ASTM A669-83
(Specification)Specification for Seamless Ferritic-Austenitic Alloy Steel Tubes (Withdrawn 1983)
Specification for Seamless Ferritic-Austenitic Alloy Steel Tubes (Withdrawn 1983)
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
1916 Rw* St., PhiluMphi8. Pa. 19103
Rlprintd from thr AnW Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright Am
If not listad in th. curront -bind idox. will rppur in the next edition.
Standard Spdtkation tor
SEAMLESS FERRITIC-AUSTENITIC ALLOY STEEL TUBES'
Thh standard u issued under tho Iabd duignaiion A669; ~hc number immediately following ~bc &siption iadi ~e
iml ~doption or, in the use of mirion, the yCa~ of lut nvision. A nrcnbtr m p81cntBcsaio~~ :be yut of last
F"?
mpptov. A superscript epsilon (e) indicrtu an cdilori.1 churgc sin- tht Iw rcvi* or reapproval.
tion shall include tbe fbIlowiog. as required, to
dcsuibe the desired material adcquatek.
I. I This s~tcation2 covers seasnkss fa-
4.1.1 Quantity (fcct or number of kngths),
riti~ustcnitic st-1 tubes for heat cxcbaager
4.1 2 Diienshs (outside diem and av-
and ge~d setvia. The steel is Ltcnded for
enge wall ad lea%th, cut or random),
use ia general ~~on-~t applications
4-13 Name of matuial (sumless tubes).
with paraiaiar emphasis om mistma to smss-
4.1.4 SpuScati~#~ number,
w&on awkiq. This material stmy &VCIQP
4.8.5 Candirion (bot or ooldl finished).
cmbrit1Perncnt if usad aa tavw above
41.6 sp#irrl q-~s.
6as0~ (32s0c$,
4.1.7 Opiaal quimmeo~ ((see 9.4), andl
1.2 me wb'i siaes and ahidmesses 14~1a1Oy
4.1.8 Cd6draa (sac U.2 of Specification
furnished lfCb fQ&i S8CCiflcatiost me % PO 6 h, (4.4
A 4903. i
80 142.4 mm), inol, in ooWa diamtscr and
8.020 to h, (43.51 $0 2'8.9 m), in arc-
5, Mrada and Madaawc
wal4 thidta,es.%, hbiq hawig &ut-shs
5.1 The -d bc made by the dtclric-
may be ff~rnilad, podded wdh auks omp\y
~u~~o~~*@~PBoQcI'$#~~-
with a84 otikw mq~mc~do~ofabh-~iQlr.
pwd by anbe p&sclr. Tk primary mentin&
8 -3 lYle
has a nvimmac3~c omsi&q
may iimaqmMc ~Ic dqpsbg w mfmimg.
of dmu3 50 % R~QQ~S sf amwbw&e h a ff&c
d~ybcfWIby~&~
m-wix.
red* olr wmamm-an: RC-
1-4 Tub8 aLmW os his vipmi@p1#4m
-, If sxmdq di is cm~~, nhc
mustbe~ckc~dbd~~uar~~
llbta.4MbCWlkbQ=ddIbtb*rr-
by rht oon~l~~dmd mdmis,
~adl~a~p8immy~1.
1.4 1AE vnPues ~r(d riar bda-pud \pmiib
5.2 Tblbea k made by llbf sumkm
a~t~be~~d~YsDAIEd.
~anvQ~beci~~Gmi5ilbuJ~cdd
tiwadcdm-
5.3 AMMbcssbabcliuPsisbadhIhthI-
~~~~ln#~~~bC
#Bmkmd d a 8lempatw ad 118% * 5QQF
r(!?OJlQ & 28'OCO with sdlhqma qdag in
MRC~ aw uqMy oodlirag by &r mans.
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
hcat which am hat trtoted in !he rune fLrnsct c-.
5.4 The tub shall be pickled frce from
Whcn the find heat Utltmmt is in a continuous fur-
&. Whcn brigbt anneJin8 in acwrdmcc
-, a lot shll include dl tuhe of the sune & rad
with 5.3 is perfond, pickling is not required.
hat, hart treated in the same furnra at tbc sune
tempmature, time at heat and funt~ce speed.
9. Mcclunial Reqmire~~~nts
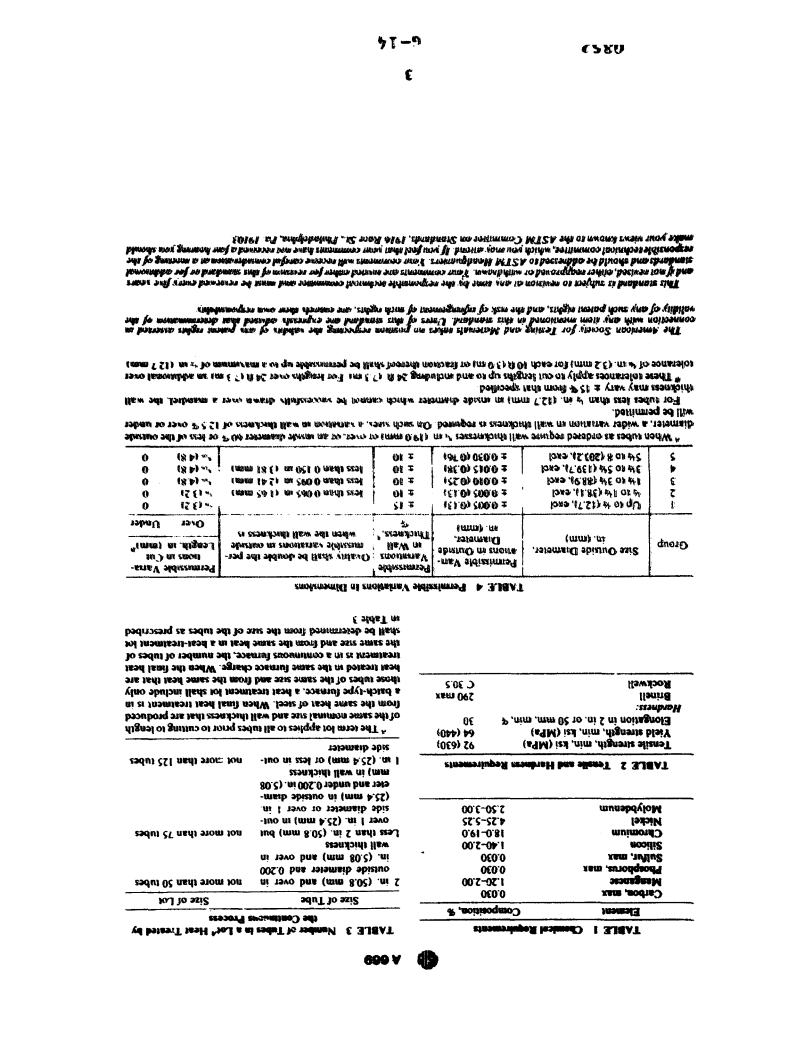
6.1 The tubes shall conform to the require-
ments as to chemical composition prescribed in 9.1 Tension Test--One tension test shall be
Table 1. made on a specimen for lots of not mom than
SO tubes. Tension tests shall be madc on speci-
mens from two tubes for iots of more than SO
7.1 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be tubes (Note 2). Results of tests shall oonfonn to
made by the stbtl manufaCZum to determine
the tensile properties prescribed in Table 2.
the percentages of the elements specified. If 9.2 Hardness Test-Brine11 or Rockwell hard-
secondary melting processes an employed, the
ness tests shall be made on specimens fom two
hcat analysis shaU be obtained from one re-
tubes from each lot (Note 2). Results of tests shall
metted ingot or the product of one remelted
conform to th
...
This May Also Interest You
ABSTRACT
This specification covers several grades of carbon and low alloy steel forged or ring-rolled flanges, forged fittings and valves for low-temperature service. The steel specimens shall be melt processed using open-hearth, basic oxygen, electric furnace or vacuum-induction melting. A sufficient discard shall be made to secure freedom from injurious piping and undue segregation. The materials shall be forged and shall undergo heat treatment such as normalizing, tempering, quenching and precipitation heat treatment. Heat analysis and product analysis shall be performed wherein the steel materials shall conform to the required chemical compositions of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, copper, columbium, vanadium, and nitrogen. The materials shall also undergo tension tests and shall conform to the required values of tensile strength, yield strength and elongation. Impact tests shall also be performed and the steel materials shall conform to the required values of minimum impact energy, temperature, and minimum equivalent absorbed energy. Hardness and hydrostatic tests shall also be performed.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers several grades of carbon and low-alloy steel forged or ring-rolled flanges, forged fittings and valves intended primarily for low-temperature service and requiring notch toughness testing. They are made to specified dimensions, or to dimensional standards, such as the ASME and API Specifications referenced in Section 2. Although this specification covers some piping components machined from rolled bar and seamless tubular materials (see 5.3.3), it does not cover raw material produced in these product forms.
1.2 No limitation on size is intended beyond the ability of the manufacturer to obtain the specified requirements. However, Class 3 of Grade LF787 is only available in the quenched-and-precipitation heat treated condition.
1.3 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply only when specified by the purchaser in the order.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation (SI units), the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification covers forged or rolled alloy and stainless steel pipe flanges, forged fittings, and valves and parts for high-temperature service. After hot working, forgings shall be cooled to a specific temperature prior to heat treatment, which shall be performed in accordance with certain requirements such as heat treatment type, austenitizing/solution temperature, cooling media, and quenching. The materials shall conform to the required chemical composition for carbon, manganese, phosphorus, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, columbium, titanium. The material shall conform to the requirements as to mechanical properties for the grade ordered such as tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, Brinell hardness. All H grades and grade F 63 shall be tested for average grain size.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers forged low alloy and stainless steel piping components for use in pressure systems. Included are flanges, fittings, valves, and similar parts to specified dimensions or to dimensional standards, such as the ASME specifications that are referenced in Section 2.
1.2 For bars and products machined directly from bar or hollow bar (other than those directly addressed by this specification; see 6.4), refer to Specifications A479/A479M, A739, or A511/A511M for the similar grades available in those specifications.
1.3 Products made to this specification are limited to a maximum weight of 10 000 lb [4540 kg]. For larger products and products for other applications, refer to Specifications A336/A336M and A965/A965M for the similar ferritic and austenitic grades, respectively, available in those specifications.
1.4 Several grades of low alloy steels and ferritic, martensitic, austenitic, and ferritic-austenitic stainless steels are included in this specification. Selection will depend upon design and service requirements. Several of the ferritic/austenitic (duplex) grades are also found in Specification A1049/A1049M.
1.5 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply only when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.6 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation (SI units), the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.7 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification17 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification17 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification covers hot isostatically-pressed, powder metallurgy, stainless steel piping components such as flanges, fittings, valves, and similar parts, for use in pressure systems and temperature service applications. The specification includes several grades of martensitic, austenitic, age hardening, and austenitic-ferritic stainless steels. Compacts shall be manufactured by placing a single powder blend into a can, evacuating the can, and sealing it. The powder shall be prealloyed and made by a melting method (such as but not limited to air or vacuum induction melting, followed by gas atomization) to produce the specified chemical composition for carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, columbium, tantalum, copper, tungsten, and nitrogen. Other manufacturing requirements including compact homogeneity, microstructure, and can material removal are given. Heat treatment requirements, such as austenitizing or solutioning, cooling, quenching, tempering, and ageing, and structural integrity requirements, such as density, hydrostatic tests, and ultrasonic tests are detailed as well. Mechanical properties include tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and hardness. Product analysis shall conform to the chemical requirements.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers hot isostatically-pressed, powder metallurgy, stainless steel piping components for use in pressure systems. Included are flanges, fittings, valves, and similar parts made to specified dimensions or to dimensional standards, such as in ASME specification B16.5.
1.2 Several grades of martensitic, austenitic, age hardening, and austenitic-ferritic stainless steels are included in this specification.
1.3 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply only when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. Unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation (SI units), however, the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to test methods portions 8.1, 8.2, 9.5 – 9.7, and Section 10 of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification13 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification13 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the common requirements that shall apply to wrought steel piping fittings. The material shall consist of forgings, bars, plates, and seamless or welded tubular products. Ferritic steels shall be fully killed. Hollow cylindrically shaped parts up to and including NPS 4 may be machined from bar or seamless tubular material. Elbows, return bends, tees, and header tees shall not be machined directly from bar stock. The following procedures shall be done for heat treatment: full annealing, solution annealing, isothermal annealing, normalizing, tempering and post-weld heat treatment, stress relieving, and quench and temper. Chemical analysis, heat analysis, and product analysis shall also be done. The chemical requirements shall conform to the required compositions of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, columbium, titanium, aluminum, lead, and copper. The following tests shall be done for the mechanical requirements: tension, hardness, impact, and hydrostatic tests.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers a group of common requirements that shall apply to wrought steel piping fittings covered in any of the following individual product specifications or any other ASTM specification that invokes this specification or portions thereof:
Title of Specification
ASTM
Designation
Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought
Carbon Steel and Alloy Steel for Moderate and
High Temperature Service
A234/A234M
Specification for Wrought Austenitic Stainless
Steel Piping Fittings
A403/A403M
Specification for Piping Fittings of Wrought Carbon
Steel and Alloy Steel for Low-Temperature Service
A420/A420M
Specification for Wrought-Carbon Steel Butt-Welding
Piping Fittings with Improved Notch Toughness
A758/A758M
Specification for As-Welded Wrought Austenitic
Stainless Steel Fittings for General Corrosive
Service at Low and Moderate Temperatures
A774/A774M
Specification for Wrought Ferritic, Ferritic/Austenitic,
and Martensitic Stainless Steel Piping Fittings
A815/A815M
Specification for Heat-Treated Carbon Steel
Fittings for Low-Temperature and Corrosive Service
A858/A858M
Specification for Wrought High-Strength
Ferritic Steel Butt-Welding Fittings
A860/A860M
1.2 In case of conflict between a requirement of the individual product specification and a requirement of this general requirement specification, the requirements of the individual product specification shall prevail over those of this specification.
1.3 By mutual agreement between the purchaser and the supplier, additional requirements may be specified (See 4.1.8). The acceptance of any such additional requirements shall be dependent on negotiations with the supplier and must be included in the order as agreed upon by the purchaser and supplier.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text and the tables, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the specification. The inch-pound units shall apply unless the “M” designation [SI] of the product specification is specified in the order.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification covers two general classes, WP and CR, of wrought ferritic, ferritic/austenitic, and martensitic stainless steel fittings of seamless and welded construction. Class WP fittings are subdivided into four subclasses: Classes WP-S, WP-W, WP-WX, and WP-WU. The material for fittings shall consist of forgings, bars, plates, or seamless or welded tubular products. The steel shall be melted by electric furnace, vacuum furnace, or electric furnace followed by vacuum or electroslag-consumable remelting. Forging or shaping operations shall be performed by hammering, pressing, piercing, extruding, upsetting, rolling, bending, fusion welding, machining or by combination of two or more of these operations. The materials shall undergo heat treatment and shall follow the required cooling process and tempering temperature. Chemical and product analyses shall be performed and shall conform to the required chemical composition in carbon, manganese, phosphorus, silicon, sulfur, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, copper, nitrogen, and titanium. The mechanical properties of the fitting material shall conform to the required values in yield strength, tensile strength, elongation, and hardness.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers two general classes, WP and CR, of wrought ferritic, ferritic/austenitic, and martensitic stainless steel fittings of seamless and welded construction covered by the latest revision of Specification A960/A960M. Fittings differing from these standards may be furnished in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S58 of Specification A960/A960M.
1.1.1 Class WP fittings are subdivided into four subclasses: Classes WP-S, WP-W, WP-WX, and WP-WU. They are manufactured to the requirements of Specification A960/A960M, and they shall have pressure ratings compatible with 13.2. Class WP-S fittings are those manufactured from seamless product by a seamless method of manufacture (marked with class symbol WP-S); Class WP-W fittings are those which contain welds where the fitting fabrication or construction welds have been radiographed (marked with class symbol WP-W); and Class WP-WX fittings are those which contain welds where all welds have been radiographed (marked with class symbol WP-WX); and Class WP-WU fittings are those which contain welds where all welds have been ultrasonically tested (marked with class symbol WP-WU).
1.1.2 Class CR fittings are those manufactured to the requirements of MSS SP-43, and they shall have pressure ratings compatible with 13.3.
1.2 This specification does not apply to cast fittings.
1.3 Optional supplementary requirements are provided. When desired, one or more of these may be specified in the order.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation [SI units], the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification8 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification8 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification covers wrought carbon steel and alloy steel fittings of seamless and welded construction. These fittings are for use in pressure piping and in pressure vessel fabrication for service at moderate and elevated temperatures. The material for fittings shall consist of killed steel, forgings, bars, plates, seamless or fusion-welded tubular products with filler metal added. Forging or shaping operations may be performed by hammering, pressing, piercing, extruding, upsetting, rolling, bending, fusion welding, machining, or by a combination of two or more of these operations. The forming procedure shall be so applied that it will not produce injurious imperfections in the fittings. Fittings, after forming at an elevated temperature, shall be cooled to a temperature below the critical range under suitable conditions to prevent injurious defects caused by too rapid cooling, but in no case more rapidly than the cooling rate in still air. The fittings shall be subjected to tension test, hardness test, and hydrostatic test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers wrought carbon steel and alloy steel fittings of seamless and welded construction covered by the latest revision of ASME B16.9, B16.11, MSS-SP-79, MSS-SP-83, MSS-SP-95, and MSS-SP-97. These fittings are for use in pressure piping and in pressure vessel fabrication for service at moderate and elevated temperatures. Fittings differing from these ASME and MSS standards shall be furnished in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S58 of Specification A960/A960M.
1.2 Optional supplementary requirements are provided for fittings where a greater degree of examination is desired. When desired, one or more of these supplementary requirements may be specified in the order.
1.3 This specification does not cover cast welding fittings or fittings machined from castings. Cast steel welding fittings are governed by Specifications A216/A216M and A217/A217M.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation (SI units), the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification covers wrought carbon steel and alloy steel fittings of seamless and welded construction. These fittings are for use in pressure piping and in pressure vessel fabrication for service at moderate and elevated temperatures. The material for fittings shall consist of killed steel, forgings, bars, plates, seamless or fusion-welded tubular products with filler metal added. Forging or shaping operations may be performed by hammering, pressing, piercing, extruding, upsetting, rolling, bending, fusion welding, machining, or by a combination of two or more of these operations. The forming procedure shall be so applied that it will not produce injurious imperfections in the fittings. Fittings, after forming at an elevated temperature, shall be cooled to a temperature below the critical range under suitable conditions to prevent injurious defects caused by too rapid cooling, but in no case more rapidly than the cooling rate in still air. The fittings shall be subjected to tension test, hardness test, and hydrostatic test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers wrought carbon steel and alloy steel fittings of seamless and welded construction covered by the latest revision of ASME B16.9, B16.11, MSS-SP-79, MSS-SP-83, MSS-SP-95, and MSS-SP-97. These fittings are for use in pressure piping and in pressure vessel fabrication for service at moderate and elevated temperatures. Fittings differing from these ASME and MSS standards shall be furnished in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S58 of Specification A960/A960M.
1.2 Optional supplementary requirements are provided for fittings where a greater degree of examination is desired. When desired, one or more of these supplementary requirements may be specified in the order.
1.3 This specification does not cover cast welding fittings or fittings machined from castings. Cast steel welding fittings are governed by Specifications A216/A216M and A217/A217M.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation (SI units), the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification covers forged or rolled alloy and stainless steel pipe flanges, forged fittings, and valves and parts for high-temperature service. After hot working, forgings shall be cooled to a specific temperature prior to heat treatment, which shall be performed in accordance with certain requirements such as heat treatment type, austenitizing/solution temperature, cooling media, and quenching. The materials shall conform to the required chemical composition for carbon, manganese, phosphorus, silicon, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, columbium, titanium. The material shall conform to the requirements as to mechanical properties for the grade ordered such as tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, Brinell hardness. All H grades and grade F 63 shall be tested for average grain size.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers forged low alloy and stainless steel piping components for use in pressure systems. Included are flanges, fittings, valves, and similar parts to specified dimensions or to dimensional standards, such as the ASME specifications that are referenced in Section 2.
1.2 For bars and products machined directly from bar or hollow bar (other than those directly addressed by this specification; see 6.4), refer to Specifications A479/A479M, A739, or A511/A511M for the similar grades available in those specifications.
1.3 Products made to this specification are limited to a maximum weight of 10 000 lb [4540 kg]. For larger products and products for other applications, refer to Specifications A336/A336M and A965/A965M for the similar ferritic and austenitic grades, respectively, available in those specifications.
1.4 Several grades of low alloy steels and ferritic, martensitic, austenitic, and ferritic-austenitic stainless steels are included in this specification. Selection will depend upon design and service requirements. Several of the ferritic/austenitic (duplex) grades are also found in Specification A1049/A1049M.
1.5 Supplementary requirements are provided for use when additional testing or inspection is desired. These shall apply only when specified individually by the purchaser in the order.
1.6 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation (SI units), the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.7 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as the standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification17 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification17 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This specification covers two general classes, WP and CR, of wrought ferritic, ferritic/austenitic, and martensitic stainless steel fittings of seamless and welded construction. Class WP fittings are subdivided into four subclasses: Classes WP-S, WP-W, WP-WX, and WP-WU. The material for fittings shall consist of forgings, bars, plates, or seamless or welded tubular products. The steel shall be melted by electric furnace, vacuum furnace, or electric furnace followed by vacuum or electroslag-consumable remelting. Forging or shaping operations shall be performed by hammering, pressing, piercing, extruding, upsetting, rolling, bending, fusion welding, machining or by combination of two or more of these operations. The materials shall undergo heat treatment and shall follow the required cooling process and tempering temperature. Chemical and product analyses shall be performed and shall conform to the required chemical composition in carbon, manganese, phosphorus, silicon, sulfur, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, copper, nitrogen, and titanium. The mechanical properties of the fitting material shall conform to the required values in yield strength, tensile strength, elongation, and hardness.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers two general classes, WP and CR, of wrought ferritic, ferritic/austenitic, and martensitic stainless steel fittings of seamless and welded construction covered by the latest revision of Specification A960/A960M. Fittings differing from these standards may be furnished in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S58 of Specification A960/A960M.
1.1.1 Class WP fittings are subdivided into four subclasses: Classes WP-S, WP-W, WP-WX, and WP-WU. They are manufactured to the requirements of Specification A960/A960M, and they shall have pressure ratings compatible with 13.2. Class WP-S fittings are those manufactured from seamless product by a seamless method of manufacture (marked with class symbol WP-S); Class WP-W fittings are those which contain welds where the fitting fabrication or construction welds have been radiographed (marked with class symbol WP-W); and Class WP-WX fittings are those which contain welds where all welds have been radiographed (marked with class symbol WP-WX); and Class WP-WU fittings are those which contain welds where all welds have been ultrasonically tested (marked with class symbol WP-WU).
1.1.2 Class CR fittings are those manufactured to the requirements of MSS SP-43, and they shall have pressure ratings compatible with 13.3.
1.2 This specification does not apply to cast fittings.
1.3 Optional supplementary requirements are provided. When desired, one or more of these may be specified in the order.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable “M” specification designation [SI units], the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification8 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification8 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
ABSTRACT
This guide covers standard specification for round, square, rectangular, and special shape, electric-resistance-welded mechanical tubing, either zinc-coated (galvanized) after welding or produced from aluminum-coated, zinc-coated (galvanized), zinc-iron alloy-coated (galvannealed), or aluminum-zinc alloy-coated steel sheet. Low-carbon steels and other carbon steels shall conform to the required chemical composition for carbon, manganese, phosphorus, and sulfur. The steels shall conform to elemental tolerances for product analysis. Wall thickness tolerances for premetallic coated as-welded tubing and diameter tolerances for metallic-coated round tubing shall be provided.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers round, square, rectangular, and special shape, electric-resistance-welded carbon steel mechanical tubing, either zinc-coated (galvanized) after welding or produced from aluminum-coated, zinc-coated (galvanized), zinc-iron alloy-coated (galvannealed), 55 % aluminum-zinc alloy-coated, or zinc-aluminum-magnesium alloy-coated carbon steel sheet. Tubing for use as electrical conduit (EMT) or intermediate metallic conduit (IMC) is not covered by this specification.
1.1.1 The product is available in various grades based on chemical requirements (Sections 5 and 9).
1.1.2 The product is available in various Types (Section 3).
1.2 This specification covers mechanical tubing with outside diameters or maximum outside dimensions ranging from 1/2 to 15 in. [12.7 to 380.0 mm] and wall thickness from 0.028 to 0.180 in. [0.70 to 4.60 mm]. Indeterminate wall thicknesses may be ordered. In those cases the more stringent tolerances of Tables 3, 4, 5, 6, 12 and 13 shall apply.
1.3 When sizes within the ranges listed above are ordered, all other requirements of the specification shall be met.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units; however, unless the purchase order specifies the applicable M specification designation (SI units), the inch-pound units shall apply. The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off
- Technical specification10 pagesEnglish languagesale 15% off








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.