ASTM D4802-94
(Specification)Standard Specification for Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Acrylic Plastic Sheet
Standard Specification for Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Acrylic Plastic Sheet
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers monolithic methacrylate sheets produced by various processes. For this specification, methacrylate sheet shall be composed of polymerized acrylic monomers of which at least 80 % shall be methyl methacrylate.
Note 1—This specification is intended to consolidate the requirements of the Cast Methacrylate Plastic Sheets portion of discontinued Fed. Spec. L-P-391D, discontinued Specification D 702. Cast Methacrylate Plastic Sheets, Rods, Tubes and Shapes, and discontinued Specification D 1547, Extruded Acrylic Plastic Sheet.
1.2 This specification is intended to cover acrylic sheet for general-purpose applications. For specialty applications consult the appropriate use standards.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 Acrylic sheet is used frequently in applications in which extreme clarity, lack of optical distortion and absence of any foreign particulate matter are of primary significance. Reground material may be used as long as careful control is used to eliminate adverse effects on these properties. The use of recycled material in type B-1 and B-2 sheet, may have adverse effects on these properties which would preclude its use in most cases. The use of recycled or reground material is not possible for type A-1 and A-2 materials since the sheet is produced directly from monomer
Note 2—This standard is similar to ISO 7823-1:1987 (E) in title only. The technical content is significantly different.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4802 – 94 An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Specification for
Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Acrylic Plastic Sheet
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4802; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 1003 Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance
1.1 This specification covers monolithic methacrylate sheets
of Transparent Plastics
produced by various processes. For this specification, meth-
D 1044 Test Method for Resistance of Transparent Plastics
acrylate sheet shall be composed of polymerized acrylic
to Surface Abrasion
monomers of which at least 80 % shall be methyl methacrylate.
D 1308 Test Method for Effect of Household Chemicals on
NOTE 1—This specification is intended to consolidate the requirements
Clear and Pigmented Organic Finishes
of the Cast Methacrylate Plastic Sheets portion of Fed. Spec. L-P-391D,
D 1499 Practice for Operating Light- and Water-Exposure
discontinued Specification D 702. Cast Methacrylate Plastic Sheets, Rods,
Apparatus (Carbon-Arc Type) for Exposure of Plastics
Tubes and Shapes, and discontinued Specification D 1547, Extruded
D 2565 Practice for Operating Xenon Arc-Type Light Ex-
Acrylic Plastic Sheet.
posure Apparatus With and Without Water for Exposure of
1.2 This specification is intended to cover acrylic sheet for
Plastics
general-purpose applications. For specialty applications con-
D 3002 Recommended Practice for Evaluation of Coatings
sult the appropriate use standards.
for Plastics
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
D 3359 Test Method for Measuring Adhesion by Tape
test methods portion, Section 8, of this specification: This
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
Determine Conformance with Specifications
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
2.2 ISO Standard:
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
ISO 7823-1:1987 (E) Plastics—Poly(Methyl Methacrylate)
tions prior to use.
Sheets—Types, Dimensions, and Characteristics
NOTE 2—This standard is similar to ISO 7823-1:1987 (E) in title only.
3. Terminology
The technical content is significantly different.
3.1 Definitions:
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.1 General—The definitions given in Terminology
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 883 are applicable to this specification.
D 256 Test Method for Impact Resistance of Plastics and
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Electrical Insulating Materials
3.2.1 bow warp, n—distortion in the form of a simple curve
D 542 Test Methods for Index of Refraction of Transparent
or arc extending across the sheet and displaced from the
Organic Plastic
horizontal when the sheet is laying flat.
D 570 Test Method for Water Absorption of Plastics
3.2.2 edge kink warpage, n—distortion in the form of a
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
twist, wrinkle, or scallop occurring along the perimeter of the
D 648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
sheet.
Under Flexural Load
3.2.3 letgoes, n—an area on the sheet over which the initial
D 673 Test Method for Mar Resistance of Plastics
adhesion between the polymer and the mold glass has been lost
D 756 Practice for Determination of Weight and Shape
before polymerization, causing an uneven surface.
Changes of Plastics Under Accelerated Service Condi-
3.2.4 “S” warp, n—distortion in the form of a compound
tions
curve or “S” shape caused by a nonuniform change in internal
D 792 Test Methods for Specific Gravity (Relative Density)
stresses.
and Density of Plastics by Displacement
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.02.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
Materials. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.01.
Current edition approved March 15, 1994. Published May 1994. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
published as D 4802 – 88. Last previous edition D 4802 – 93a. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
D 4802
4. Classification no specific UV-transmission requirements for material of
unspecified type.
4.1 Categories:
4.1.1 Category A-1—Methacrylate sheet typically manufac-
5. Detail Requirements
tured by the cell-casting process. This category represents the
5.1 The following applies to all specified limits in this
best optical-quality sheet. It is characterized by the highest
specification. For purposes of determining conformance with
long-term design stress and the highest degree of chemical
this specification, an observed value or a calculated value shall
resistance found in methacrylate sheet.
be rounded to the nearest 1 MPa (100 psi) for tensile strength,
4.1.2 Category A-2—Methacrylate sheet typically manufac-
and for all other properties shall be rounded to the nearest unit
tured by the continuous-casting method. The physical, chemi-
in the last righthand place of fingers used in expressing the
cal, and thermal properties are similar to Category A-1 sheet.
limiting value, in accordance with the rounding method of
The optical quality is lower than Category A-1 sheet. This
Practice E 29.
category has better thickness control than that of Category A-1
5.2 Sheet shall conform to the requirements prescribed in
sheet.
Table 2. In addition, Category A-1 sheet shall conform to the
4.1.3 Category B-1—Methacrylate sheet manufactured by
the permissible-thickness variations listed in Table 3.
any of several processes (typically described as continuously
5.3 Shrinkage—Test in accordance with 8.1.7.
manufactured sheet). This sheet possesses lower heat, chemi-
5.4 Thermal Stability—Sheet shall show no evidence of
cal, and stress-craze resistance than Category A-1 and Cat-
bubbling or blistering when tested in accordance with 8.1.8.
egory A-2 sheet. It has equivalent or better optical quality and
5.5 Abrasion-Resistant Material—Finish 3 material
thickness tolerances than Category A-2 sheet.
(abrasion-resistant coated material) shall meet the requirements
4.1.4 Category B-2—Methacrylate sheet typically manufac-
of the substrate material it is designated as and the properties
tured by conventional extrusion processes. This sheet is char-
shown in Table 1.
acterized by excellent thickness control similar to Category
5.6 Workmanship—Sheet, as delivered, shall be free from
A-2 and Category B-1 sheet. This sheet has reduced long-term
warpage, cracks, scratches, blisters, voids, foreign matter, die
design stress, chemical resistance, optical quality, and thermal
lines, and other defects that may affect appearance or service-
stability.
ability.
4.2 Finish—The following finishes of methacrylate sheet
5.6.1 Flatness of Sheet—Sheet shall be free from edge kink
may be specified. The physical and optical properties in this
warpage and from edge “S” warp when lying on a flat surface.
specification are based on Finish 1 material unless otherwise
Overall bow warp is permitted for all types of sheet to a
noted.
maximum of 6.3 mm (0.250 in.) displacement from the
4.2.1 Finish 1—Smooth or polished.
horizontal for each 4-ft length, or fraction thereof, of a sheet
4.2.2 Finish 2—Patterned, including textures and frosting.
under its own weight when laying in the horizontal position on
4.2.3 Finish 3—Abrasion-resistant coated.
a flat continuous surface. “S” warp that disappears or becomes
4.2.3.1 Finish 3 material can be of any category provided it
bow warp when turned over is permitted.
meets the requirements of that category plus the additional
5.6.2 Corner Letgoes for Sheet (Applicable to Category A-1
requirements listed in Table 1.
and A-2 Sheet Only)—Masked sheet in thicknesses equal to or
4.2.4 Type UVA (UV-Absorbing)—Materials that contain an
less than 51 mm (2.008 in.) shall be free of corner letgoes.
ultraviolet absorber to limit the transmission of UV radiation
Unmasked sheet in thicknesses no greater than 6.00 mm (0.236
through the sheet especially for protection of items sensitive to
in.) may have letgoes within any or all of the corner areas that
sunlight or UV radiation.
are defined as isosceles triangles with 76.0 mm (3.0 in.) sides.
4.2.5 Type UVT (UV-Transmitting)—Materials that do not
Corner letgoes in unmasked sheets that are thicker than 6.0 mm
contain any UV absorbers and are used where there is a need
(0.236) up to and including 51 mm (2.008 in.) are permitted
to transmit a greater portion of UV radiation.
within any or all of the corner areas that are defined as isosceles
4.2.6 For general-purpose applications neither type need be
triangles with 150 mm (5.91 in.) sides. For unmasked sheets,
specified. If not specified, materials will usually contain UV
out-of-tolerance corner letgoes, within an isosceles triangle
absorbers only sufficient to protect the polymer from degrada-
that has no more than twice the allowable length for sides, shall
tion from exposure to direct sunlight or UV radiation. There are
be accepted if removed. For masked and unmasked sheets in
thicknesses greater than 51 mm (2.008 in.), letgoes may exist
TABLE 1 Finish 3 Abrasion Resistant Material
provided they do not extend more than 0.4 mm (0.016 in.)
Property Test Method Requirement
below the surface. For Category A-2 sheet only, edge letgoes
Abrasion resistance, 100 cycles at D 1044
less than 0.4 mm (0.016 in.) in depth may exist within 25 mm
500 g load
A
Haze, max, % 4.0
(0.984 in.) of the sheet edges, provided physical integrity is not
Mar resistance, 1000 g No. 80 grit D 673
impaired.
A
Haze, max,% 4.0
5.6.3 Chips and Dirt in Sheet:
Coating adhesion, percent retention, see 8.1.13.5 Minimum Classification
A
min 4B, Fig. 1, Test 5.6.3.1 Chips in Sheet of Thickness Equal to or Less Than
Methods D 3359
51 mm (2.008 in.)—The maximum permissible chip size shall
Chemical resistance, visual see 8.1.14 no change
be 3.2 mm (0.125 in.). Chips that are approximately the
examination
A maximum permissible size shall not have a frequency greater
Tests are to be performed before and after the simulated weathering resis-
2 2
tance and the accelerated-service conditions described in 8.1.13. than 1 chip per 0.4 m (4.3 ft ) of sheet area. Chips less than 0.8
D 4802
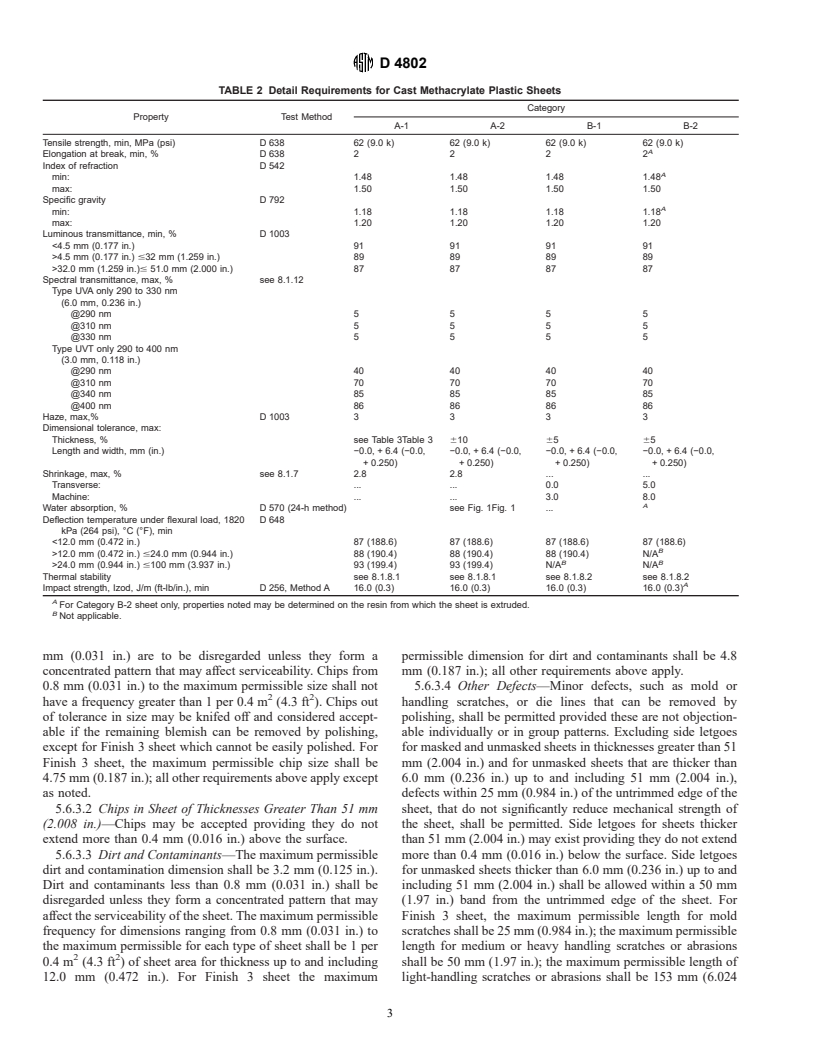
TABLE 2 Detail Requirements for Cast Methacrylate Plastic Sheets
Category
Property Test Method
A-1 A-2 B-1 B-2
Tensile strength, min, MPa (psi) D 638 62 (9.0 k) 62 (9.0 k) 62 (9.0 k) 62 (9.0 k)
A
Elongation at break, min, % D 638 2 2 2 2
Index of refraction D 542
A
min: 1.48 1.48 1.48 1.48
max: 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.50
Specific gravity D 792
A
min: 1.18 1.18 1.18 1.18
max: 1.20 1.20 1.20 1.20
Luminous transmittance, min, % D 1003
<4.5 mm (0.177 in.) 91 91 91 91
>4.5 mm (0.177 in.) #32 mm (1.259 in.) 89 89 89 89
>32.0 mm (1.259 in.)# 51.0 mm (2.000 in.) 87 87 87 87
Spectral transmittance, max, % see 8.1.12
Type UVA only 290 to 330 nm
(6.0 mm, 0.236 in.)
@290 nm 5 5 5 5
@310 nm 5 5 5 5
@330 nm 5 5 5 5
Type UVT only 290 to 400 nm
(3.0 mm, 0.118 in.)
@290 nm 40 40 40 40
@310 nm 70 70 70 70
@340 nm 85 85 85 85
@400 nm 86 86 86 86
Haze, max,% D 1003 3 3 3 3
Dimensional tolerance, max:
Thickness, % see Table 3Table 3 610 65 65
Length and width, mm (in.) −0.0, + 6.4 (−0.0, −0.0, + 6.4 (−0.0, −0.0, + 6.4 (−0.0, −0.0, + 6.4 (−0.0,
+ 0.250) + 0.250) + 0.250) + 0.250)
Shrinkage, max, % see 8.1.7 2.8 2.8 . .
Transverse: . . 0.0 5.0
Machine: . . 3.0 8.0
A
Water absorption, % D 570 (24-h method) see Fig. 1Fig. 1 .
Deflection temperature under flexural load, 1820 D 648
kPa (264 psi), °C (°F), min
<12.0 mm (0.472 in.) 87 (188.6) 87 (188.6) 87 (188.6) 87 (188.6)
B
>12.0 mm (0.472 in.) #24.0 mm (0.944 in.) 88 (190.4) 88 (190.4) 88 (190.4) N/A
B B
>24.0 mm (0.944 in.) #100 mm (3.937 in.) 93 (199.4) 93 (199.4) N/A N/A
Thermal stability see 8.1.8.1 see 8.1.8.1 see 8.1.8.2 see 8.1.8.2
A
Impact strength, Izod, J/m (ft-lb/in.), min D 256, Method A 16.0 (0.3) 16.0 (0.3) 16.0 (0.3) 16.0 (0.3)
A
For Category B-2 sheet only, properties noted may be determined on the resin from which the sheet is extruded.
B
Not applicable.
mm (0.031 in.) are to be disregarded unless they form a permissible dimension for dirt and contaminants shall be 4.8
concentrated pattern that may affect serviceability. Chips from mm (0.187 in.); all other requirements above apply.
0.8 mm (0.031 in.) to the maximum permissible size shall not 5.6.3.4 Other Defects—Minor defects, such as mold or
2 2
have a frequency greater than 1 per 0.4 m (4.3 ft ). Chips out handling scratches, or die lines that can be removed by
of tolerance in size may be knifed off and considered accept- polishing, shall be permitted provided these are not objection-
able if the remaining blemish can be removed by polishing, able individually or in group patterns. Excluding side letgoes
except for Finish 3 sheet which cannot be easily polished. For for masked and unmasked sheets in thicknesses greater than 51
Finish 3 sheet, the maximum permissible chip size shall be mm (2.004 in.) and for unmasked sheets that are thicker than
4.75 mm (0.187 in.); all other requirements above apply except 6.0 mm (0.236 in.) up to and including 51 mm (2.004 in.),
as noted. defects within 25 mm (0.984 in.) of the untrimmed edge of the
5.6.3.2 Chips in Sheet of Thicknesses Greater Than 51 mm sheet, that do not significantly reduce mechanical strength of
(2.008 in.)—Chips may be accepted providing they do not the sheet, shall be permitted. Side letgoes for sheets thicker
extend more than 0.4 mm (0.016 in.) above the surface. than 51 mm (2.004 in.) may exist providing they do not extend
5.6.3.3 Dirt and Contaminants—The maximum permissible more than 0.4 mm (0.016 in.) below the surface. Side letgoes
dirt and contamination dimension shall be 3.2 mm (0.125 in.). for unmasked sheets thicker than 6.0 mm (0.236 in.) up to and
Dirt and contaminants less than 0.8 mm (0.031 in.) shall be including 51 mm (2.004 in.) shall be allowed within a 50 mm
disregarded unless they form a concentrated pattern that
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.