ASTM D4066-94b
(Classification)Standard Classification System for Nylon Injection and Extrusion Materials (PA)
Standard Classification System for Nylon Injection and Extrusion Materials (PA)
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers nylon materials suitable for injection molding and extrusion. Some of these compositions are also suitable for compression molding and application from solution.
1.2 The properties included in this specification are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specialized applications. These shall be agreed upon between the user and the supplier, by using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific hazards statement is given in 11.2. ^REFERENCE:
ASTM Standards:
D 149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at Commercial Power Frequencies
D 150 Test Methods for A-C Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials
D 256 Test Methods for Impact Resistance of Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials
D 257 Test Methods for D-C Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials for Testing
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
D 648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics Under Flexural Load
D 789 Test Methods for Determination of Relative Viscosity, Meting Point, and Moisture Content of Polyamide (PA)
D 790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials
D 792 Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) and Density of Plastics by Displacement
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D 1897 Practice for Injection Molding Test Specimens of Thermoplastic Molding and Extrusion Materials
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
D 2584 Test Method for Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced Resins
D 3418 Test Method for Transition Temperatures of Polymers by Thermal Analysis
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materials
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
Military and Federal Specifications and Standards:
MIL-STD-105 Sampling Procedure and Tables for Inspection by Attributes
L-P-410 Plastic, Polyamide (Nylon) Rigid: Rods, Tubes, Flats, Molded and Cast Parts
VV-I-530 Insulating Oil, Electrical (for Transformers, Switches, and Circuit Breakers)
Underwriters Laboratories:
UL 94 Standards for Tests for Flammability for Parts in Devices and Appliances
ISO Standard:
ISO 307 Determination of Viscosity Number of Polyamides in Dilute Solutions
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D4066 – 94b
Standard Specification for
Nylon Injection and Extrusion Materials (PA)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4066; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This specification is intended to be a means of calling out plastic materials used in the fabrication
of end items or parts. It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material selection should be
made by those having expertise in the plastics field after careful consideration of the design and the
performance required of the part, the environment to which it will be exposed, the fabrication process
to be employed, the inherent properties of the material other than those covered by this specification,
and the economics.
1. Scope D 256 Test Methods for Impact Resistance of Plastics and
Electrical Insulating Materials
1.1 This specification covers nylon materials suitable for
D 257 Test Methods for D-C Resistance or Conductance of
injection molding and extrusion. Some of these compositions
Insulating Materials
arealsosuitableforcompressionmoldingandapplicationfrom
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
solution.
Insulating Materials for Testing
1.2 The properties included in this specification are those
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
required to identify the compositions covered. There may be
D 648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
other requirements necessary to identify particular character-
Under Flexural Load
istics important to specialized applications. These shall be
D 789 Test Methods for Determination of Relative Viscos-
agreed upon between the user and the supplier, by using the
ity, Meting Point, and Moisture Content of Polyamide
suffixes as given in Section 5.
(PA)
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
D 790 TestMethodsforFlexuralPropertiesofUnreinforced
standard.
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
als
test methods portion, Section 11, of this specification. This
D 792 TestMethodsforDensityandSpecificGravity(Rela-
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
tive Density) and Density of Plastics by Displacement
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
Plastics
tions prior to use.Aspecifichazardsstatementisgivenin11.2.
D 1897 Practice for Injection Molding Test Specimens of
2. Referenced Documents
Thermoplastic Molding and Extrusion Materials
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 2584 Test Method for Ignition Loss of Cured Reinforced
D 149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
Resins
Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials
D 3418 Test Method for Transition Temperatures of Poly-
at Commercial Power Frequencies
mers by Thermal Analysis
D 150 Test Methods for A-C Loss Characteristics and
D 3892 Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insu-
D 4000 Classification System for Specifying Plastic Mate-
lating Materials
rials
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials (Section D20.15.09).
Current edition approved Oct. 15, 1994. Published December 1994. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
published as D 4066 – 82. Last previous edition D 4066 – 94a. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 10.01.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D4066 – 94b
Determine Conformance with Specifications
Tolerance
Symbol Material
(Based on the Total Mass)
2.2 Military and Federal Specifications and Standards:
L Lubricants (for example, by agreement between the
MIL-STD-105 Sampling Procedure and Tables for Inspec-
PTFE, graphite, silicone, supplier and the user
tion by Attributes and molybdenum disulfide)
M Mineral 62%
L-P-410 Plastic, Polyamide (Nylon) Rigid: Rods, Tubes,
R Combinations of reinforce- 6 3 % for the total reinforce-
Flats, Molded and Cast Parts
ments or fillers, or both ment
VV-I-530 Insulating Oil, Electrical (for Transformers,
NOTE 2—This part of the system uses percent of reinforcements or
Switches, and Circuit Breakers)
additives, or both, in the control of the modified basic material. The types
2.3 Underwriters Laboratories:
and percentages of reinforcements and additives should be shown on the
UL 94 Standards for Tests for Flammability for Parts in supplier’s technical data sheet unless they are proprietary in nature. If
necessary, additional control of these reinforcements and additives can be
Devices and Appliances
established by the use of the suffix part of the system, Section 5.
2.4 ISO Standard:
NOTE 3—Ash content of filled or reinforced materials may be deter-
ISO 307 Determination of Viscosity Number of Polyamides
mined using Test Method D 2584 where applicable.
in Dilute Solutions
4.2.2 TableA, Detail Requirements–Reinforced Nylons—An
identifying number is made up of the letter A and five digits
3. Terminology
comprising the cell numbers for the new requirements in the
3.1 For definitions of technical terms pertaining to plastics
designated order as they appear in Table A.
used in this specification, see Terminology D 883.
4.2.2.1 Although the values listed are necessary to include
the range of properties available in existing materials, users
4. Classification
should not infer that every possible combination of the
4.1 Unreinforced nylon materials are classified into groups
properties exists or can be obtained.
according to their chemical composition. These groups are
4.2.3 When the grade of the basic material is not known or
subdivided into classes and grades as shown in the Basic
isnotimportant,theuseof“0”gradeclassificationwillbeused
Property Table (Table PA).
for reinforced materials in this system. (See Note 6.)
NOTE 1—An example of this classification system is as follows. The
NOTE 4—Anexampleofareinforcednylonofthisclassificationsystem
designation PA0123 would indicate:
is as follows. The designation PA0315G30A22450 would indicate the
PA = polyamide (nylon) as found in Terminology D 1600,
following material requirements from Table A:
01 (group) = 66 nylon,
PA0315 = 11 nylon, from Table PA,
2 (class) = heat stabilized, and
G30 = glass reinforced at 30 % nominal (see 4.2.1),
3 (grade) = with a minimum relative viscosity of 100 and the
A = Table A property requirements,
requirements given in Table 1.
2 = 70 MPa tensile strength, min,
4.1.1 To facilitate the incorporation of future or special 2 = 4500 MPa flexural modulus, min,
4 = 100 J/m Izod impact, min,
materials not covered by the Basic Property Table, the “other/
5 = 160°C deflection temperature at 1.82 MPa, min, and
unspecified” category (O) for group, class, and grade is shown
0 = unspecified.
If no properties are specified, the designation would be PA0315G30A00000.
on the table with the basic properties to be obtained from
Tables A or B as they apply (see 4.3).
4.3 To facilitate the specification of special materials where
4.2 Reinforced and lubricated versions of the nylon materi-
the basic property table does not reflect the properties required,
als are classified in accordance with Tables PA and A or B;
TableBhasbeenincorporatedintothisspecification.Thistable
where Table PA specifies the unreinforced material and Tables
will be used in a manner similar to Table A.
A or B the properties after the addition of reinforcements or
NOTE 5—Pigmented or colored nylons can differ significantly from the
lubricants at the nominal level indicated (see 4.2.1).
natural polymers in mechanical properties depending on the choice of
4.2.1 Reinforcements and additive materials. A symbol
colorants and concentrations. The main property affected is ductility, as
(single-letter) will be used for the major reinforcement or illustratedbyareductioninIzodimpactandelongationvalues.Inatypical
white pigmented nylon, elongation losses of up to 50 % and Izod impact
combination, or both, along with two numbers which indicate
losses of up to 30 % are common. If specific properties of pigmented
the percentage of addition by mass with the tolerances as
nylons are required, a testing program should be arranged by the material
tabulated below.
supplier or the end user, or both. Once these arrangements are reached, a
Tolerance
cell callout using Table B should be employed to insure proper property
Symbol Material
(Based on the Total Mass)
compliance.
C Carbon and graphite fiber 62%
NOTE 6—An example of a special material using this classification
G Glass 62%
system is as follows. The designation PA0220B54220 would indicate the
following, with the material requirements from Table B:
PA0220 = 6 nylon, heat stabilized, from Table PA,
B = Table B property requirements,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
5 = 70 MPa tensile strength, min,
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4, Section D,
4 = 2400 MPa flexural modulus, min,
700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
7 2 = 40 J/m Izod impact, min,
Available from Underwriters Laboratories, Inc., Publication Stock, 333 Pfing-
2 = 55°C deflection temperature at 1.82 MPa, min, and
sten Road, Northbrook, IL 60062.
0 = unspecified.
Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd St., 13th
Floor, New York, NY 10036.
D4066 – 94b
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Please contact ASTM International
(www.astm.org) for the latest information.
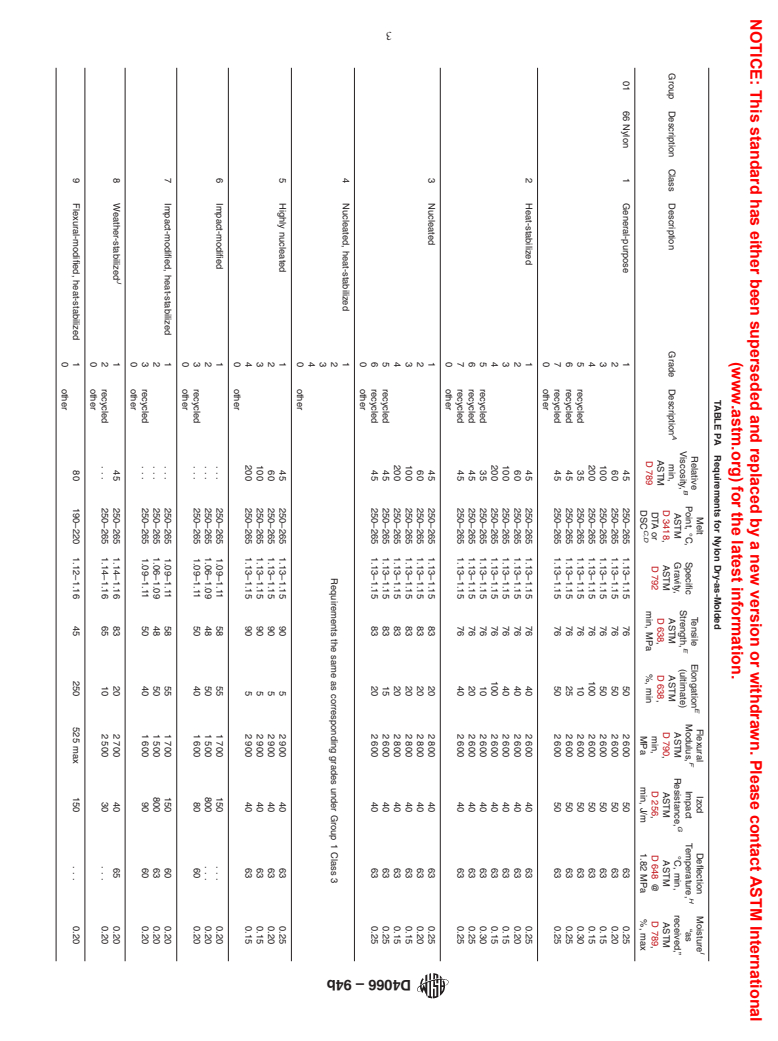
TABLE PA Requirements for Nylon Dry-as-Molded
I
Melt Flexural Izod Deflection Moisture
E
Relative Tensile Elongation
F H
Point, °C, Specific Modulus, Impact Temperature, “as
B E
Viscosity, Strength, (ultimate)
G
ASTM Gravity, ASTM Resistance, °C, min, received,”
A
Group Description Class Description Grade Description min, ASTM ASTM
D 3418, ASTM D 790, ASTM ASTM ASTM
ASTM D 638, D 638,
DTA or D 792 min, D 256, D 648 @ D 789,
D 789 min, MPa %, min
C,D
DSC MPa min, J/m 1.82 MPa %, max
01 66 Nylon 1 General-purpose 1 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 50 2 600 50 63 0.25
2 60 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 50 2 600 50 63 0.20
3 100 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 50 2 600 50 63 0.15
4 200 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 100 2 600 50 63 0.15
5 recycled 35 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 10 2 600 50 63 0.30
6 recycled 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 25 2 600 50 63 0.25
7 recycled 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 50 2 600 50 63 0.25
0 other
2 Heat-stabilized 1 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 40 2 600 40 63 0.25
2 60 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 40 2 600 40 63 0.20
3 100 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 40 2 600 40 63 0.15
4 200 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 100 2 600 40 63 0.15
5 recycled 35 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 10 2 600 40 63 0.30
6 recycled 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 20 2 600 40 63 0.25
7 recycled 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 76 40 2 600 40 63 0.25
0 other
3 Nucleated 1 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 83 20 2 800 40 63 0.25
2 60 250–265 1.13–1.15 83 20 2 800 40 63 0.20
3 100 250–265 1.13–1.15 83 20 2 800 40 63 0.15
4 200 250–265 1.13–1.15 83 20 2 800 40 63 0.15
5 recycled 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 83 15 2 600 40 63 0.25
6 recycled 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 83 20 2 600 40 63 0.25
0 other
4 Nucleated, heat-stabilized 1
2 Requirements the same as corresponding grades under Group 1 Class 3
0 other
5 Highly nucleated 1 45 250–265 1.13–1.15 90 5 2 900 40 63 0.25
2 60 250–265 1.13–1.15 90 5 2 900 40 63 0.20
3 100 250–265 1.13–1.15 90 5 2 900 40 63 0.15
4 200 250–265 1.13–1.15 90 5 2 900 40 63 0.15
0 other
6 Impact-modified 1 . . . 250–265 1.09–1.11 58 55 1 700 150 . . . 0.20
2 . . . 250–265 1.06–1.09 48 50 1 500 800 . . . 0.20
3 recycled . . . 250–265 1.09–1.11 50 40 1 600 80 60 0.20
0 other
7 Impact-modified, heat-stabilized 1 . . . 250–265 1.09–1.11 58 55 1 700 150 60 0.20
2 . . . 250–265 1.06–1.09 48 50 1 500 800 63 0.20
3 recycled . . . 250–265 1.09–1.11 50 40 1 600 90 60 0.20
0 other
J
8 Weather-stabilized 1 45 250–265 1.14–1.16 83 20 2 700 40 65 0.20
2 recycled . . . 250–265 1.14–1.16 65 10 2 500 30 . . . 0.20
0 other
9 Flexural-modified, heat-stabilized 1 80 190–220 1.12–1.16 45 250 525 max 150 . . . 0.20
0 other
D4066 – 94b
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn. Please contact ASTM International
(www.astm.org) for the latest information.
TABLE PA Requirements for Nylon Dry-as-Molded
I
Melt Flexural Izod Deflection Moisture
E
Relative Tensile Elongation
F H
Point, °C, Specific Modulus, Impact Temperature, “as
B E
Viscosity, Strength, (ultimate)
G
ASTM Gravity, ASTM Resistance, °C, min, received,”
A
Group Description Class Description Grade Description min, ASTM ASTM
D 3418, ASTM D 790, ASTM ASTM ASTM
ASTM D 638, D 638,
DTA or D 792 min, D 256, D 648 @ D 789,
D 789 min, MPa %, min
C,D
DSC MPa min, J/m 1.82 MPa %, max
0 Other 0 other
02 6 Nylon 1 General-purpose 1 30 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 40 2 600 40 58 0.20
2 40 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 40 2 600 50 58 0.20
3 50 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 100 2 600 50 58 0.20
4 95 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 150 2 600 55 58 0.20
5 200 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 200 2 600 55 58 0.20
6 recycled 30 210–225 1.12–1.14 68 25 2 600 40 58 0.20
7 recycled 40 210–225 1.12–1.14 68 35 2 600 40 58 0.20
8 recycled 40 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 40 2 600 40 58 0.20
0 other
2 Heat-stabilized 1 30 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 40 2 600 40 58 0.20
2 40 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 40 2 600 50 58 0.20
3 50 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 100 2 600 50 58 0.20
4 95 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 150 2 600 55 58 0.20
5 200 210–225 1.12–1.14 68 200 2 600 55 58 0.20
6 recycled 30 210–225 1.12–1.14 68 25 2 600 40 58 0.20
7 recycled 40 210–225 1.12–1.14 68 35 2 600 40 58 0.20
8 recycled 40 210–225 1.12–1.14 76 40 2 600 40 58 0.20
0 other
G10 10 % glass . . . . . . . . . 70 . . . 3 200 25 135 . . .
G15 15 % glass . . . . . . . . . 105 . . . 4 500 40 185 . . .
G30 30 % glass . . . . . . . . . 140 . . . 7 500 7
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.