ASTM F749-20
(Practice)Standard Practice for Evaluating Material Extracts by Intracutaneous Injection in the Rabbit
Standard Practice for Evaluating Material Extracts by Intracutaneous Injection in the Rabbit
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This practice is to be used to help assess the biocompatibility of materials used in medical devices. It is an acute toxicological test designed to evaluate any irritation caused by device materials by gross assessment.
4.2 This practice may not be appropriate for all types of implant applications. The user is cautioned to consider the appropriateness of this practice in view of the materials being tested, their potential applications, and the recommendations contained in Practice F748.
Note 1: Some materials (e.g., absorbables) may result in an extract pH (e.g., ≤2.0 or ≥11.5) that cannot be used with this practice.
4.3 The only applicable limitation is the extract preparation. Refer to Section 4.3 of Practice F619 for a description of this limitation.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice is an intracutaneous reactivity test used to assess the potential of the material under test to produce irritation following intradermal injections of extracts of the material.
1.2 The liquids injected into the rabbits are those obtained by Practice F619 where the extraction vehicles are saline, vegetable oil, or other liquids simulating human body fluids.
1.3 This practice is one of several developed for the assessment of the biocompatibility of materials. Practice F748 may provide guidance for the selection of appropriate methods for testing materials for a specific application.
1.4 The values stated in SI units, including units officially accepted for use with the SI, are to be regarded as standard. No other systems of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F749 − 20
Standard Practice for
Evaluating Material Extracts by Intracutaneous Injection in
1
the Rabbit
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF749;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope or other extraction vehicles can be used, as described in
PracticeF619.Theextractliquidisinjectedintorabbitsandthe
1.1 This practice is an intracutaneous reactivity test used to
animals are observed at regular intervals for 72 h for erythema,
assess the potential of the material under test to produce
edema, eschar formation or necrosis.
irritation following intradermal injections of extracts of the
material.
4. Significance and Use
1.2 The liquids injected into the rabbits are those obtained
4.1 This practice is to be used to help assess the biocom-
by Practice F619 where the extraction vehicles are saline,
patibility of materials used in medical devices. It is an acute
vegetable oil, or other liquids simulating human body fluids.
toxicological test designed to evaluate any irritation caused by
1.3 This practice is one of several developed for the
device materials by gross assessment.
assessment of the biocompatibility of materials. Practice F748
4.2 This practice may not be appropriate for all types of
may provide guidance for the selection of appropriate methods
implant applications. The user is cautioned to consider the
for testing materials for a specific application.
appropriateness of this practice in view of the materials being
1.4 The values stated in SI units, including units officially
tested, their potential applications, and the recommendations
accepted for use with the SI, are to be regarded as standard. No
contained in Practice F748.
other systems of measurement are included in this standard.
NOTE 1—Some materials (e.g., absorbables) may result in an extract pH
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
(e.g., ≤2.0 or ≥11.5) that cannot be used with this practice.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4.3 The only applicable limitation is the extract preparation.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Refer to Section 4.3 of Practice F619 for a description of this
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
limitation.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5. Apparatus
2. Referenced Documents
5.1 Cages—There shall be one cage for each rabbit exposed
2
to one extract liquid. Each rabbit shall be uniquely identified
2.1 ASTM Standards:
with this identity recorded.
F619 Practice for Extraction of Medical Plastics
F748 PracticeforSelectingGenericBiologicalTestMethods
5.2 Syringes—Sterile syringes, not greater than 2 mL in
for Materials and Devices volume, with a precision of no less than 60.10 mL shall be
used. Sterile needles of 21 to 26 gauge shall be used.
3. Summary of Practice
6. Test Animals
3.1 The extract liquid is prepared in accordance with Prac-
tice F619. The extraction vehicles are saline and vegetable oil,
6.1 Rabbits—The rabbits shall be healthy thin-skinned al-
binotype,notpreviouslyusedforanytest.Animalcareshallbe
in accordance with the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory
1
ThispracticeisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF04onMedicaland
3
Animals. Rabbits with significant scars or wounds are not
Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
suitableforthistest.Aminimumofthreerabbitsareusedinthe
F04.16 on Biocompatibility Test Methods.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2020. Published March 2020. Originally
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as F749 – 13. DOI:
10.1520/F0749-20.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or National Research Council Guide for the Care and Use of LaboratoryAnimals,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 8th ed. (2011), Institute of LaboratoryAnimal Research Division on Earth and Life
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Sciences, Washington, D.C., National Academies of Science Press (http://
the ASTM website. www.nap.edu/catalog.php?record_id=12910).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F749 − 20
test. If the results of the first test are inconclusive, three more c
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F749 − 13 F749 − 20
Standard Practice for
Evaluating Material Extracts by Intracutaneous Injection in
1
the Rabbit
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F749; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice is a nonspecific, acute toxicity an intracutaneous reactivity test used to help determine assess the
biocompatibility of materials used in medical devices.potential of the material under test to produce irritation following intradermal
injections of extracts of the material.
1.2 The liquids injected into the rabbits are those obtained by Practice F619 where the extraction vehicles are saline, vegetable
oil, or other liquids simulating human body fluids.
1.3 This practice is one of several developed for the assessment of the biocompatibility of materials. Practice F748 may provide
guidance for the selection of appropriate methods for testing materials for a specific application.
1.4 The values stated in SI units units, including units officially accepted for use with the SI, are to be regarded as standard.
No other unitssystems of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F619 Practice for Extraction of Medical Plastics
F748 Practice for Selecting Generic Biological Test Methods for Materials and Devices
3. Summary of Practice
3.1 The extract liquid is prepared in accordance with Practice F619. The extraction vehicles are saline and vegetable oil, or other
extraction vehicles can be used, as described in Practice F619. The extract liquid is injected into rabbits and the animals are
observed at regular intervals for 72 h for erythema, edema, eschar formation or necrosis.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This practice is to be used to help assess the biocompatibility of materials used in medical devices. It is an acute
toxicological test designed to detect the presence of injurious leachable substances.evaluate any irritation caused by device
materials by gross assessment.
4.2 This practice may not be appropriate for all types of implant applications. The user is cautioned to consider the
appropriateness of the methodthis practice in view of the materials being tested, their potential applications, and the
recommendations contained in Practice F748.
NOTE 1—Some materials (e.g., absorbables) may result in an extract pH (e.g., ≤2.0 or ≥11.5) that cannot be used with this practice.
4.3 The only applicable limitation is the extract preparation. Refer to SectionsSection 4.3 and 4.4 of Practice F619 for a
description of this limitation.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F04.16
on Biocompatibility Test Methods.
Current edition approved March 1, 2013Feb. 1, 2020. Published March 2013March 2020. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 20122013 as
F749 – 98 (2012).F749 – 13. DOI: 10.1520/F0749-13.10.1520/F0749-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F749 − 20
5. Apparatus
5.1 Cages—There shall be one cage for each rabbit exposed to one extract liquid. Each rabbit shall be uniquely identified with
this identity recorded.
5.2 Syringes—Sterile syringes, not greater than 2 mL in volume, with a precision of no less than 60.10 mL shall be used. Sterile
needles of 21 to 26 gauge shall be used.
6. Test Animals
6.1 Rabbits—The rabbits shall be healthy thin-skinned albino type, not previously used for any test. Animal care shall be in
3
accordance with the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Rabbits with
...









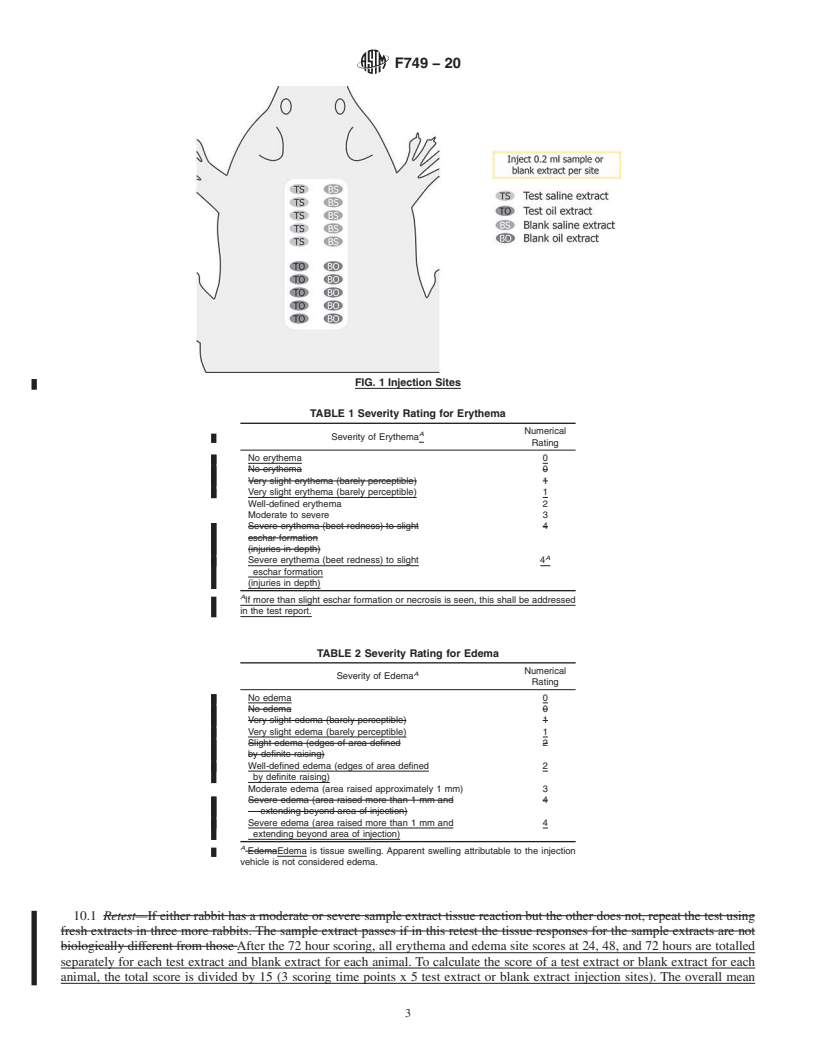
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.