ASTM C952-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Bond Strength of Mortar to Masonry Units
Standard Test Method for Bond Strength of Mortar to Masonry Units
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides two procedures for measuring bond strength of mortar to masonry units: a crossed brick couplet tensile test for evaluating mortar-brick bonding and a stacked-bond, flexural test for evaluating mortar-concrete block bonding.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: C 952 – 02
Standard Test Method for
1
Bond Strength of Mortar to Masonry Units
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 952; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope * C 1437 Test Method For Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mor-
3
tar
1.1 This test method provides two procedures for measuring
E 518 Test Methods for Flexural Bond Strength of Ma-
bond strength of mortar to masonry units: a crossed brick
2
sonry
couplet tensile test for evaluating mortar-brick bonding and a
stacked-bond, flexural test for evaluating mortar-concrete
3. Significance and Use
block bonding.
3.1 These procedures are useful for research into bonding of
1.2 This standard does not purport to address the safety
masonry. They are not intended to predict the bond strength of
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
commercial masonry construction. The bonding in commer-
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and
cially built structures is determined by many factors beyond the
health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
characteristics of mortar, masonry units, and the procedures of
limitations prior to use.
this test method.
2. Referenced Documents
NOTE 1—The crossed-brick couplets method measures a direct tensile
2.1 ASTM Standards:
strength of the bond between the mortar and masonry unit. It does not
determine the flexural strength of the unit mortar assembly. There are
C 67 Test Methods of Sampling and Testing Brick and
2
other test methods that may be more appropriate for determining the
Structural Clay Tile
flexural bond strength between mortar and masonry units. These include,
C 90 Specification for Loadbearing Concrete Masonry
C 1072 Test Method for Measurement of Masonry Flexural Bond
2
Units
Strength, C 1357 Test Methods for Evaluating Masonry Bond Strength,
3
C 91 Specification for Masonry Cement
and E 518 Test Methods for Flexural Bond Strength of Masonry.
C 129 Specification for Nonloadbearing Concrete Masonry
2
PREPARATION AND TESTING OF FRESH MORTAR
Units
C 140 Test Methods of Sampling and Testing Concrete
4. Preparation of Mortar
2
Masonry Units and Related Units
2
4.1 Proportion mortar materials by weights equivalent to
C 270 Specification for Mortar for Unit Masonry
volume proportions to be used in prism construction. Use unit
C 305 Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement
3
weights for individual materials as given in Specification C
Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency
270. Sand shall be permitted to be used in a damp loose
C 780 Test Method for Preconstruction and Construction
condition, provided that moisture content of sand is determined
Evaluation of Mortars for Plain and Reinforced Unit
2
with reference to the oven-dried condition and batch propor-
Masonry
tions are adjusted accordingly. Record weight of ingredients
C 1072 Test Method for Measurement of Masonry Flexural
2
(including water) added to the batch of mortar.
Bond Strength
4.2 Mix mortar in a mechanical paddle-type mortar mixer.
C 1357 Test Method for Evaluating Masonry Bond
2
Time periods referenced below are measured from when water
Strength
and cementitious materials are combined.
4.2.1 For standard concrete masonry units, add an estimated
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C15 on
amount of water to the mortar to achieve the desired consis-
Manufactured Masonry Units and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
tency (Note 2). Mix mortar for three minutes and determine
C15.04 on Research. Committee E-6 maintains a continued interest in these
consistency. If the desired consistency is specified by flow
practices and will make use of them in the future.
Current edition approved December 10, 2002. Published March 2003. Originally
determine it in accordance with Test Method C 1437. If the
published as E 149 – 59 T. Redesignated C 952 – 76 in 1981. Last previous edition
desired consistency is specified as initial cone penetration,
C 952 – 91 (1997).
2 determine it in accordance with Test Method C 780. Once
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.05.
3
consistency is recorded, return the material used to measure the
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.01.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C952–02
consistency to the mixer. If the consistency is within the 6. Crossed-Brick Couplets
desired range, continue mixing the batch for an additional two
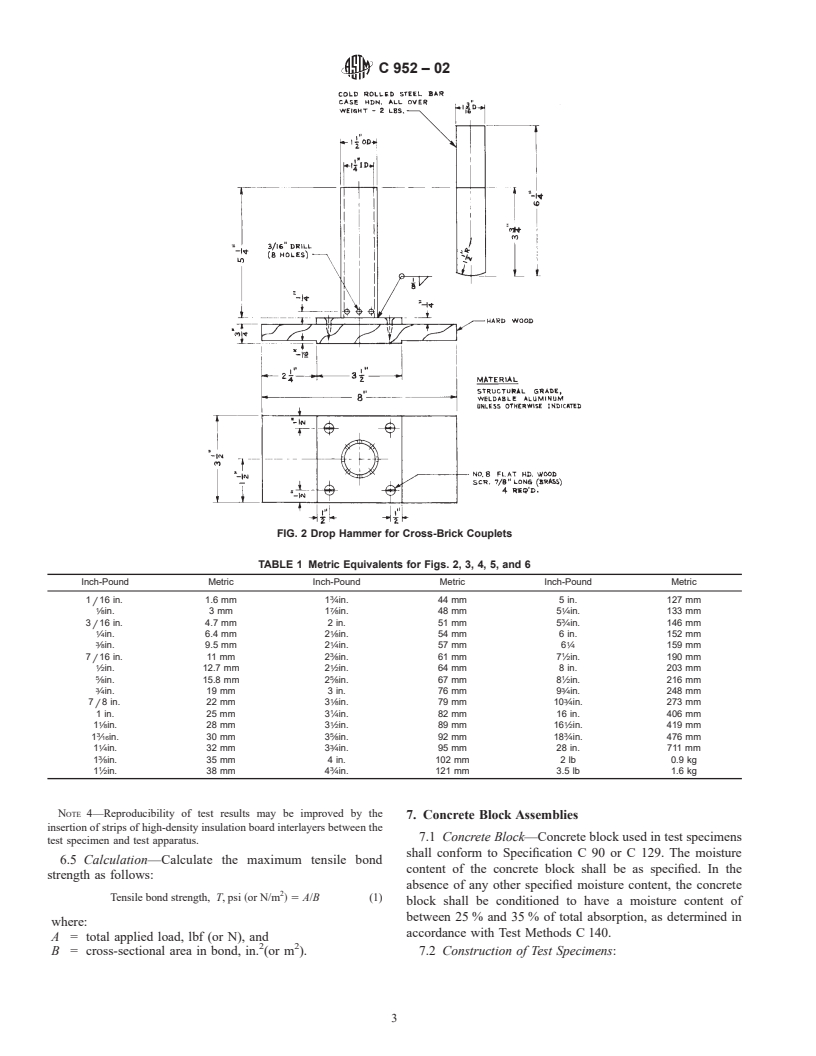
6.1 Brick—Test specimens consisting of crosse
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.