ASTM C1639-07
(Specification)Standard Specification for Fabrication of Cellular Glass Pipe and Tubing Insulation
Standard Specification for Fabrication of Cellular Glass Pipe and Tubing Insulation
ABSTRACT
This specification covers fabrication techniques for cellular glass block into billets to fabricate pipe and tubing insulation. The optimization of the thermal performance of installed cellular glass insulation systems is discussed. This is best achieved by limiting the number of joints, in particular through joints. Cellular glass pipe and tubing insulation shall be fabricated from the minimum number of insulation blocks. Sectional pipe insulation shall contain not more than four through joints per full section of insulation, excluding the half section mating plane. Fabrication adhesive shall be hot asphalt, Type II operating at some temperature. For operating temperatures above ambient, fabrication adhesive shall include but not be limited to Type II hot asphalt, elastomeric asphalt, or gypsum-based cement of the type and grade specified. Fabricating adhesive shall be applied such that there is 100% coverage of adhesive on the mating surfaces. Billet and miter construction shall conform to the following: insulation blocks or sections shall be hand rubbed if necessary to fit prior to bonding and bond joints shall be made with a full depth of approved adhesive. Bond joints can be classified as “non-through“ joints which start at the outside circumference and run continuously in a straight line to the opposite side terminating at the outside circumference. “Through” joints start at the outside circumference and runs continuously in a straight line to the opposite side and terminates at the inside circumference. All segmented pipe insulation shall be edge trimmed at the fabrication site. Either a grinder or a saw shall be used to edge trim segmented pipe insulation. If segmented pipe insulation is edge trimmed using a saw blade, edges shall be rubbed to remove uneven patterns caused by flexing blade where needed. Fittings for all sizes shall be either factory ground or factory mitered.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers fabrication techniques for cellular glass block into billets to fabricate pipe and tubing insulation. All materials shall be in accordance with Specification C 552.
1.2 The purpose of this specification is to optimize the thermal performance of installed cellular glass insulation systems. This is best achieved by limiting the number of joints, in particular through joints.
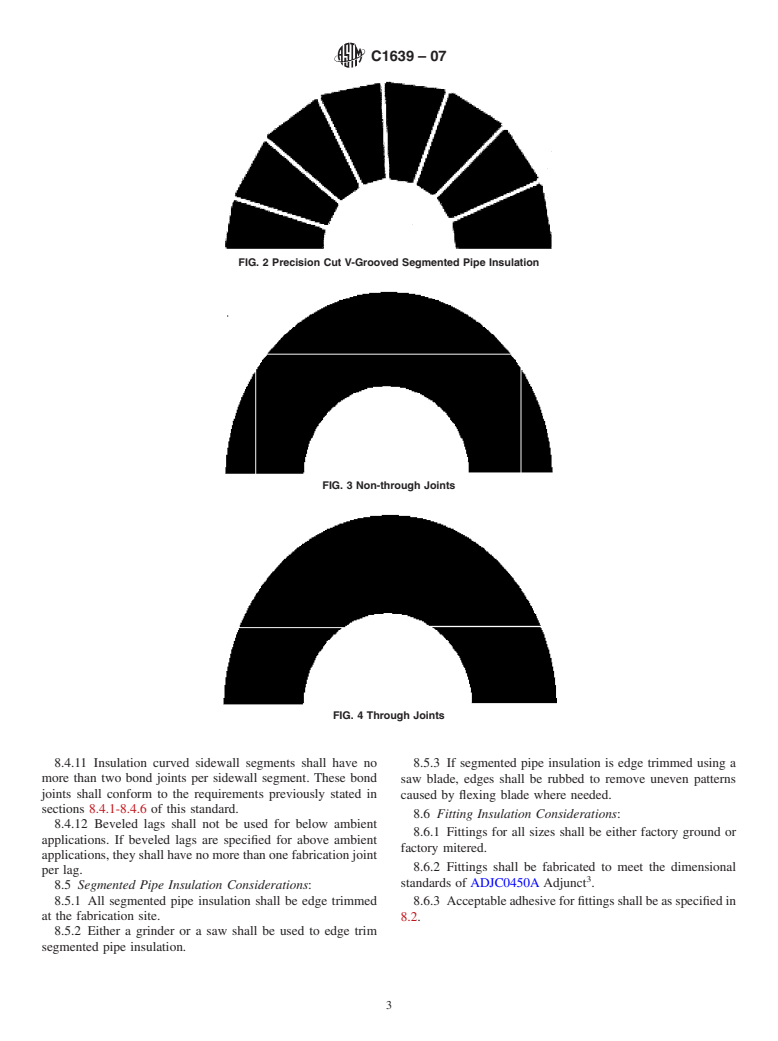
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in the parentheses are provided for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C1639 – 07
Standard Specification for
Fabrication Of Cellular Glass Pipe And Tubing Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1639; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.3 billet / bun— a single piece of insulation made up from
1.1 This specification covers fabrication techniques for
a number of smaller blocks held together with an adhesive.
cellular glass block into billets to fabricate pipe and tubing
3.4 lags—pieces of insulation typically curved or tapered
insulation. All materials shall be in accordance with Specifi-
used for insulating pipes, tanks and other cylindrical equip-
cation C552.
ment.
1.2 The purpose of this specification is to optimize the
3.5 precision cut V-grooved pipe insulation , n—rigid insu-
thermal performance of installed cellular glass insulation
lationpiecescutinto4-sidedpolygons,oftwoparallelsurfaces
systems.Thisisbestachievedbylimitingthenumberofjoints,
and two non-parallel surfaces of equal angles = 180° / N, such
in particular through joints.
thatwhen Nnumberofthesesectionsareassembled,theyform
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
an approximate circle and can be installed around a pipe.
as the standard. The values given in the parentheses are
3.5.1 Discussion—the adjective precision refers to the fact
provided for information only.
that when these N sections are installed onto a pipe, they fit
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
exactly with no appreciable gaps between sections.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Classification
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 SpecificationC552definesTypeIandTypeIImaterials.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
The same classifications shall be used in this standard.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 The insulation shall have no visible defects that will
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
adversely affect its performance.
C450 Practice for Fabrication of Thermal Insulating Fitting
Covers for NPS Piping, and Vessel Lagging
6. Standard Sizes, Dimensions, and Fabrication
C552 Specification for Cellular Glass Thermal Insulation
Configurations of Cellular Glass Pipe and Tubing
C585 Practice for Inner and Outer Diameters of Thermal
Insulation
Insulation for Nominal Sizes of Pipe and Tubing
6.1 Cellular glass pipe and tubing insulation shall be
D312 Specification for Asphalt Used in Roofing
fabricated in lengths as agreed to by the purchaser and the
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
supplier. Typical lengths are 23 ⁄2-in. (597mm), 24 in. (610
ADJC0450A ASTMRecommendedDimensionalStandards
mm), or 36 in. (914 mm).
for Fabrication of Thermal Insulation Fitting Covers
6.2 CellularglasspipeandtubinginsulationforNPS4(102
mm)andsmallerpipeshallbemadetoaminimumthicknessof
3. Terminology
1-in. (25 mm). Pipe insulation for pipes larger than 4 in. NPS
3.1 Terminology C168 shall be considered as applying to
(102 mm) shall be made to a minimum 1 ⁄2-in. (38 mm)
the terms in this specification.
thickness. Sizes shall conform to Practice C585.Aminimum 2
in. (51 mm) thickness should be used for pipe sizes larger than
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on
12 in. NPS (324 mm).
Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.40 on
6.3 Cellular glass pipe insulation must be provided in half
Insulation Systems.
Current edition approved April 1, 2007. Published May 2007. DOI: 10.1520/
sections for up to and including 12 in. NPS (324 mm). Half
C1639-07.
sections shall consist of hollow cylindrical sections split
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
lengthwise in a plane that includes the cylindrical axis.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on 6.4 Cellular glass pipe insulation for pipe sizes 14 in. (356
the ASTM website.
mm) to 24 in. NPS (406 mm) must be fabricated in half-
Available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No.
sections or in quarter-sections. At 26 in. NPS (660 mm) and
ADJC0450A.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C1639 – 07
above, segmented pipe insulation shall be furnished. Seg- asphalt, elastomeric asphalt, or gypsum-based cement of the
mented pipe insulation (see Fig. 1) shall be fabricated in equal type and grade specified by the insulation manufacturer.
widths such that no additional field cuts are required. Adhesives shall be suitable for specified design conditions.
6.5 Foroperatingtemperaturesaboveambient,precisioncut 8.2.1 Fabricatingadhesiveshallbeappliedsuchthatthereis
V-grooved pipe insulation specifically cut to fit the required 100% coverage of adhesive on the mating surfaces.
diameter or segmented fabrication is an acceptable alternative. 8.2.2 Thereshallbenovisiblevoidsintheadheredjointnor
6.6 For operating temperatures between 0°F (-18°C) and shall any adhered joint exceed ⁄16 in. (1.6 mm) in width.
ambient, precision cut V-grooved pipe insulation, as shown on 8.3 Billet and miter construction shall conform to the
Fig. 2, is an acceptable alternative provided an acceptable following:
vapor retarder is used. 8.3.1 Insulation blocks or sections shall be hand rubbed if
6.7 For operating temperatures below 0° F (-18°C), necessary to fit prior to bonding.
V-grooved material, as shown on Fig. 2 is not acceptable. 8.3.2 Bond joints shall be made with a full depth of
approved adhesive. (See 3.3.)
7. Dimensional Tolerances
8.4 Bond Joints for Segmented Fabrication—Bond joints
7.1 Fabrication tolerances for the bore diameter and wall are defined as an adhesive joint in insulation for construction
purposes:
thickness shall be as specified in Practice C585.
7.2
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.