ASTM C835-06
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Total Hemispherical Emittance of Surfaces up to 1400°C
Standard Test Method for Total Hemispherical Emittance of Surfaces up to 1400°C
SCOPE
1. Scope
1.1 This calorimetric test method covers the determination of total hemispherical emittance of metal and graphite surfaces and coated metal surfaces up to approximately 1400C. The upper-use temperature is limited only by the characteristics (for example, melting temperature, vapor pressure) of the specimen and the design limits of the test facility. This test method has been demonstrated for use up to 1400 C. The lower-use temperature is limited by the temperature of the bell jar.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C835 − 06
StandardTest Method for
1
Total Hemispherical Emittance of Surfaces up to 1400°C
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C835; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
σ = Stefan-Boltzmann constant,
−8 2 4
= 5.669×10 W/m ·K ,
1.1 This calorimetric test method covers the determination
Q = heat flow rate, W,
oftotalhemisphericalemittanceofmetalandgraphitesurfaces
T = temperature of heated specimen, K,
1
and coated metal surfaces up to approximately 1400°C. The
T = temperature of bell jar inner surface, K,
2
upper-usetemperatureislimitedonlybythecharacteristics(for
A = surfaceareaofspecimenoverwhichheatgenerationis
1
example,meltingtemperature,vaporpressure)ofthespecimen
2
measured, m ,
and the design limits of the test facility. This test method has
2
A = surface area of bell jar inner surface, m ,
2
been demonstrated for use up to 1400°C. The lower-use
F = the gray body shape factor, which includes the effect
temperature is limited by the temperature of the bell jar.
of geometry and the departure of real surfaces from
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
blackbody conditions, dimensionless, and
2
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the Pa = absolute pressure, pascal (N/m ). One pascal is
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
equivalent to 0.00750 mm Hg.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4. Summary of Test Method
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
statements, see Section 7. 4.1 Astrip specimen of the material, approximately 13 mm
wide and 250 mm long, is placed in an evacuated chamber and
2. Referenced Documents
is directly heated with an electric current to the temperature at
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: which the emittance measurement is desired. The power
dissipated over a small central region of the specimen and the
C168Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
E230Specification and Temperature-Electromotive Force temperature of this region are measured. Using the Stefan-
Boltzmannequation,thispowerisequatedtotheradiativeheat
(EMF) Tables for Standardized Thermocouples
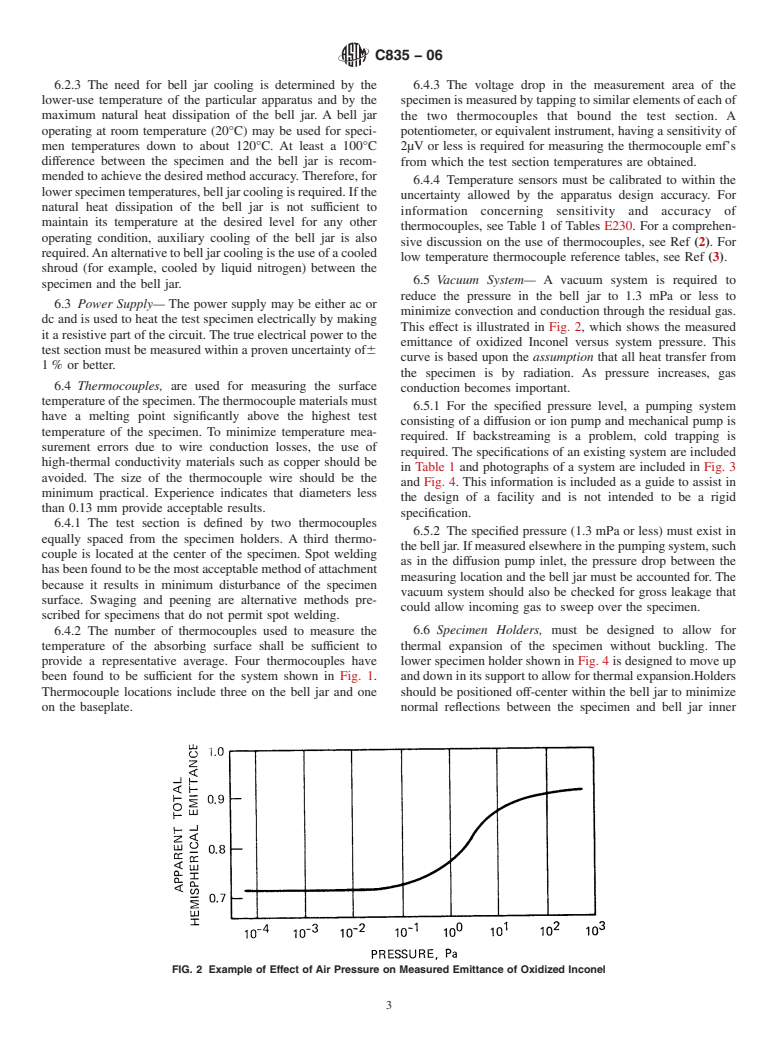
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to transfer to the surroundings and, with the measured
Determine the Precision of a Test Method temperature, is used to calculate the value of the total hemi-
spherical emittance of the specimen surface.
3. Terminology
5. Significance and Use
3.1 Definitions—The terms and symbols are as defined in
5.1 The emittance as measured by this test method can be
Terminology C168 with exceptions included as appropriate.
used in the calculation of radiant heat transfer from surfaces
3.2 Symbols:
that are representative of the tested specimens, and that are
e = error in the variable i, 6 %,
within the temperature range of the tested specimens.
i
ε = total hemispherical emittance of heated specimen,
1
5.2 This test method can be used to determine the effect of
dimensionless,
service conditions on the emittance of materials. In particular,
ε = total hemispherical emittance of bell jar inner surface,
2
the use of this test method with furnace exposure (time at
dimensionless,
temperature) of the materials commonly used in all-metallic
insulationscandeterminetheeffectsofoxidationonemittance.
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC16onThermal
5.3 The measurements described in this test method are
Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.30 on Thermal
conducted in a vacuum environment. Usually this condition
Measurement.
will provide emittance values that are applicable to materials
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2006. Published December 2006. Originally
used under other conditions, such as in an air environment.
approvedin1976.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2006asC835–01(2006).DOI:
10.1520/C0835-06.
However, it must be recognized that surface properties of
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
materials used in air or other atmospheres may be different. In
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
addition, preconditioned surfaces, as described in 5.2, may be
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. altered in a vacuum environment because of vacuum stripping
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C835 − 06
of absorbed gases and other associated
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.