ASTM B208-14
(Practice)Standard Practice for Preparing Tension Test Specimens for Copper Alloy Sand, Permanent Mold, Centrifugal, and Continuous Castings
Standard Practice for Preparing Tension Test Specimens for Copper Alloy Sand, Permanent Mold, Centrifugal, and Continuous Castings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The mechanical properties determined from test bars for sand, permanent mold, and centrifugal castings poured in accordance with this practice represent the properties of the metal going into castings poured from the same heat. These mechanical properties may not be the same as the properties of the corresponding castings because of the solidification effects of varying size, section, and design.
4.2 Test bars for continuous castings are taken from the castings and therefore represent the properties of the castings.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice establishes procedures for preparing test coupons and specimens (machined and unmachined) for tension tests of copper alloys for sand, permanent mold, centrifugal and continuous castings.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B208 − 14 Endorsed by
American Foundrymen’s Society
Standard Practice for
Preparing Tension Test Specimens for Copper Alloy Sand,
1
Permanent Mold, Centrifugal, and Continuous Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B208; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 5. Test Coupons
5.1 Sand Castings—The test bar coupons shall be made by
1.1 This practice establishes procedures for preparing test
the same manufacturing process as the castings they represent
coupons and specimens (machined and unmachined) for ten-
wherever possible. If the castings are cast entirely in green
sion tests of copper alloys for sand, permanent mold, centrifu-
sand, partial cores shall be permitted for the test bars but in no
gal and continuous castings.
case shall chills be permitted. Unless otherwise agreed upon
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
between the manufacturer and purchaser, test bars may be
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
poured in cores on a production line. The use of filters in the
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
gating system is permitted.
and are not considered standard.
5.1.1 High-Shrinkage Sand-Cast Alloys—The test specimen
coupons for copper casting alloys exhibiting high shrinkage
2. Referenced Documents
during freezing and cooling shall be cast to the form and
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
dimensions shown in Fig. 1 (a or b) or 2 (a or b). If specimens
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
having threaded ends are to be used in the tension tests, the
1
length of the keel blocks in Fig. 1a may be reduced to 6 ⁄4 in.
3. Terminology (159 mm). See Appendix X1 for SI equivalents.
5.1.2 Low-Shrinkage Sand-Cast Alloys—The test specimen
3.1 Definitions of terms relating to copper alloys can be
coupons for copper casting alloys exhibiting low shrinkage
found in Terminology B846.
during freezing and cooling shall be cast to the form and
dimensionsshowninFig.2(AorB),Fig.3,orFig.4orasmay
4. Significance and Use
be prescribed in the casting specifications.
4.1 The mechanical properties determined from test bars for
5.2 CentrifugalCastings—Unlessotherwisespecifiedbythe
sand, permanent mold, and centrifugal castings poured in
purchaser, the manufacturer shall pour the test bars in the same
accordance with this practice represent the properties of the
type of mold as the castings themselves. That is, test bars for
metal going into castings poured from the same heat. These
sand mold castings shall be poured in sand molds, and test bars
mechanical properties may not be the same as the properties of
for chill mold castings shall be poured in chill molds.
the corresponding castings because of the solidification effects
5.2.1 The centrifugally cast test specimen coupons shall be
of varying size, section, and design.
cast to the form and dimensions of Fig. 5a.
4.2 Test bars for continuous castings are taken from the
5.2.2 Static test bar coupons shall be cast in open keel block
castings and therefore represent the properties of the castings.
molds as dimensioned in Fig. 5b.
5.3 Continuous Castings—Test bars shall be taken from the
continuous cast product. Test bars may be taken before
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B05 on Copper and
mechanical straightening.
CopperAlloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.05 on Castings
5.3.1 Test bar coupons shall be taken in a longitudinal
and Ingots for Remelting.
direction from the continuous cast product at the mid-wall of
Current edition approved April 1, 2014. Published May 2014. Originally
hollow castings or at one-half the distance between the center
approved in 1946. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as B208 – 06. DOI:
10.1520/B0208-14.
and the side of solid castings as illustrated in Fig. 6.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
5.3.2 For irregular shapes, the location of the test bar
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
coupon shall be as agreed upon between the manufacturer and
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. purchaser.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B208 − 14
(a) Bottom
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B208 − 06 B208 − 14 Endorsed by
American Foundrymen’s Society
Standard Practice for
Preparing Tension Test Specimens for Copper Alloy Sand,
1
Permanent Mold, Centrifugal, and Continuous Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B208; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This practice establishes procedures for preparing test coupons and specimens (machined and unmachined) for tension tests
of copper alloys for sand, permanent mold, centrifugal and continuous castings.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are the standard. SIto be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
for information only.mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of terms relating to copper alloys can be found in Terminology B846.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The mechanical properties determined from test bars for sand, permanent mold, and centrifugal castings poured in
accordance with this practice represent the properties of the metal going into castings poured from the same heat. These mechanical
properties may not be the same as the properties of the corresponding castings because of the solidification effects of varying size,
section, and design.
4.2 Test bars for continuous castings are taken from the castings and therefore represent the properties of the castings.
5. Test Coupons
5.1 Sand Castings—The test bar coupons shall be made by the same manufacturing process as the castings they represent
wherever possible. If the castings are cast entirely in green sand, partial cores shall be permitted for the test bars but in no case
shall chills be permitted. Unless otherwise agreed upon between the manufacturer and purchaser, test bars may be poured in cores
on a production line. The use of filters in the gating system is permitted.
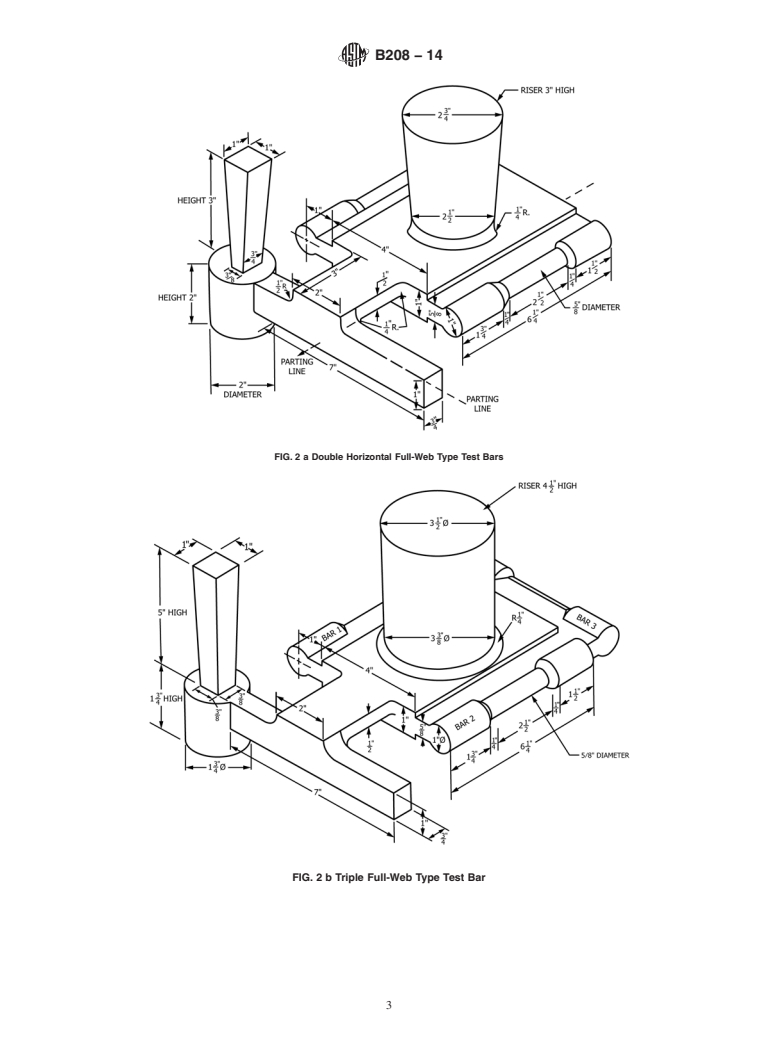
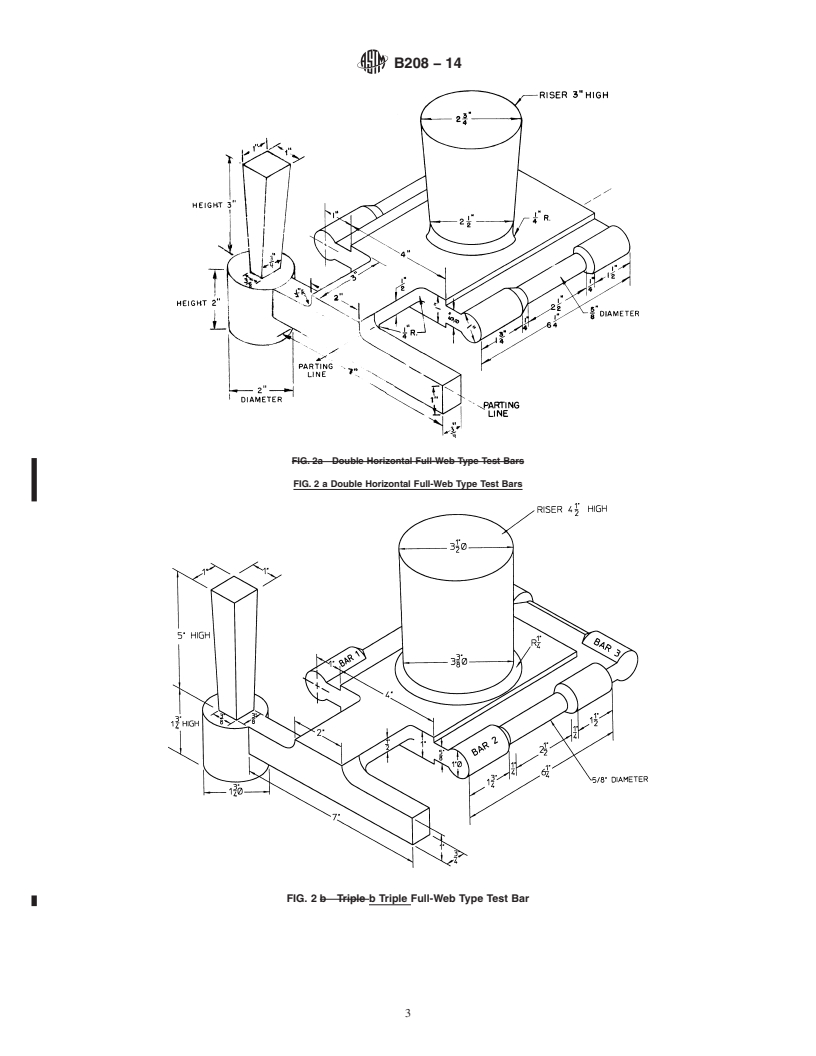
5.1.1 High-Shrinkage Sand-Cast Alloys—The test specimen coupons for copper casting alloys exhibiting high shrinkage during
freezing and cooling shall be cast to the form and dimensions shown in Fig. 1 (a or b) or 2 (a or b). If specimens having threaded
1
ends are to be used in the tension tests, the length of the keel blocks in Fig. 1a may be reduced to 6 ⁄4 in. (159 mm). See Appendix
X1 for SI equivalents.
5.1.2 Low-Shrinkage Sand-Cast Alloys—The test specimen coupons for copper casting alloys exhibiting low shrinkage during
freezing and cooling shall be cast to the form and dimensions shown in Fig. 2 (A or B), Fig. 3, or Fig. 4 or as may be prescribed
in the casting specifications.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.05 on Castings and
Ingots for Remelting.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2006April 1, 2014. Published February 2006May 2014. Originally approved in 1946. Last previous edition approved in 20042006 as
B208 – 04.B208 – 06. DOI: 10.1520/B0208-06.10.1520/B0208-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B208 − 14
(a) Bottom Gating
(a) Bottom Gating
(b) Bottom ) Bottom Gating (Lower Weight Version)
NOTE 1—Where this type of test bar design is used, bottom gating is recommended for alloys such as aluminum bronze, where turbulence and oxidation
are factors.
FIG. 1 Double Keel Block Test Bar
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
B208 − 14
FIG. 2a Double Horizontal Full-Web Type Test Bars
FIG. 2 a Double Horizontal Full-Web Type Test Bars
FIG. 2 b Triple b Triple Full-Web Type Test Bar
3
---------------------- Page: 3 ----------------------
B208 − 14
(a) Gating Design for Double Vertical Full-Web or Gri
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.