ASTM F1971-12(2018)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Electrical Resistance of Tires Under Load On the Test Bench
Standard Test Method for Electrical Resistance of Tires Under Load On the Test Bench
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Occasions exist where static charges on the vehicle must be dissipated by way of the tires. Electrical resistance inversely measures the tire's ability to dissipate static charge from the vehicle.
SCOPE
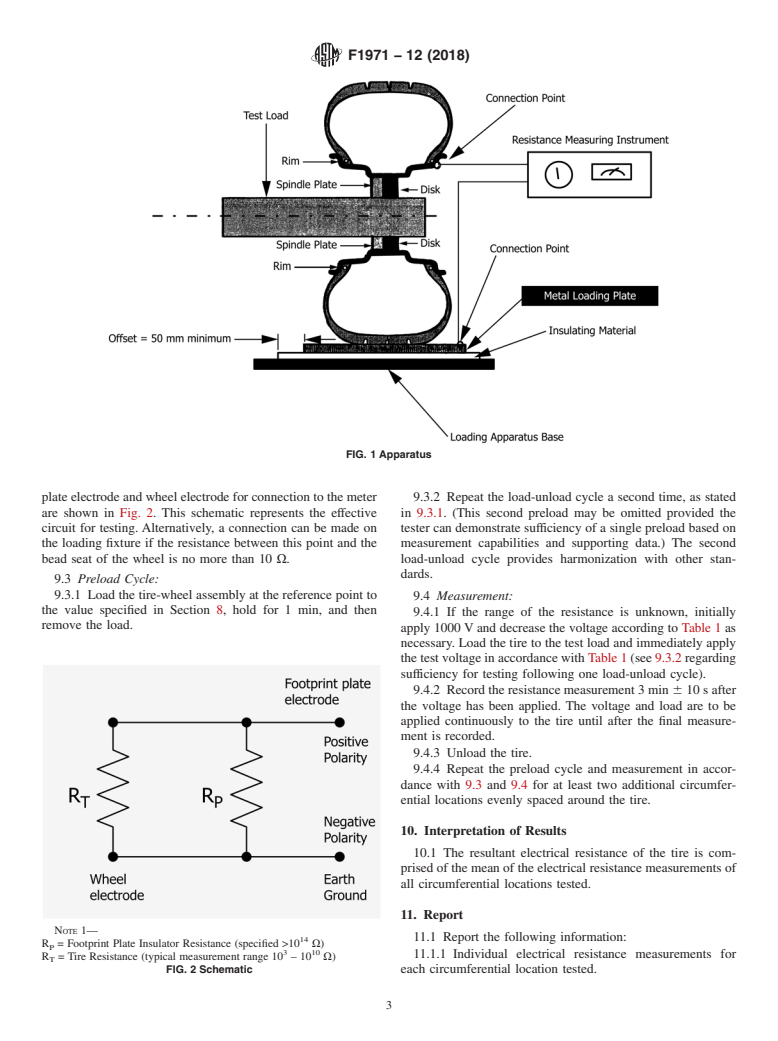
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the electrical resistance between the wheel of a mounted and inflated tire-wheel assembly and a flat conducting surface in loaded contact with the tire.
1.2 This test method specifies procedures and equipment such that electrical resistance can be accurately determined for tires with values up to 1012 Ω (ohms).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F1971 − 12 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Test Method for
Electrical Resistance of Tires Under Load On the Test
Bench
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1971; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope The European Tyre and Rim Technical Organization
(ETRTO), current issue
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the electri-
The JapanAutomobile Tire ManufacturersAssociation, Inc.
cal resistance between the wheel of a mounted and inflated
Yearbook (JATMA), current issue
tire-wheel assembly and a flat conducting surface in loaded
International Standard ISO 16392Electrical Resistance—
contact with the tire.
Test Methods to Measure the Electrical Resistance of
1.2 This test method specifies procedures and equipment 6
Tyres on a Test Rig
such that electrical resistance can be accurately determined for
Wirtschaftsverband der deutschen Kautschukindustrie e.V.
tires with values up to 10 Ω (ohms).
(W.d.K) 110Measurement of the Electrical Resistance of
Tyres
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3. Terminology
only.
3.1 Definitions:
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.1 connection point, n—any point on the wheel or metal
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
loading plate where the resistance measuring instrument’s
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
leads are connected. F538
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 3.1.2 rim, n—the specially shaped circular periphery to
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor- which a tire may be mounted with appropriate bead fitment.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- F538
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.1.3 test load, n—the force applied to a tire through the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
rim; it is normal to the metal loading plate onto which the tire
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
is loaded. F538
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.1.4 tire electrical resistance, n—theelectricalresistancein
ohms (Ω) measured between the wheel of a mounted and
2. Referenced Documents
inflated tire-wheel assembly and a metallic plate onto which
2.1 ASTM Standards:
the tire is loaded at a specified load. F538
F538Terminology Relating to the Characteristics and Per-
2 3.1.5 wheel, n—a rigid structure consisting of a rim con-
formance of Tires
nected to a central disk that permits rotationally centered
2.2 Other Standards:
attachment to an axle. F538
TheTire and RimAssociation Inc.Yearbook (TRA), current
3.1.6 For additional definitions of terms used in this test
issue
method, refer to Terminology F538.
4. Summary of Test Method
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F09 on Tires
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F09.30 on Laboratory (Non-
4.1 Theelectricalresistanceofaninflatedtire-wheelassem-
Vehicular) Testing.
bly (see Note 1) is measured between the wheel and the
Current edition approved April 1, 2018. Published April 2018. Originally
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as F1971–12. DOI:
10.1520/F1971-12R18.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from the European Tyre and Rim Technical Organization, 32/2
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM avenue Brugmann, B-1060 Brussels, Belgium.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from the Japan Automobile Tire Manufacturers Association, No. 33
th
the ASTM website. Mori Building, 8 Floor, 3-8-21 Toranomon, Minato-Ku, Tokyo, Japan 105-0001.
3 6
Available from the Tire and Rim Association, Inc., 175 Montrose West Ave., Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1 rue de
Suite 150, Copley, OH 44321. Varembé, Case postale 56, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1971 − 12 (2018)
conducting surface against which the tire is loaded. This 6.5 Pressure Gage—Acommercially available gage with an
measurement involves the use of an appropriate resistance accuracy of 63 kPa (60.5 psi).
meter and voltage application system, as well as a special test
7. Conditioning
fixture or measuring stand.
NOTE 1—A tire mounted on an approved wheel and inflated to a
7.1 For at least 8 h prior to measurement of passenger, light
specified pressure.
truck,andmotorcycletireapplications(24hforallothertires),
the tire to be tested shall be kept at an ambient temperature of
5. Significance and Use
23 6 5°C [73 6 9°F], and at a relative humidity less than
5.1 Occasionsexistwherestaticchargesonthevehiclemust
60%.
bedissipatedbywayofthetires.Electricalresistanceinversely
measures the tire’s ability to dissipate static charge from the 8. Measurement Conditions
vehicle.
8.1 The test load applied during the measurement is 80 6
5% of the maximum load capacity of the tire as listed in the
6. Apparatus
applicable TRA, ETRTO, or JATMA standards.
6.1 Resistance Measuring Instrument (ohmmeter)—
8.2 The inflation pressure is equal to 80 6 5% of the
Resistance shall be measured by a commercial instrument
pressure corresponding to the maximum load of the tire.
capable of measuring electrical resistance in ohms and having
8.3 If the tire size is not listed in the applicable TRA,
a power source capable of 1000 V. The voltage shall be
ETRTO, or JATMAstandards, the above percentages apply to
controlled as described in Table 1 and shall not dissipate more
the loads and inflations as marked on the sidewall of the tire.
than3Winthetestsample.Theinstrumentshallbecapableof
determining the resistance up to a value of 10 Ω with an
8.4 Ambient temperature during the measurement shall be
accuracy of 62%. The input impedance shall be at least 10
maintained at 23 6 5°C (73 6 9°F).
Ω.
8.5 Relative humidity during the measurement shall be
6.2 Metal Loading Plate—A flat plate of dimensions suffi-
maintained at ≤60%.
cient to encompass the entire contact surface of the tire under
test and with sufficient thickness to support the test loads 9. Procedure
described in Section 8 without visible deformation. This plate
9.1 Preparation of the Tire-Wheel Assembly:
shallbemadeofaconductivenoncorrosivemetal,forexample,
9.1.1 The approved wheel (see Note 2) (steel preferred)
brass or stainless steel, free from any coating or obvious
must be stripped clean in the bead seat area, as well as at the
surface contamination, such as oxidation or corrosion. Alumi-
connection point. As an alternative, if the electrical resistance
num shall not be used for the plate because of its high
of the wheel is known to be two orders of magnitude lower
susceptibility to the rapid development of surface oxides,
than the tire to be measured, stripping is not necessary.
which may adversely affect reading accuracy.
NOT
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.