ASTM D3147-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Testing Stop-Leak Additives for Engine Coolants
Standard Test Method for Testing Stop-Leak Additives for Engine Coolants
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The screening procedures simulate the conditions of temperature, pressure, and circulation encountered in service. This test method will indicate whether a product is suitable for further evaluation in vehicles.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers screening procedures for the preliminary evaluation of leak-stopping materials intended for use in engine cooling systems. (Heavy-duty users are referred to X1.2.21 in Specification D4485 for additional information.)
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in 10.1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3147 − 21
Standard Test Method for Testing
1
Stop-Leak Additives for Engine Coolants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3147; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3.1.1 leaking—frequent drops forming (more than 5 drops/
min).
1.1 This test method covers screening procedures for the
3.1.2 sealed—completely plugged with no leaking or seep-
preliminary evaluation of leak-stopping materials intended for
ing.
use in engine cooling systems. (Heavy-duty users are referred
to X1.2.21 in Specification D4485 for additional information.)
3.1.3 seeping—occasional drops forming (fewer than
5 drops⁄min).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. The values given in parentheses after SI units are
3.2 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to
provided for information only and are not considered standard.
Terminology D4725.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4. Summary of Test Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 Aheated test solution is circulated through a pressurized
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
cubical metal reservoir which contains a slit and holes to
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
simulate leaks in an engine cooling system. The effectiveness
Specific warning statements are given in 10.1.
of the stop-leak material is measured by its ability to seal the
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
leaks under the prescribed conditions of flow rate, temperature,
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
pressure, and time.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.2 The presence of particles in the test material that are
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
larger than 0.84 mm (0.033 in.) or the presence of gumming or
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
gelling in stop-leak additives is determined by screening a test
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
solution through a 850 µm (U.S. No. 20) standard sieve. The
screening is done both before and after the circulating test.
2. Referenced Documents
Particles that remain on the sieve may be too large to pass
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
through some passages of the cooling system.
D1176 Practice for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous Solu-
tions of Engine Coolants orAntirusts forTesting Purposes
5. Significance and Use
D4485 Specification for Performance of Active API Service
5.1 The screening procedures simulate the conditions of
Category Engine Oils
temperature, pressure, and circulation encountered in service.
D4725 Terminology for Engine Coolants and Related Fluids
This test method will indicate whether a product is suitable for
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test
further evaluation in vehicles.
Sieves
3. Terminology
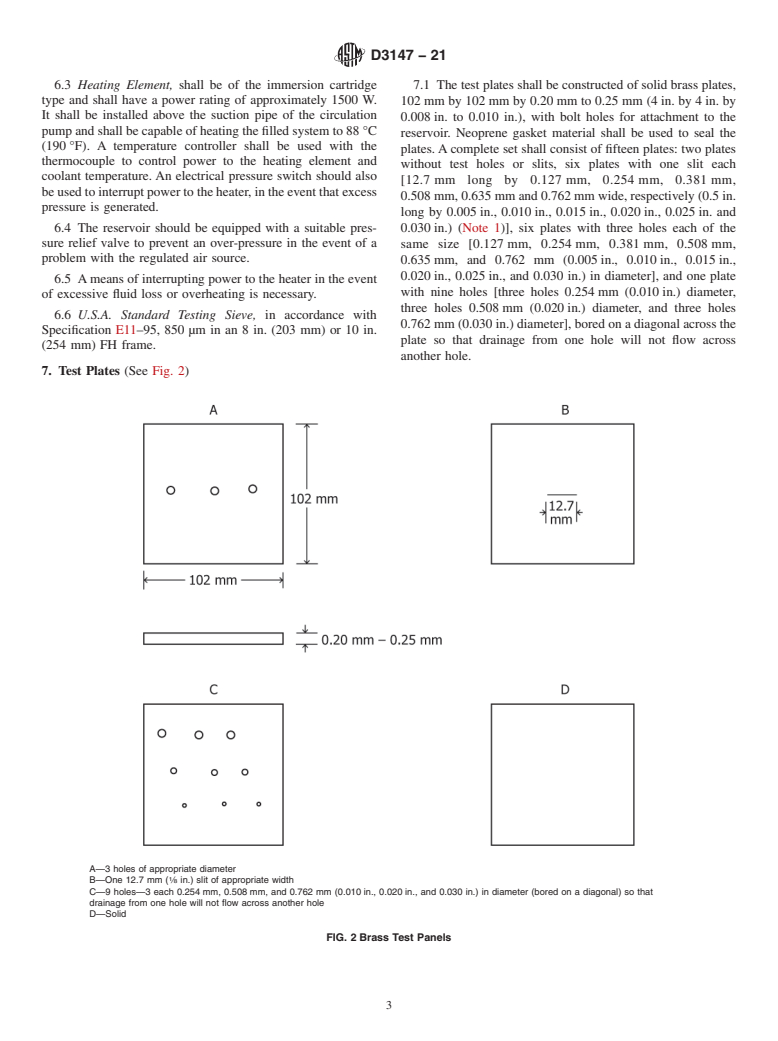
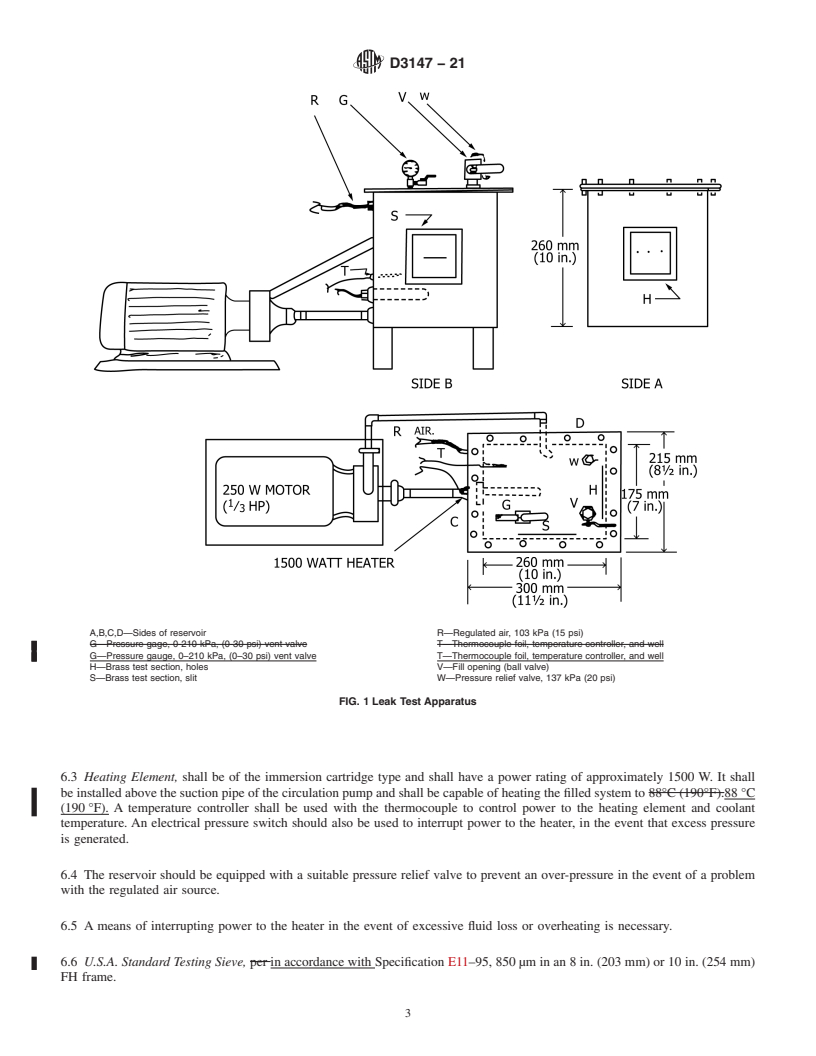
6. Apparatus (See Fig. 1)
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
6.1 Reservoir:
6.1.1 The reservoir shall be constructed of stainless steel,
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D15 on Engine
aluminum, or brass, 260 mm by 175 mm by 260 mm (10 in. by
Coolants and Related Fluids and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
7 in. by 10 in.) high, and the total capacity of the assembled
D15.09 on Simulated Service Tests.
unit shall be between 12 L and 13.5 L (3.2 gal to 3.6 gal). The
Current edition approved April 1, 2021. Published April 2021. Originally
3
reservoir shall have a 20 mm ( ⁄4 in.) flange at the top, to which
approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D3147 – 06 (2013).
DOI: 10.1520/D3147-21.
a cover plate is fitted.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.1.2 The reservoir and cover shall have a minimum thick-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ness of 1.6 mm (0.06 in.) in order to withstand a pressure of
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. 140 kPa (20 psi).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3147 − 21
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3147 − 06 (Reapproved 2013) D3147 − 21
Standard Test Method for Testing
1
Stop-Leak Additives for Engine Coolants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3147; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers screening procedures for the preliminary evaluation of leak-stopping materials intended for use in
engine cooling systems. (Heavy-duty users are referred to X1.2.21 in Specification D4485 for additional information.)
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only. after
SI units are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in 10.1.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1176 Practice for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous Solutions of Engine Coolants or Antirusts for Testing Purposes
D4485 Specification for Performance of Active API Service Category Engine Oils
D4725 Terminology for Engine Coolants and Related Fluids
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test Sieves
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 leaking—frequent drops forming (more than 5 drops/min).
3.1.2 sealed—completely plugged with no leaking or seeping.
3.1.3 seeping—occasional drops forming (fewer than 5 5 drops drops/min).⁄min).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D15 on Engine Coolants and Related Fluids and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D15.09 on
Simulated Service Tests.
Current edition approved May 1, 2013April 1, 2021. Published June 2013April 2021. Originally approved in 1972. Last previous edition approved in 20062013 as
D3147 – 06.D3147 – 06 (2013). DOI: 10.1520/D3147-06R13.10.1520/D3147-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3147 − 21
3.2 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D4725.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A heated test solution is circulated through a pressurized cubical metal reservoir which contains a slit and holes to simulate
leaks in an engine cooling system. The effectiveness of the stop-leak material is measured by its ability to seal the leaks under the
prescribed conditions of flow rate, temperature, pressure, and time.
4.2 The presence of particles in the test material that are larger than 0.84 mm (0.033 in.) or the presence of gumming or gelling
in stop-leak additives is determined by screening a test solution through a 850-μm850 μm (U.S. No. 20) standard sieve. The
screening is done both before and after the circulating test. Particles that remain on the sieve may be too large to pass through some
passages of the cooling system.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 The screening procedures simulate the conditions of temperature, pressure, and circulation encountered in service. This test
method will indicate whether a product is suitable for further evaluation in vehicles.
6. Apparatus (See Fig. 1)
6.1 Reservoir:
6.1.1 The reservoir shall be constructed of stainless steel, aluminum, or brass, 260260 mm by 175175 mm by 260-mm (10260 mm
(10 in. by 77 in. by 10 in.) high, and the total capacity of the assembled unit sha
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.