of this guide
can increase acceptance of more environmentally friendly incorporatedintoatestplanthatisuniquetoeachcoating.This
will include a detailed design of experiments and a schematic
technologies for product finishing with an accompanying
diagram of testing to be performed.
reduction in emissions to the atmosphere. The specific objec-
tivesofthisguideareto(1)quantifytheVOCandHAPcontent 4.2.2 Critical and noncritical factors will be listed. Noncriti-
ofliquidcoatingsand(2)verifythebasicqualityanddurability cal factors will remain constant throughout the testing. Critical
performance of these coatings. factors will be listed as control (process) factors or response
(coating product quality) factors.
3.3 The primary criteria for verification of liquid coatings
4.2.3 The T/QAP will identify the testing site.
will be:
4.2.4 Regardless of where the testing is performed, the
3.3.1 Confirm that use of the coating will significantly
approved test facility will ensure that the integrity of third-
reduce VOC and HAP content or emissions (or both) during
party testing is maintained.
application or cure, or both.
4.2.5 Regardless of where the testing is performed, the
3.3.2 Confirm that the coating can provide an acceptable
Quality Assurance (QA) portion of the guide will be strictly
finish (appearance, hardness, flexibility, etc.) for the intended
adhered to.
end use.
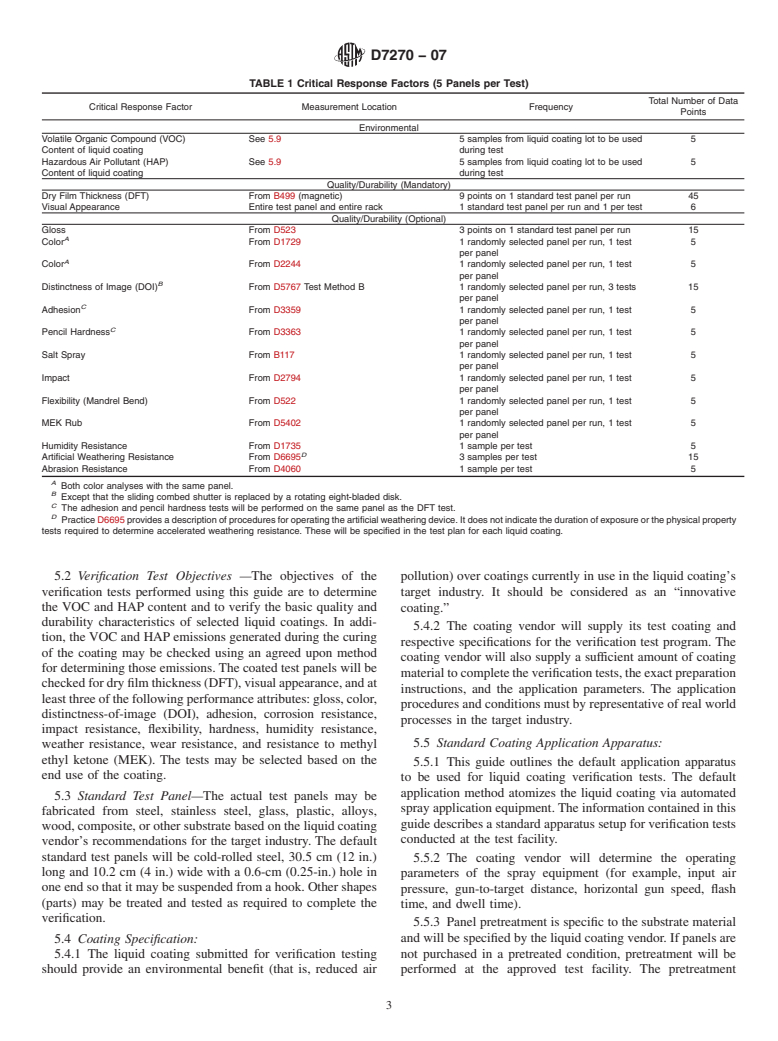
4.2.6 A statistically significant number of samples will be
3.4 The test results from this guide can provide to potential
analyzed for each critical response factor (see Table 1).
users the best data available to determine whether the coating
Variances (or standard deviations) of each critical response
will provide a pollution-prevention benefit while meeting the
factor will be reported for all results.
finish quality requirements for its intended use. This guide
4.3 The test facility will be selected and must meet the
intends to supply end users with unbiased technical data to
standards of the individual T/QAP and the test facility’s
assist them in this decision-making process.
Quality Management Plan (QMP). Example QMPs can be
3.5 The quantitative air pollution-prevention potential de-
found at the ETV Website (http://epa.gov/etv). Testing person-
pends on a multitude of factors; therefore, the liquid coatings
nelwilldocumentallcriticalandnoncriticalcontrolfactorsand
are to be applied in accordance with the coating vendor’s
qualitative noncritical control factors.
instructions and the resulting verification data reflect only the
specific conditions of the test. To quantify the environmental
5. Procedure
benefit (air pollution-prevention potential), a test to quantify
the VOC or HAP emissions from the new liquid coatings will 5.1 Test Approach—Thefollowingapproachforverification
be conducted and compared to data for existing coatings of coating performance will be used in the test protocol:
typically used in the target industry. 5.1.1 Determine the performance parameters to be verified.
5.1.2 Choose a standard test panel (and possibly other
4. Testing Site
items) that will enable thorough testing of coating perfor-
mance.
4.1 To accelerate the transition of environmentally friendly
processes to the manufacturing base, the test facility should 5.1.3 Select the test coating and the optimum equipment
offertheabilitytotestprocessesandproductsonrepresentative
settings for application and curing based on information
furnished by the coating manufacturer.
5.1.4 Complete the verification test.
US EPA, Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards (OAQPS), TTN EMC
5.1.5 Analyze the results using a statistically valid test
Webmaster (C304-03), Research Triangle Park, NC 27711(website, www.epa.gov/
ttn/emc). program that efficiently accomplishes the required objectives.
D7270−07
TABLE 1 Critical Response Factors (5 Panels per Test)
Total Number of Data
Critical Response Factor Measurement Location Frequency
Points
Environmental
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) See 5.9 5 samples from liquid coating lot to be used 5
Content of liquid coating during test
Hazardous Air Pollutant (HAP) See 5.9 5 samples from liquid coating lot to be used 5
Content of liquid coating during test
Quality/Durability (Mandatory)
Dry Film Thickness (DFT) From B499 (magnetic) 9 points on 1 standard test panel per run 45
Visual Appearance Entire test panel and entire rack 1 standard test panel per run and 1 per test 6
Quality/Durability (Optional)
Gloss From D523 3 points on 1 standard test panel per run 15
A
Color From D1729 1 randomly selected panel per run, 1 test 5
per panel
A
Color From D2244 1 randomly selected panel per run, 1 test 5
per panel
B
Distinctness of Image (DOI) From D5767 Test Method B 1 randomly selected panel per run, 3 tests 15
per panel
C
Adhesion From D3359 1 randomly selected panel per run, 1 test 5
per panel
C
Pencil Hardness From D3363 1 randomly selected panel per run, 1 test 5
per panel
Salt Spray From B117 1 randomly selected panel per run, 1 test 5
per panel
Impact From D2794 1 randomly selected panel per run, 1 test 5
per panel
Flexibility (Mandrel Bend) From D522 1 randomly selected panel per run, 1 test 5
per panel
MEK Rub From D5402 1 randomly selected panel per run, 1 test 5
per panel
Humidity Resistance From D1735 1 sample per test 5
D
Artificial Weathering Resistance From D6695 3 samples per test 15
Abrasion Resistance From D4060 1 sample per test 5
A
Both color analyses with the same panel.
B
Except that the sliding combed shutter is replaced by a rotating eight-bladed disk.
C
The adhesion and pencil hardness tests will be performed on the same panel as the DFT test.
D
PracticeD6695providesadescriptionofproceduresforoperatingtheartificialweatheringdevice.Itdoesnotindicatethedurationofexposureorthephysicalproperty
tests required to determine accelerated weathering resistance. These will be specified in the test plan for each liquid coating.
5.2 Verification Test Objectives —The objectives of the pollution) over coatings currently in use in the liquid coating’s
verification tests performed using this guide are to determine target industry. It should be considered as an “innovative
the VOC and HAP content and to verify the basic quality and
coating.”
durability characteristics of selected liquid coatings. In addi-
5.4.2 The coating vendor will supply its test coating and
tion, the VOC and HAPemissions generated during the curing
respective specifications for the verification test program. The
of the coating may be checked using an agreed upon method
coating vendor will also supply a sufficient amount of coating
for determining those emissions.The coated test panels will be
materialtocompletetheverificationtests,theexactpreparation
checkedfordryfilmthickness(DFT),visualappearance,andat
instructions, and the application parameters. The application
leastthreeofthefollowingperformanceattributes:gloss,color,
procedures and conditions must by representative of real world
distinctness-of-image (DOI), adhesion, corrosion resistance,
processes in the target industry.
impact resistance, flexibility, hardness, humidity resistance,
weather resistance, wear resistance, and resistance to methyl 5.5 Standard Coating Application Apparatus:
ethyl ketone (MEK). The tests may be selected based on the
5.5.1 This guide outlines the default application apparatus
end use of the coating.
to be used for liquid coating verification tests. The default
application method atomizes the liquid coating via automated
5.3 Standard Test Panel—The actual test panels may be
spray application equipment.The information contained in this
fabricated from steel, stainless steel, glass, plastic, alloys,
guide describes a standard apparatus setup for verification tests
wood,composite,orothersubstratebasedontheliquidcoating
conducted at the test facility.
vendor’s recommendations for the target industry. The default
standard test panels will be cold-rolled steel, 30.5 cm (12 in.) 5.5.2 The coating vendor will determine the operating
long and 10.2 cm (4 in.) wide with a 0.6-cm (0.25-in.) hole in
parameters of the spray equipment (for example, input air
one end so that it may be suspended from a hook. Other shapes
pressure, gun-to-target distance, horizontal gun speed, flash
(parts) may be treated
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.