ASTM E619-84(1995)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Evaluating Foreign Odors in Paper Packaging
Standard Practice for Evaluating Foreign Odors in Paper Packaging
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the evaluation of odors in paper packaging and establishes smelling and testing procedures for trained sensory panels.
1.2 This practice covers effective techniques for determining the type and source of the odor and establishing the severity of contamination.
1.3 The techniques used in this practice are applicable to all paper packaging products and to auxiliary components, such as coatings, inks, and adhesives, as well as plastic materials used in conjunction with paper.
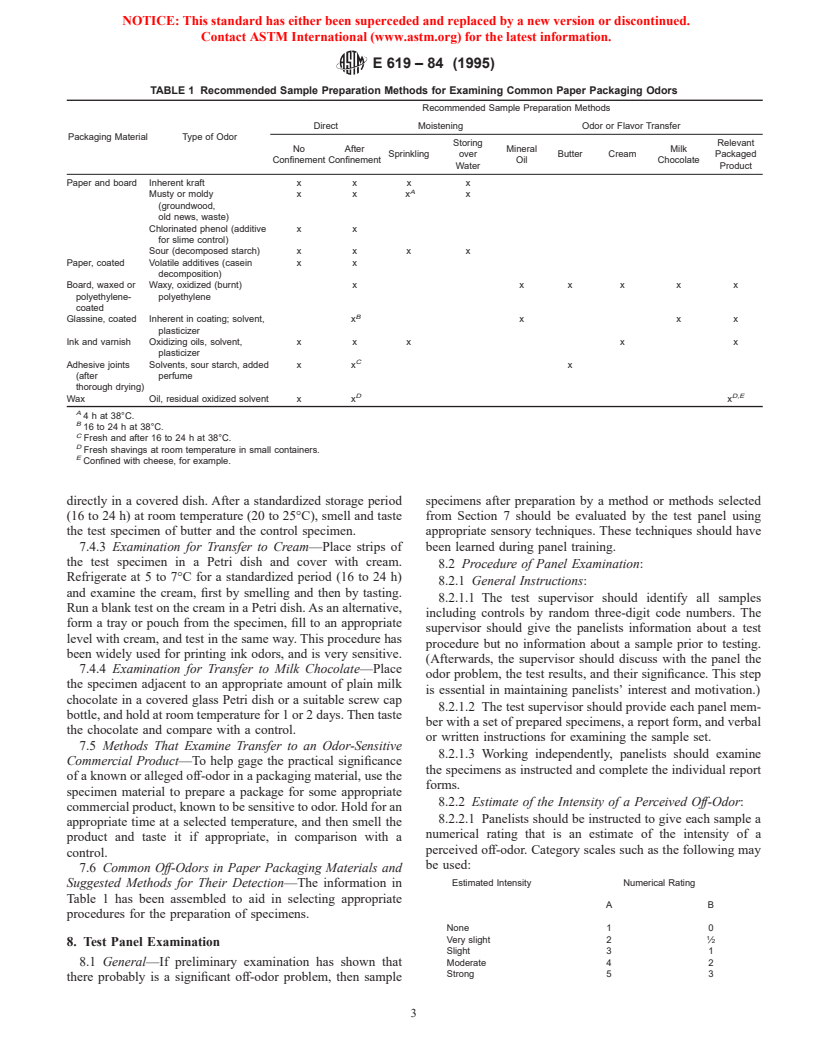
1.4 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems associated with its use. It is the responsibility of whoever uses this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: E 619 – 84 (Reapproved 1995)
Standard Practice for
1
Evaluating Foreign Odors in Paper Packaging
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 619; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 4. Sensory Test Panel Selection and Training
1.1 This practice covers the evaluation of odors in paper 4.1 General—Sensory panel selection and training are de-
packaging and establishes smelling and testing procedures for scribed in STP 758 and in references therein.
trained sensory panels. 4.2 Size—The test panel on a specific odor problem should
1.2 This practice covers effective techniques for determin- consist of at least five members and should render a minimum
ing the type and source of the odor and establishing the severity total of ten judgments per sample. A maximum of twelve
of contamination. subjects may be used, if available. When possible, the subjects
1.3 The techniques used in this practice are applicable to all should be drawn from a larger pool of qualified panelists.
paper packaging products and to auxiliary components, such as 4.3 Selection—The important criteria in panel selection are:
coatings, inks, and adhesives, as well as plastic materials used (a) normal ability to detect and identify odors and flavors; (b)
in conjunction with paper. ability to discriminate differences, and reproduce results; and
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the (c) interest in the testing work for which the panelists are to be
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the trained. Usually a suitable panel can be recruited from avail-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- able employees unless their number is limited. It is helpful if
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- panel members have a scientific background, with some
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. knowledge of chemistry or food technology; however, this
should not be a criterion for selection. Nontechnical personnel
2. Summary of Practice
have often proved to be excellent panel members after appro-
2.1 Under the leadership of the test supervisor, qualified and
priate training. No willing and available person should be
trained subjects individually examine sample specimens by one excluded from consideration. Panel members should be
or more of the test procedures described in this practice.
requalified periodically.
Subjects judge the intensity of a perceived off-odor in terms of
5. Testing Facilities and Apparatus
a numerical rating scale and also attempt to give a qualitative
description of the taint. The assembled observations are then 5.1 General—Appropriate physical conditions for sensory
3
interpreted by the supervisor. panel operations are described in STP 434.
5.2 Testing Room—Detection of low levels of odor requires
3. Significance and Use
a working space in which individual members of the panel can
3.1 Use—This practice should be used by panelists, trained concentrate on the task. The room should be comfortable as to
2
as described in ASTM STP 758 , under the direction of a
temperature, humidity, and noise, and relatively free of labo-
knowledgeable supervisor. ratory industrial odors. If ambient odor levels are too high,
3.2 Significance—This practice can be used to evaluate
testing of the samples must be transferred to another location.
indigenous and foreign odors in paper packaging materials as Interruptions and other distracting influences should be
to type and intensity. A knowledgeable supervisor may be able
avoided.
to determine the source of a foreign odor from the information 5.3 Sample Containers—Clean, dry, closed, odor-free con-
obtained from this procedure.
tainers of appropriate sizes are needed for storing samples and
for confining specimens to develop maximum odor intensity or
to test for taste transfer. Laboratory glassware, capped glass
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-18 on Sensory
jars, and glass battery jars with plate glass lids are suitable for
Evaluation Materials and Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
this purpose. Rubber gaskets or stoppers should not be used.
E18.05 on Sensory Applications—General.
Current edition approved Nov. 30, 1984. Published January 1985.
2
Guidelines for the Selection and Training of Sensory Evaluation Panels, ASTM
3
STP 758, ASTM, 1981. Manual on Sensory Testing Methods, ASTM STP 434, ASTM, 1968.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr H
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.