ASTM D5599-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Oxygenates in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography and Oxygen Selective Flame Ionization Detection
Standard Test Method for Determination of Oxygenates in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography and Oxygen Selective Flame Ionization Detection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 In gasoline blending, the determination of organic oxygenated compounds is important. Alcohols, ethers, and other oxygenates are added to gasoline to increase the octane number and to reduce tailpipe emissions of carbon monoxide. They must be added in the proper concentration and ratios to meet regulatory limitations and to avoid phase separation and problems with engine performance or efficiency.
5.2 This test method provides sufficient oxygen-to-hydro-carbon selectivity and sensitivity to allow determination of oxygenates in gasoline samples without interference from the bulk hydrocarbon matrix.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a gas chromatographic procedure for the quantitative determination of organic oxygenated compounds in gasoline having a final boiling point not greater than 220 °C and oxygenates having a boiling point limit of 130 °C. It is applicable when oxygenates are present in the 0.1 % to 20 % by mass range.
1.2 This test method is intended to determine the mass concentration of each oxygenate compound present in a gasoline. This requires knowledge of the identity of each oxygenate being determined (for calibration purposes). However, the oxygen-selective detector used in this test method exhibits a response that is proportional to the mass of oxygen. It is, therefore, possible to determine the mass concentration of oxygen contributed by any oxygenate compound in the sample, whether or not it is identified. Total oxygen content in a gasoline may be determined from the summation of the accurately determined individual oxygenated compounds. The summed area of other, uncalibrated or unknown oxygenated compounds present, may be converted to a mass concentration of oxygen and summed with the oxygen concentration of the known oxygenated compounds.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5599 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Oxygenates in Gasoline by Gas
Chromatography and Oxygen Selective Flame Ionization
1
Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5599; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1 This test method covers a gas chromatographic proce-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
dure for the quantitative determination of organic oxygenated
compounds in gasoline having a final boiling point not greater
2. Referenced Documents
than 220 °C and oxygenates having a boiling point limit of
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
130 °C. It is applicable when oxygenates are present in the
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API
0.1 % to 20 % by mass range.
Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Prod-
1.2 This test method is intended to determine the mass
ucts by Hydrometer Method
concentration of each oxygenate compound present in a gaso-
D1744 Test Method for Determination of Water in Liquid
line.This requires knowledge of the identity of each oxygenate
Petroleum Products by Karl Fischer Reagent (Withdrawn
being determined (for calibration purposes). However, the
3
2016)
oxygen-selective detector used in this test method exhibits a
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
response that is proportional to the mass of oxygen.Itis,
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
therefore, possible to determine the mass concentration of
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
oxygen contributed by any oxygenate compound in the sample,
Fuels, and Lubricants
whether or not it is identified. Total oxygen content in a
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as
gasoline may be determined from the summation of the
Analytical Standards
accurately determined individual oxygenated compounds. The
E594 Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used
summed area of other, uncalibrated or unknown oxygenated
in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
compounds present, may be converted to a mass concentration
E1064 Test Method for Water in Organic Liquids by Coulo-
of oxygen and summed with the oxygen concentration of the
metric Karl Fischer Titration
known oxygenated compounds.
E1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatographs
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
3. Terminology
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1 Definitions:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.1 independent reference standards, n—calibration
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
samples of the oxygenates which are purchased or prepared
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
from materials independent of the quality control check stan-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
dards and used for intralaboratory accuracy.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1.2 oxygenate, n—an oxygen-containing compound, such
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
as an alcohol or ether, which may be used as a fuel or fuel
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
supplement.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved May 1, 2017. Published June 2017. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D5599 – 15. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/D5599-17. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5599 − 17
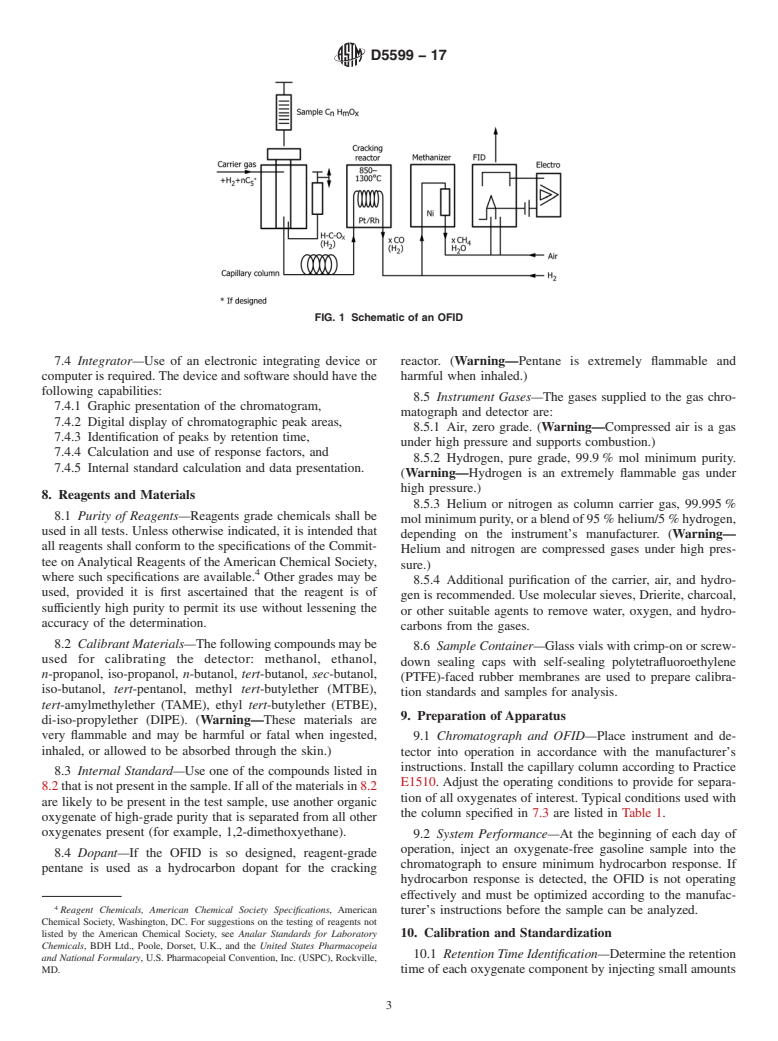
3.1.3 quality control check standards, n—calibration 6.3 The carbon monoxide formed in the cracking reactor is
samples of the oxygenates for intralaboratory repeatability. convertedtomethaneinthehydrog
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5599 − 15 D5599 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Oxygenates in Gasoline by Gas
Chromatography and Oxygen Selective Flame Ionization
1
Detection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5599; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a gas chromatographic procedure for the quantitative determination of organic oxygenated
compounds in gasoline having a final boiling point not greater than 220 °C and oxygenates having a boiling point limit of 130 °C.
It is applicable when oxygenates are present in the 0.1 % to 20 % by mass range.
1.2 This test method is intended to determine the mass concentration of each oxygenate compound present in a gasoline. This
requires knowledge of the identity of each oxygenate being determined (for calibration purposes). However, the oxygen-selective
detector used in this test method exhibits a response that is proportional to the mass of oxygen. It is, therefore, possible to determine
the mass concentration of oxygen contributed by any oxygenate compound in the sample, whether or not it is identified. Total
oxygen content in a gasoline may be determined from the summation of the accurately determined individual oxygenated
compounds. The summed area of other, uncalibrated or unknown oxygenated compounds present, may be converted to a mass
concentration of oxygen and summed with the oxygen concentration of the known oxygenated compounds.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by
Hydrometer Method
3
D1744 Test Method for Determination of Water in Liquid Petroleum Products by Karl Fischer Reagent (Withdrawn 2016)
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as Analytical Standards
E594 Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
E1064 Test Method for Water in Organic Liquids by Coulometric Karl Fischer Titration
E1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatographs
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04.0L on Gas Chromatography Methods.
Current edition approved June 1, 2015May 1, 2017. Published July 2015June 2017. Originally approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 20102015 as
D5599 – 00 (2010).D5599 – 15. DOI: 10.1520/D5599-15.10.1520/D5599-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5599 − 17
3.1.1 independent reference standards—standards, n—calibration samples of the oxygenates which are purchased or prepared
from materials independent of the quality control check standards and used for intralabora
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.