ASTM D3352-08
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Strontium Ion in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines
Standard Test Method for Strontium Ion in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method can be used to determine strontium ions in brackish water, seawater, and brines.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of soluble strontium ion in brackish water, seawater, and brines by atomic absorption spectrophotometry.
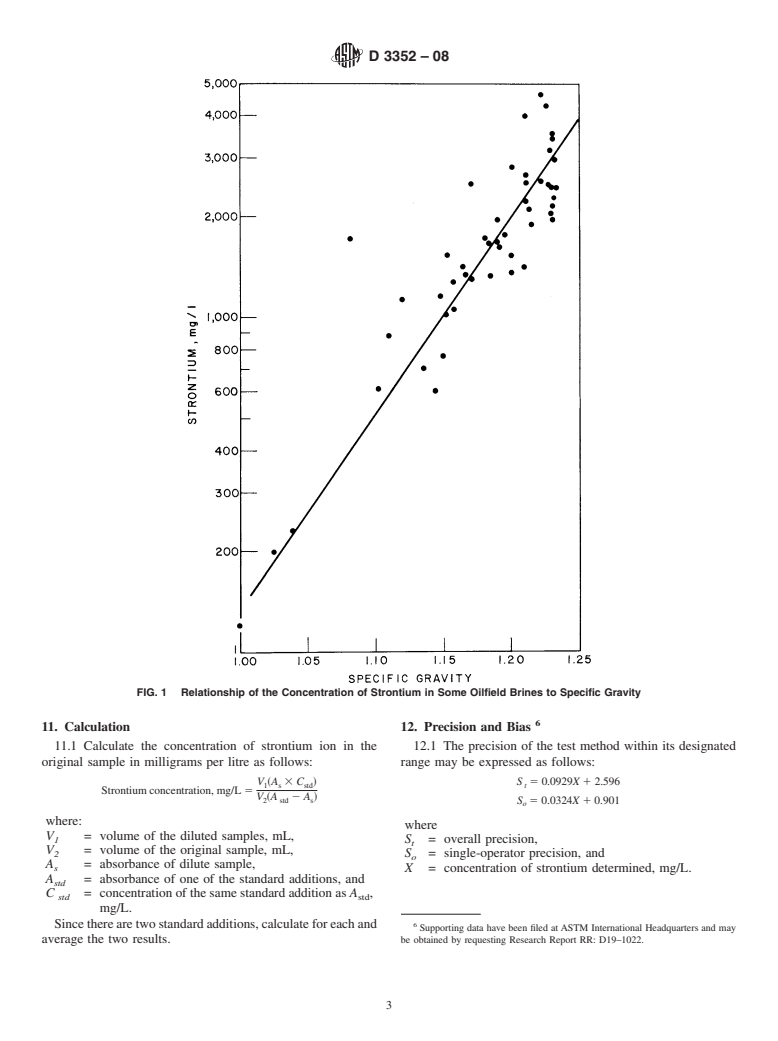
1.2 Samples containing from 5 to 2100 mg/L of strontium may be analyzed by this test method.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 3352 – 08
Standard Test Method for
1
Strontium Ion in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3352; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ground state atoms of that element, the intensity of the
transmitted radiation will decrease in proportion to the amount
1.1 This test method covers the determination of soluble
of the ground state element in the flame. A hollow cathode
strontium ion in brackish water, seawater, and brines by atomic
lamp whose cathode is made of the element to be determined
absorption spectrophotometry.
3
provides the radiation. The metal atoms to be measured are
1.2 Samples containing from 5 to 2100 mg/L of strontium
placed in the beam of radiation by aspirating the specimen into
may be analyzed by this test method.
an oxidant-fuel flame. A monochromator isolates the charac-
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
teristic radiation from the hollow cathode lamp and a photo-
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
sensitive device measures the attenuated transmitted radiation.
standard.
4.2 Sincethevariableandsometimeshighconcentrationsof
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
matrix materials in the waters and brines affect absorption
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
differently,itisdifficulttopreparestandardssufficientlysimilar
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
to the waters and brines. To overcome this difficulty, the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
method of additions is used in which three identical samples
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
are prepared and varying amounts of a standard added to two
2. Referenced Documents of them. The three samples are then aspirated, the concentra-
2
tion readings recorded, and the original sample concentration
2.1 ASTM Standards:
calculated.
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
5. Significance and Use
D 2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
4
5.1 This test method can be used to determine strontium
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
ions in brackish water, seawater, and brines.
D 3370 PracticesforSamplingWaterfromClosedConduits
D 5810 Guide for Spiking into Aqueous Samples
6. Interferences
D 5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
6.1 The chemical suppression caused by silicon, aluminum,
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
and phosphate is controlled by adding lanthanum. The lantha-
3. Terminology num also controls ionization interference.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
7. Apparatus
method, refer to Terminology D 1129.
7.1 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer—The instrument
4. Summary of Test Method shall consist of atomizer and burner, suitable pressure-
regulating devices capable of maintaining constant oxidant and
4.1 This test method is dependent on the fact that metallic
fuelpressureforthedurationofthetest,ahollowcathodelamp
elements, in the ground state, will absorb light of the same
for each metal to be tested, an optical system capable of
wavelength they emit when excited. When radiation from a
given excited element is passed through a flame containing
3
For additional information on atomic absorption, see the following references:
Angino, E. E., and Billings, G. K., Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry in
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water Geology, Elsevier Publishing Co., NewYork, N.Y., 1967. Dean, J.A., and Rains, T.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic Constituents C., Editors, Flame Emission and Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Vol 1−Theory,
in Water. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 1969.
4
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally Additional information is contained in the following references: Fletcher, G. F.,
´1
approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 3352 – 03 . and Collins, A. G., “Atomic Absorption Methods of Analysis of Oilfield Brines:
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Barium,Calcium,Copper,Iron,Lead,Lithium,Magnesium,Manganese,Potassium,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Sodium, Strontium, and Zinc,” U.S. Bureau of Mines, Report of Investigations
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on 7861, 1974, 14 pp. Collins, A. G., Geochemi
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation:D 3352–03 Designation: D 3352 – 08
Standard Test Method for
1
Strontium Ion in Brackish Water, Seawater, and Brines
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3352; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Editorial corrections were made throughout in August 2003.
1. Scope *
1.1 This test method covers the determination of soluble strontium ion in brackish water, seawater, and brines by atomic
absorption spectrophotometry.
1.2 Samples containing from 5 to 2100 mg/L of strontium may be analyzed by this test method.
1.3
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D 2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
D 3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D 5810 Guide for Spiking into Aqueous Samples
D 5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods infor Water Analysis
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D 1129.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Thistestmethodisdependentonthefactthatmetallicelements,inthegroundstate,willabsorblightofthesamewavelength
they emit when excited. When radiation from a given excited element is passed through a flame containing ground state atoms of
that element, the intensity of the transmitted radiation will decrease in proportion to the amount of the ground state element in the
3
flame. A hollow cathode lamp whose cathode is made of the element to be determined provides the radiation. The metal atoms
tobemeasuredareplacedinthebeamofradiationbyaspiratingthespecimenintoanoxidant-fuelflame.Amonochromatorisolates
the characteristic radiation from the hollow cathode lamp and a photosensitive device measures the attenuated transmitted
radiation.
4.2 Since the variable and sometimes high concentrations of matrix materials in the waters and brines affect absorption
differently, it is difficult to prepare standards sufficiently similar to the waters and brines. To overcome this difficulty, the method
of additions is used in which three identical samples are prepared and varying amounts of a standard added to two of them. The
three samples are then aspirated, the concentration readings recorded, and the original sample concentration calculated.
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD19onWaterandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.05onInorganicConstituentsinWater.
Current edition approved June 10, 2003. Published July 2003. Originally approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D3352–94(1999).
´1
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 3352 – 03 .
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.02.
3
For additional information on atomic absorption, see the following references: Angino, E. E., and Billings, G. K., Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry in Geology,
Elsevier Publishing Co., NewYork, N.Y., 1967. Dean, J.A., and Rains, T. C., Editors, Flame Emission andAtomicAbsorption Spectrometry Vol 1−Theory, Marcel Dekker,
New York, NY, 1969.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 3352 – 08
5. Significance and Use
4
5.1 This test method can be used to determine strontium ions in brackish water, seawater, and brines.
6. Interfe
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.