ASTM D4322-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Residual Acrylonitrile Monomer Styrene-Acrylonitrile Copolymers and Nitrile Rubber by Headspace Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Residual Acrylonitrile Monomer Styrene-Acrylonitrile Copolymers and Nitrile Rubber by Headspace Gas Chromatography
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is suitable for determining the residual acrylonitrile (RAN) content of styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN) copolymer, rubber-modified acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) resins, and nitrile rubber (NBR).
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 9.
Note 1--Although the packed column option of this test method and ISO 4581:1994 (E) differ in some details, data obtained using either test method should be technically equivalent. There is no equivalent ISO standard for the capillary column option of this test method.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4322 – 96
Standard Test Method for
Residual Acrylonitrile Monomer Styrene-Acrylonitrile
Copolymers and Nitrile Rubber by Headspace Gas
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4322; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.8 PC—propylene carbonate.
3.2.9 ppm—μg RAN/g polymer (parts per million).
1.1 This test method is suitable for determining the residual
acrylonitrile (RAN) content of styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN)
4. Summary of Test Method
copolymer, rubber-modified acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene
4.1 A dispersion of the polymer in a suitable solvent is
(ABS) resins, and nitrile rubber (NBR).
prepared in a headspace vial and sealed. The vial is thermally
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
equilibrated in a constant temperature bath.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.2 After equilibrium, a given portion of the sample head-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
space is injected into a gas chromatographic column packed
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
with porous polymer beads or a capillary column coated with
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
an appropriate liquid phase. Sample injection is achieved using
tionary statements are given in Section 9.
available commercial automatic equipment or a manual syringe
NOTE 1—Although the packed column option of this test method and
injection technique. Passing through the column in a stream of
ISO 4581:1994 (E) differ in some details, data obtained using either test
carrier gas, acrylonitrile is separated from other components
method should be technically equivalent. There is no equivalent ISO
that may be present. The response of acrylonitrile is measured
standard for the capillary column option of this test method.
by a nitrogen-specific detector for packed column analysis or a
2. Referenced Documents flame ionization detector for capillary column analysis and this
signal is recorded to indicate the retention time and relative
2.1 ASTM Standards:
concentration of acrylonitrile.
D 4526 Practice for Determination of Volatiles in Polymers
by Headspace Gas Chromatography
5. Significance and Use
E 380 Practice for Use of the International System of Units
5.1 For various reasons one may wish to measure the
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
3 amount of unreacted or residual acrylonitrile monomer in
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
styrene-acrylonitrile copolymers, nitrile rubbers, or ABS ter-
3. Terminology polymers.
5.2 Under optimum conditions, the lowest level of detection
3.1 Units and Symbols used in this test method are those
of AN in SAN or ABS copolymers and NBR rubbers is
recommended in Practice E 380.
approximately 0.5 ppm for the packed column test method and
3.2 Abbreviations:
3 ppm for the capillary test method.
3.2.1 AN—acrylonitrile.
3.2.2 RAN—residual acrylonitrile.
6. Interferences
3.2.3 SAN—styrene-acrylonitrile copolymer.
6.1 The nitrogen-specific detector eliminates interference
3.2.4 ABS—acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer.
from all but compounds containing nitrogen or phosphorus.
3.2.5 NBR—butadiene-acrylonitrile rubber.
Any such material eluting at or near the AN or PN retention
3.2.6 DMAC—N,N-dimethylacetamide.
times will cause erroneous RAN results. The headspace above
3.2.7 PN—propionitrile (internal standard).
a polymer solution containing no internal standard should be
analyzed to determine that no sample peaks coincide with the
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Plastics
PN retention time for the packed column test method. The
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods.
capillary column test method specifies use of a flame ionization
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 1996. Published May 1997. Originally
detector. It is an external standard test method, therefore,
published as D 4322 – 83. Last previous edition D 4322 – 83 (1991)e .
This revision includes the addition of an ISO equivalency statement and a
concern with sample peaks coinciding with the retention time
suitable capillary column headspace GC test method.
of the internal standard peak is not an issue.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.03.
3 6.2 Normally the headspace will contain only air, RAN, PN,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 4322
water, solvent, and any other volatile compounds used during 7.8 Soap Film Flowmeter, if the gas chromatograph used is
polymerization. Such impurities at concentrations of 0 to 100 not capable of electronic flow programming.
ppm will have negligible effect on the equilibrium relationship
8. Reagents and Materials
upon which this test method is based.
8.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
7. Apparatus used in all tests. Unless otherwise stated, it is intended that all
reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee
7.1 Gas Chromatograph, equipped with nitrogen-
on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society,
phosphorus specific detector, and backflush valve, that is
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
capable of automatically and sequentially sampling and ana-
used provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
lyzing the headspace vapors contained in sealed vials.
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
7.1.1 If packed column analysis is preferred, the gas chro-
accuracy of the determination.
matography should be equipped with a packed column inlet, a
8.2 Acrylonitrile Standard.
nitrogen-phosphorous specific detector, and a backflush valve.
8.3 Internal Standard, propionitrile (PN) for packed column
NOTE 2—The Perkin-Elmer Model HS40XL Headspace Autosampler
analysis.
coupled with a Perkin-Elmer AutoSystem XL Gas Chromatograph can
8.4 N, N-Dimethylacetamide (DMAC) or Propylene Car-
fulfill these requirements.
bonate (PC) are suitable solvents for the packed column test
7.1.2 If capillary column analysis is preferred, the gas
method, and o-Dichlorobenzene is suitable for the capillary
chromatograph should be equipped with a capillary column
column test method.
inlet, and a flame ionization detector.
NOTE 7—A solvent blank headspace must be chromatographed to
NOTE 3—The Hewlett-Packard Model HP7694 Headspace Sampler
ensure the absence of interferences at the AN or PN retention times.
coupled with a Hewlett-Packard Model HP6890 Gas Chromatograph can
8.5 Hydrogen Cylinder, prepurified.
fulfill these requirements.
8.6 Helium or Nitrogen Cylinder, prepurified.
NOTE 4—Another suitable detector may be utilized (for example,
nitrogen-phosphorus specific detector), however, the operating procedures
NOTE 8—Either nitrogen or helium may be used as the carrier gas for
in Section 12 would have to be altered to suit the equipment used.
the packed column test method. The capillary test method is written for
NOTE 5—If “manual” analysis is to be performed (that is, syringe
use with helium as the carrier gas. Nitrogen may be substituted for helium,
injection into other chromatographs), then the following additional equip-
however, the number of effective theoretical plates may be altered. It may
ment is needed.
be necessary to adjust the head pressure and column flow to obtain
(1) Constant-Temperature Bath, capable of maintaining 90 6 1°C.
comparable chromatographic peak retention times.
(2) Gastight Gas Chromatographic Syringes for sampling and injec-
NOTE 9—Helium may also be used as the carrier gas.
tion.
8.7 Air, breathing or water-pumped.
(3) Septa, Butyl Rubber, and Aluminum Vial Seals, if headspace vials
are used.
8.8 Certified, low-residual ABS, SAN, or nitrile rubber
(4) Valve, 6-port for backflush.
material of known AN concentration to be used as a standard
7.2 Chromatographic Columns: for the capillary column test method or combination thereof.
7.2.1 Packed Column Analysis—80/100-mesh Chromosorb
9. Safety Precautions
101 or 0.2 % Carbowax 1500/Carbopack C (80/100), 3.2-mm
9.1 Do not release acrylonitrile to the laboratory atmo-
outside diameter by 1 m and 3.2-mm outside diameter by 2 m,
sphere. Prepare standards and handle samples in a well-
stainless steel.
ventilated hood. Dimethylacetamide and o-dichlorobenzene
7.2.2 Capillary Column Analysis—Quadrex 007-2, 25
are absorbed through the skin, so avoid contact.
m 3 0.32-mm internal diameter fused silica, coated with a
9.2 Be careful not to come into contact with heated chro-
5-μm film of 5 % phenyl/95 % methylsilicone liquid phase.
matographic parts such as the detector, column, rotating
NOTE 6—Other column packings may be used after suitable evaluation
sample tray, hot sample vials, etc. involving manual injections
to determine that no interfering peaks elute at the AN or PN retention
(see Note 4). Once heated, sample vials are under pressure.
times. If column packings other than those listed in 7.2 are used, then the
After analysis, vent the pressure with a hypodermic syringe
settings recommended in Sections 11 and 12 may have to be modified.
needle into a charcoal slug or vent tube leading to a hood
7.3 Recorder, 5-mV full-scale or computing integrator, or
before removing vials from the water bath.
appropriate computer data station and software.
10. Sampling and Storage
7.4 Vial Sealer, for vials.
10.1 Keep all samples in tightly sealed jars. Analyze sample
7.5 Analytical Balance, capable of weighing to 60.0001 g.
solutions within 24 h. If 24 h are exceeded, report the age of the
7.6 Pressure Regulators, for all required gas cylinders.
sample solution.
7.7 Filter-Drier Assemblies, for each required GC gas
cylinder.
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
Available from Perkin-Elmer Corp., 761 Main Ave., Norwalk, CT 06859. listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
Available from Hewlett-Packard Co., 2850 Centerville Road, Wilmington, DE Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
19808. and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
Column packing available from Supelco, Inc., Supelco Park, Bellefont, PA MD.
16823-0048. Available from Scientific Polymer Products, Inc., 6265 Dean Parkway, Ontario,
Column available from Quadrex Corp., P.O. Box 2881, New Haven, CT 06525. NY 14519.
D 4322
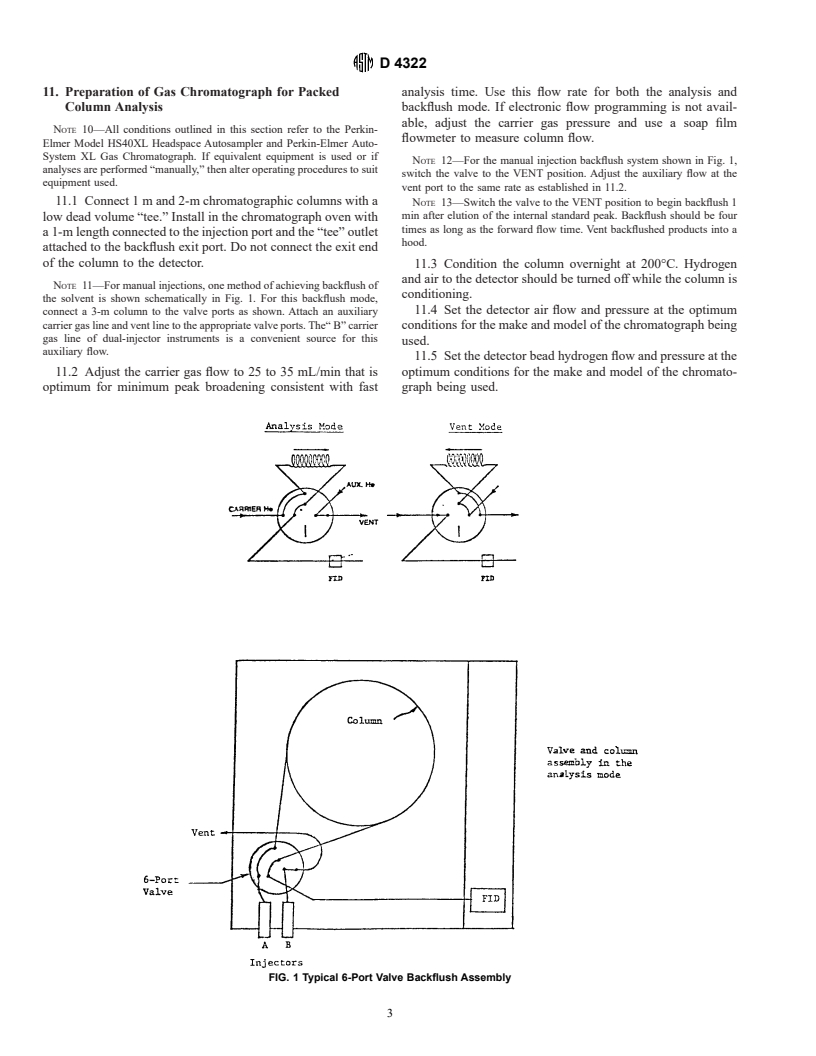
11. Preparation of Gas Chromatograph for Packed analysis time. Use this flow rate for both the analysis and
Column Analysis backflush mode. If electronic flow programming is not avail-
able, adjust the carrier gas pressure and use a soap film
NOTE 10—All conditions outlined in this section refer to the Perkin-
flowmeter to measure column flow.
Elmer Model HS40XL Headspace Autosampler and Perkin-Elmer Auto-
System XL Gas Chromatograph. If equivalent equipment is used or if
NOTE 12—For the manual injection backflush system shown in Fig. 1,
analyses are performed “manually,” then alter operating procedures to suit
switch the valve to the VENT position. Adjust the auxiliary flow at the
equipment used.
vent port to the same rate as established in 11.2.
11.1 Connect 1 m and 2-m chromatographic columns with a NOTE 13—Switch the valve to the VENT position to begin backflush 1
min after elution of the internal standard peak. Backflush should be four
low dead volume “tee.” Install in the chromatograph oven with
times as long as the forward flow time. Vent backflushed products into a
a 1-m length connected to the injection port and the “tee” outlet
hood.
attached to the backflush exit port. Do not connect the exit end
of the column to the detector.
11.3 Condition the column overnight at 200°C. Hydrogen
and air to the detector should be turned off while the column is
NOTE 11—For manual injections, one method of achieving backflush of
conditioning.
the solvent is shown schematically in Fig. 1. For this backflush mode,
11.4 Set the detector air flow and pressure at the optimum
connect a 3-m column to the valve ports as shown. Attach an auxiliary
carrier gas line and vent line to the appropriate valve ports. The“ B” carrier conditions for the make and model of the chromatograph being
gas line of dual-injector instruments is a convenient source for this
used.
auxiliary flow.
11.5 Set the detector bead hydrogen flow and pressure at the
11.2 Adjust the carrier gas flow to 25 to 35 mL/min that is optimum conditions for the make and model of the chromato-
optimum for minimum peak broadening consistent with fast graph being used.
FIG. 1 Typical 6-Port Valve Backflush Assembly
D 4322
NOTE 14—As a general rule, the lowest bead temperature that will
12.7.8.3 Fill Loop Start—23 s,
produce adequate sensitivity should be used. By turning the bead setting
12.7.8.4 Fill Loop Stop—33 s,
off or to 2.5 between usages, bead life will be prolonged.
12.7.8.5 Injection Start—34 s, and
11.6 Set temperatures as follows:
12.7.8.6 Injection Stop—74 s.
11.6.1 Chromatograph Oven (Column)—130°C.
13. Calibration by Standard Addition for Packed
11.6.2 Dosing Needle—150°C.
Column Analysis
11.6.3 Injection Block—180°C.
11.6.4 Detector—180°C.
13.1 Pipet 10.0 mL of solvent into a 3-dram (12-mL) vial.
11.6.5 Autosampler Heated Zone—90°C.
Seal with Mininertt septum cap and weigh. Using a 10-μL
11.6.6 Constant Temperature Bath (for Equilibration of
syringe, add 5.0 μL acrylonitrile to this vial through the septum
Manually Injected Samples)—90°C.
and reweigh. Shake well to mix and label Solution A. This
11.7 Set the headspace analyzer parameters as follows:
stock standard should contain AN at a concentration of about
11.7.1 Injection Time—9 s,
400 μg/mL.
11.7.2 Analysis Time—3 min,
13.2 To each of 5 headspace vials, weigh 0.5 6 0.005 g of
11.7.3 Backflush Time—3.5 min, and
polymer. Using a pipet, add 5.0 mL solvent to each vial. Cover
11.7.4 Equilibration Time—1 to 2 min.
vials with butyl rubber septa and crimp seal with aluminum
caps. Place vials on a mechanical shaker and mix until
12. Preparation of Gas Chromatograph for Capillary
dispersed (approximately 1 h).
Column Analysis
13.3 Using a 10-μL syringe, add 2, 5, 10, and 15-μL aliquots
NOTE 15—All conditions outlined in this section refer to the Hewle
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.