ASTM D5146-10
(Guide)Standard Guide to Testing Solvent-Borne Architectural Coatings
Standard Guide to Testing Solvent-Borne Architectural Coatings
ABSTRACT
This guide covers the selection and use of procedures for testing solvent-borne architectural coatings to be used on exterior, interior, or both types of surfaces. The properties that can be examined by the test methods listed herein are as follows: liquid paint properties (skinning, condition in container, coarse particles and foreign matter, density or weight per gallon, fineness of dispersion, flash point, odor, absorption, colorant acceptance, dilution stability, package stability, heat stability, and settling); coating application and film formation characteristics (brush application properties, brush drag, roller application properties, roller spatter, spray application properties, touch-up uniformity, consistency (low-shear viscosity), rheological properties of non-Newtonian liquids, sag resistance, levelling properties, and drying properties); appearance of dry film (color appearance, color differences by visual comparison, color differences using instrumental measurements, directional reflectance, gloss, sheen, hiding power, and yellowness index); properties of dry film (abrasion resistance, adhesion, flexibility, resistance to household chemicals, color change of white enamels, washability and cleansability, blister resistance, exposure resistance, chalking, checking, cracking, erosion, flaking, mildew resistance, and fume resistance); and Coating Analysis (chemical analysis, volatile content, nonvolatile volume content, water content, pigment content, pigment analysis, nonvolatile vehicle content, vehicle separation, and nonvolatile vehicle identification).
SCOPE
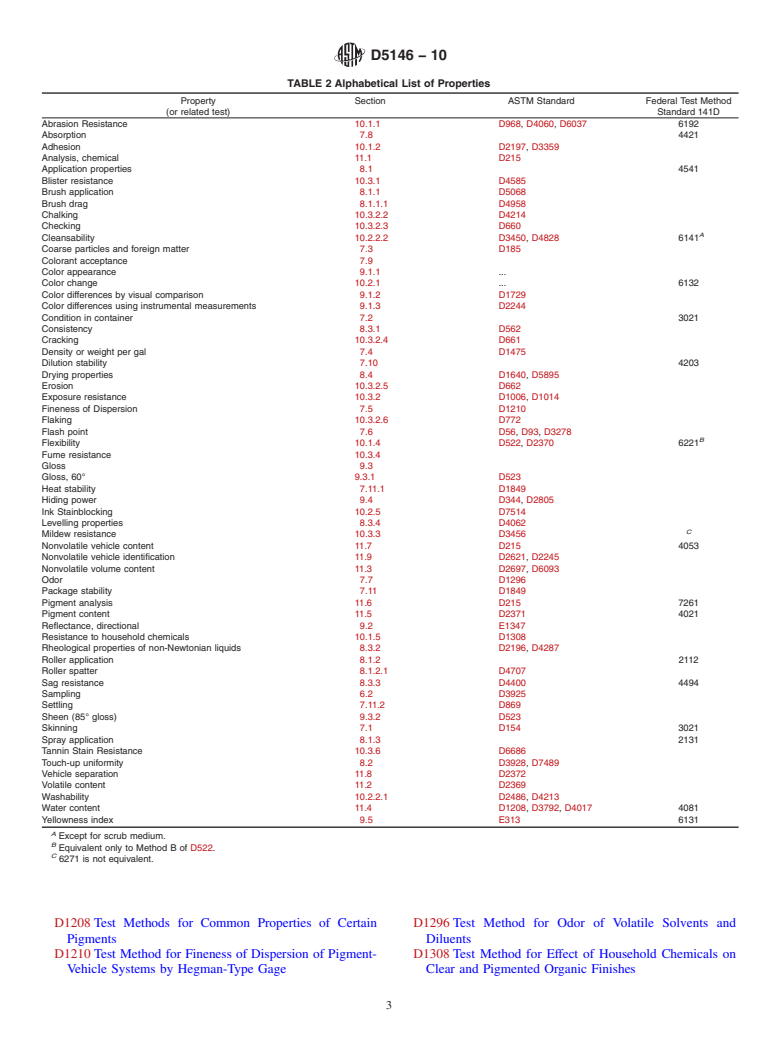
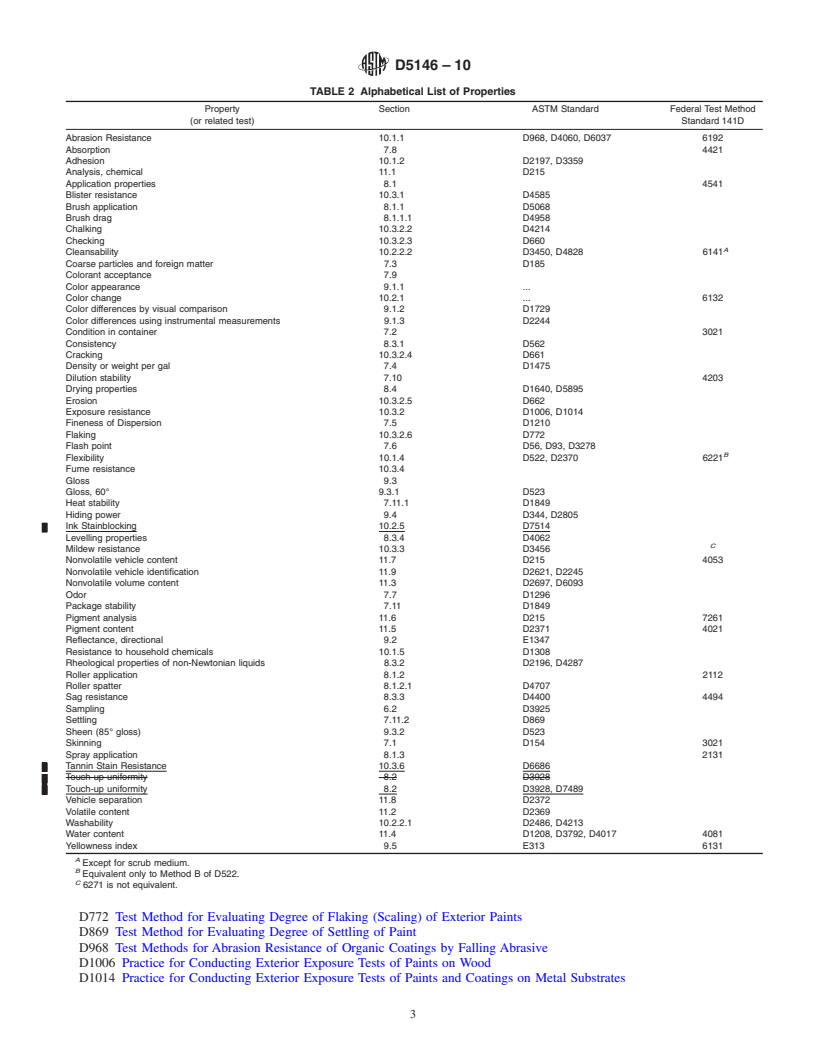
1.1 This guide covers the selection and use of procedures for testing solvent-borne coatings to be used on exterior, interior or both types of surfaces (see Note 1). The properties that can be examined or, in some cases, the relevant test procedures are listed in Table 1 and Table 2.
Note 1—The term “architectural coating” as used here combines the definition in Terminology D16 with that in the FSCT Paint/Coatings Dictionary, as follows: “Organic coatings intended for on-site application to interior or exterior surfaces of residential, commercial, institutional, or industrial buildings, in contrast to industrial coatings. They are protective and decorative finishes applied at ambient temperatures. Often called Trade Sales Coatings.”
Note 2—Architectural coatings that are designed to give better performance than most conventional coatings because they are tougher and more stain- and abrasion-resistant are covered by Guide D3730.
1.2 The types of organic coatings covered by this guide are as follows:
(1) Type 1 Interior Low-Gloss Wall Finish,
(2) Type 2 Interior Gloss and Semigloss Wall and Trim Enamels,
(3) Type 3 Exterior House and Trim Coatings, and
(4) Type 4 Floor Enamel, Exterior and/or Interior.
1.2.1 Each is intended for application by brushing, rolling, spraying, or other means to the materials appropriate for its type, which may include wood, plaster, wallboard, masonry, steel, previously painted surfaces, and other architectural substrates.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5146 − 10
Standard Guide to
1
Testing Solvent-Borne Architectural Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5146; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This guide covers the selection and use of procedures 2.1 ASTM Standards:
D16 TerminologyforPaint,RelatedCoatings,Materials,and
for testing solvent-borne coatings to be used on exterior,
Applications
interior or both types of surfaces (see Note 1). The properties
D56 Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester
that can be examined or, in some cases, the relevant test
D93 Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens
procedures are listed in Table 1 and Table 2.
Closed Cup Tester
NOTE 1—The term “architectural coating” as used here combines the
D154 Guide for Testing Varnishes
definition in Terminology D16 with that in the FSCT Paint/Coatings
D185 Test Methods for Coarse Particles in Pigments
Dictionary, as follows: “Organic coatings intended for on-site application
D215 Practice for the Chemical Analysis of White Linseed
to interior or exterior surfaces of residential, commercial, institutional, or
3
industrial buildings, in contrast to industrial coatings. They are protective
Oil Paints (Withdrawn 2005)
and decorative finishes applied at ambient temperatures. Often called
D344 Test Method for Relative Hiding Power of Paints by
Trade Sales Coatings.”
the Visual Evaluation of Brushouts
NOTE 2—Architectural coatings that are designed to give better perfor-
D358 Specification for Wood to Be Used as Panels in
mancethanmostconventionalcoatingsbecausetheyaretougherandmore
Weathering Tests of Coatings
stain- and abrasion-resistant are covered by Guide D3730.
D522 Test Methods for Mandrel Bend Test of Attached
1.2 The types of organic coatings covered by this guide are
Organic Coatings
as follows:
D523 Test Method for Specular Gloss
(1) Type 1 Interior Low-Gloss Wall Finish,
D562 Test Method for Consistency of Paints Measuring
(2) Type 2 Interior Gloss and Semigloss Wall and Trim
KrebsUnit(KU)ViscosityUsingaStormer-TypeViscom-
Enamels,
eter
(3) Type 3 Exterior House and Trim Coatings, and
D660 Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Checking of
(4) Type 4 Floor Enamel, Exterior and/or Interior.
Exterior Paints
1.2.1 Each is intended for application by brushing, rolling,
D661 Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Cracking of
spraying, or other means to the materials appropriate for its
Exterior Paints
type, which may include wood, plaster, wallboard, masonry,
D662 Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Erosion of
steel, previously painted surfaces, and other architectural
Exterior Paints
substrates.
D772 Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Flaking (Scal-
ing) of Exterior Paints
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
D869 TestMethodforEvaluatingDegreeofSettlingofPaint
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
D968 Test Methods for Abrasion Resistance of Organic
only.
Coatings by Falling Abrasive
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D1006 Practice for Conducting Exterior Exposure Tests of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Paints on Wood
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
D1014 Practice for Conducting Exterior Exposure Tests of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Paints and Coatings on Metal Substrates
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
D1038 Terminology Relating to Veneer and Plywood
1 2
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee D01.42 on Architectural Coatings. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved June 1, 2010. Published June 2010. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D5146 - 03. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/D5146-10. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5146 − 10
TABLE 1 List of Standards in Sectional Order
Property Section ASTM Standard Federal Test Method
(or related test) Standard 141D
Sampling 6.2 D3925
Liquid Paint Properties
Sk
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5146–03 Designation:D5146–10
Standard Guide to
1
Testing Solvent-Borne Architectural Coatings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5146; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide covers the selection and use of procedures for testing solvent-borne coatings to be used on exterior, interior or
both types of surfaces (see Note 1). The properties that can be examined or, in some cases, the relevant test procedures are listed
in Table 1 and Table 2.
NOTE 1—The term “architectural coating” as used here combines the definition in Terminology D16 with that in the FSCT Paint/Coatings Dictionary,
as follows: “Organic coatings intended for on-site application to interior or exterior surfaces of residential, commercial, institutional, or industrial
buildings, in contrast to industrial coatings. They are protective and decorative finishes applied at ambient temperatures. Often called Trade Sales
Coatings.”
NOTE 2—Architectural coatings that are designed to give better performance than most conventional coatings because they are tougher and more stain-
and abrasion-resistant are covered by Guide D3730.
1.2 The types of organic coatings covered by this guide are as follows:
(1) Type 1 Interior Low-Gloss Wall Finish,
(2) Type 2 Interior Gloss and Semigloss Wall and Trim Enamels,
(3) Type 3 Exterior House and Trim Coatings, and
(4) Type 4 Floor Enamel, Exterior and/or Interior.
1.2.1 Each is intended for application by brushing, rolling, spraying, or other means to the materials appropriate for its type,
which may include wood, plaster, wallboard, masonry, steel, previously painted surfaces, and other architectural substrates.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D16 Terminology for Paint, Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications
D56 Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Cup Tester
D93 Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester
D154 Guide for Testing Varnishes
D185 Test Methods for Coarse Particles in Pigments
D215 Practice for the Chemical Analysis of White Linseed Oil Paints
D344 Test Method for Relative Hiding Power of Paints by the Visual Evaluation of Brushouts
D358 Specification for Wood to Be Used as Panels in Weathering Tests of Coatings
D522 Test Methods for Mandrel Bend Test of Attached Organic Coatings
D523 Test Method for Specular Gloss
D562 Test Method for Consistency of Paints Measuring Krebs Unit (KU) Viscosity Using a Stormer-Type Viscometer
D658Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Organic Coatings by Air Blast Abrasive
D660 Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Checking of Exterior Paints
D661 Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Cracking of Exterior Paints
D662 Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Erosion of Exterior Paints
1
ThisguideisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD01onPaintandRelatedCoatings,Materials,andApplicationsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
D01.42 on Architectural Coatings.
Current edition approved Dec.June 1, 2003.2010. Published January 2004.June 2010. Originally approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 19982003 as
D5146-98.D5146 - 03. DOI: 10.1520/D5146-103.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5146–10
TABLE 1 List of Standards in Sectional Order
Property Section ASTM Standard Federal Test Method
(or related test) Standard 141D
Sampling 6.2 D3925
Liquid Paint Properties
Skinning 7.1 D154 3021
Condition in container 7.2 3011
Coarse particles and foreign matter 7.3 D185
Density or Weight per gallon 7.4 D1475
Fi
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.