ASTM C651-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Manufactured Carbon and Graphite Articles Using Four-Point Loading at Room Temperature
Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Manufactured Carbon and Graphite Articles Using Four-Point Loading at Room Temperature
ABSTRACT
This test method details the standard procedures for determining the flexural strength of manufactured carbon and graphite articles using a simple beam in four-point loading at room temperature. The four-point loading fixture shall consist of spherical bearing blocks of hardened steel or its equivalent to ensure that forces applied to the beam are normal only and without eccentricity, and distortion of the loading member is prevented. Judicious use of linkages, rocker bearings, and flexure plates may maintain the parallel direction of loads and reactions. The test specimens shall be prepared to yield a parallelepiped with cross sections that are rectangular, faces that are parallel and flat, and edges that are free from visible flaws and chips.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method may be used for material development, quality control, characterization, and design data generation purposes.
4.2 This test method determines the maximum loading on a graphite specimen with simple beam geometry in 4-point bending, and it provides a means for the calculation of flexural strength at ambient temperature and environmental conditions.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determination of the flexural strength of manufactured carbon and graphite articles using a simple beam in four-point loading at room temperature.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C651 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Flexural Strength of Manufactured Carbon and Graphite
1
Articles Using Four-Point Loading at Room Temperature
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C651; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers determination of the flexural
3.1 Definitions:
strength of manufactured carbon and graphite articles using a
3.1.1 flexural strength, n—a measure of the ultimate load
simple beam in four-point loading at room temperature.
carrying capacity of a specified beam in bending.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this 4. Significance and Use
standard.
4.1 This test method may be used for material development,
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
quality control, characterization, and design data generation
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
purposes.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.2 This test method determines the maximum loading on a
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
graphite specimen with simple beam geometry in 4-point
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
bending, and it provides a means for the calculation of flexural
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
strength at ambient temperature and environmental conditions.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- 5. Apparatus
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5.1 The testing machine shall conform to the requirements
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
of Practices E4.
2. Referenced Documents
5.2 The four-point loading fixture shall consist of bearing
2
blocks or cylindrical bearings spaced in a third-point loading
2.1 ASTM Standards:
configuration (see Test Method C78).
C78 Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using
Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading)
5.3 The fixture shall ensure that forces applied to the beam
C1161 Test Method for Flexural Strength of Advanced
are normal only and without eccentricity through the use of
Ceramics at Ambient Temperature
spherical bearing blocks (see Test Method C78) or articulating
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
roller bearing assemblies (see Test Method C1161).
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
5.3.1 The bearing block or roller bearing diameter shall be
ASTM Test Methods
1 1
between ⁄10 and ⁄20 of the specimen support span.Ahardened
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
steel bearing block or its equivalent is necessary to prevent
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
distortion of the loading member. Support surfaces must be
free to pivot or rotate to relieve frictional constraints.
1
5.4 The directions of loads and reactions may be maintained
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
parallel by judicious use of linkages, rocker bearings, and
Subcommittee D02.F0 on Manufactured Carbon and Graphite Products.
flexure plates. Eccentricity of loading can be avoided by the
Current edition approved May 1, 2020. Published May 2020. Originally
use of spherical bearing blocks or articulating roller bearings.
approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as C651 – 15.
DOI:10.1520/C0651-20.
Provision must be made in fixture design for the relief of
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
torsional loading to less than 5 % of the nominal specimen
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
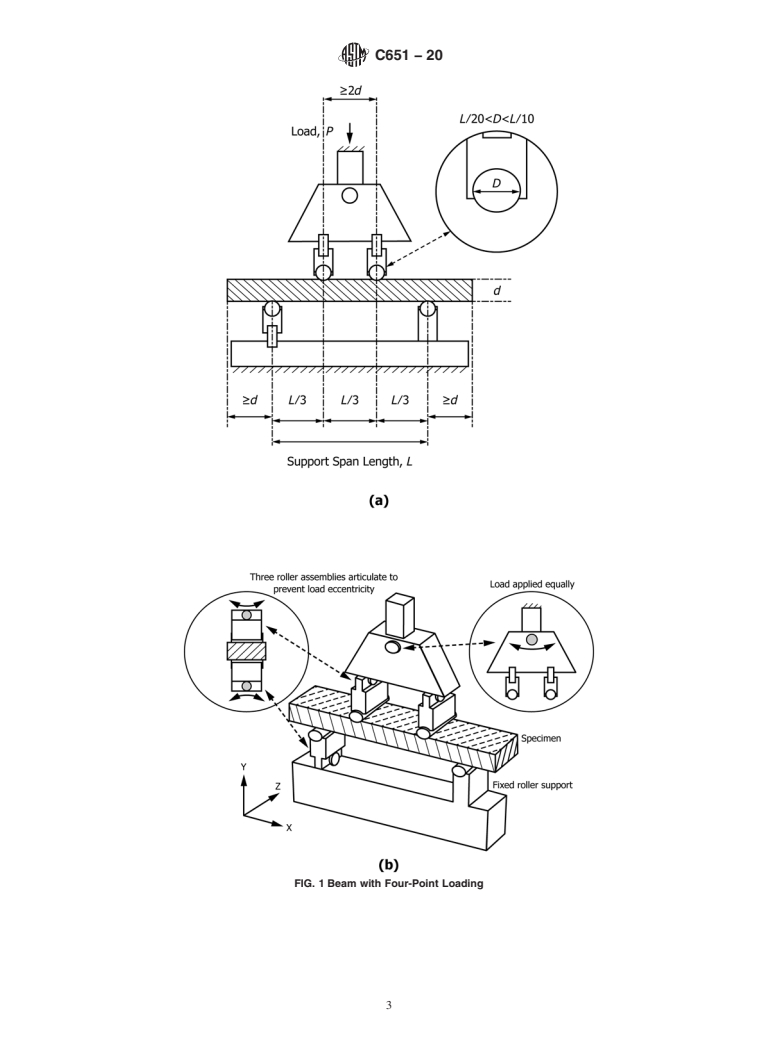
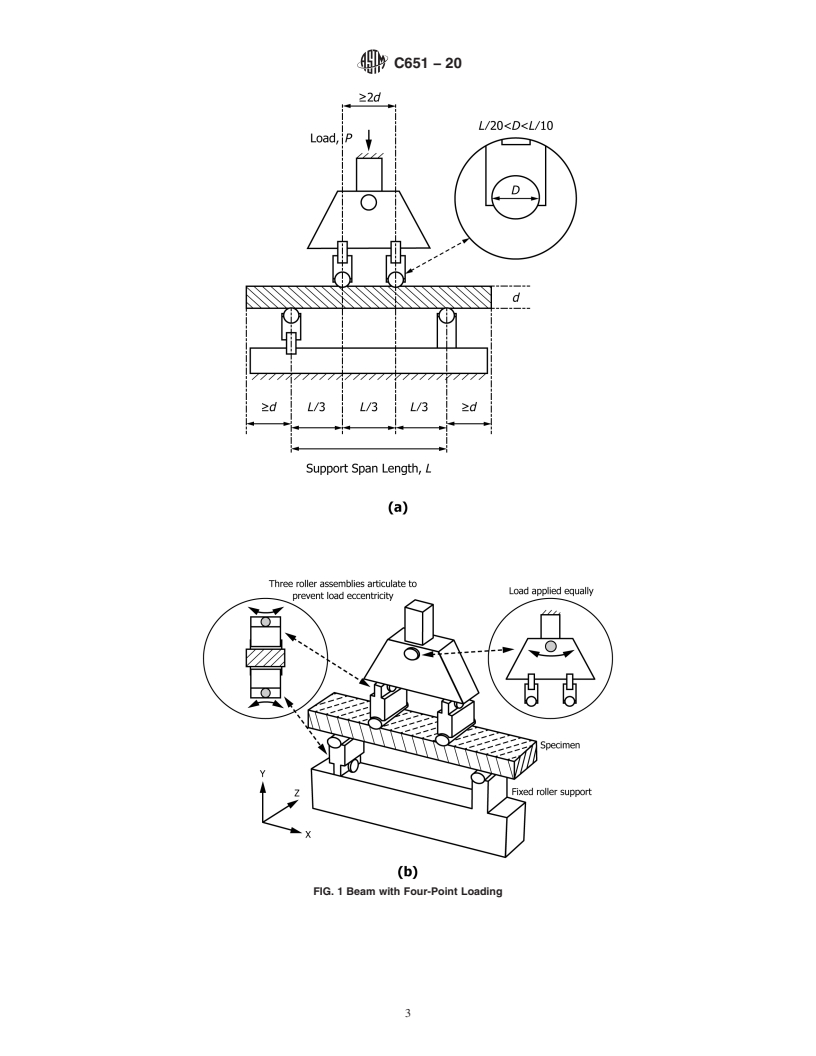
strength. Refer to the attached figure for a suggested four-point
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. loading fixture.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C651 − 20
6. Test Specimen 9. Calculation
6.1 Pre
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C651 − 15 C651 − 20 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Flexural Strength of Manufactured Carbon and Graphite
1
Articles Using Four-Point Loading at Room Temperature
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C651; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers determination of the flexural strength of manufactured carbon and graphite articles using a simple
beam in four-point loading at room temperature.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C78 Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete (Using Simple Beam with Third-Point Loading)
C1161 Test Method for Flexural Strength of Advanced Ceramics at Ambient Temperature
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 flexural strength, n—property of a solid material that indicates its ability to withstand a flexural or transverse load,
obtained through a measurement a measure of the ultimate load-carrying load carrying capacity of a specified beam in bending.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method may be used for material development, quality control, characterization, and design data generation
purposes.
4.2 This test method determines the maximum loading on a graphite specimen with simple beam geometry in 4-point bending,
and it provides a means for the calculation of flexural strength at ambient temperature and environmental conditions.
5. Apparatus
5.1 The testing machine shall conform to the requirements of Practices E4.
5.2 The four-point loading fixture shall consist of bearing blocks or cylindrical bearings spaced in a third-point loading
configuration (see Test Method C78).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.F0 on Manufactured Carbon and Graphite Products.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2015May 1, 2020. Published November 2015May 2020. Originally approved in 1970. Last previous edition approved in 20132015 as
C651 – 13.C651 – 15. DOI:10.1520/C0651-15.DOI:10.1520/C0651-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C651 − 20
5.3 The fixture shall ensure that forces applied to the beam are normal only and without eccentricity through the use of spherical
bearing blocks (see Test Method C78) or articulating roller bearing assemblies (see Test Method C1161).
1 1
5.3.1 The bearing block or roller bearing diameter shall be between ⁄10 and ⁄20 of the specimen support span. A hardened steel
bearing block or its equivalent is necessary to prevent distortion of the loading member. Support surfaces must be free to pivot
or rotate to relieve frictional constraints.
5.4 The directions of loads and reactions may be maintained parallel by judicious use of linkages, rocker bearin
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.