ASTM D7756-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases by Gas Chromatography with Liquid, On-Column Injection
Standard Test Method for Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases by Gas Chromatography with Liquid, On-Column Injection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Control over the residue content as specified in Specification D1835 is of considerable importance in end-use applications of LPG. Oily residue in LPG is contamination which can occur during production, transportation, or storage.
5.2 This test method is quicker and much more sensitive than manual methods, such as Test Method D2158, which is based on evaporation of large sample volumes followed by visual or gravimetric estimation of residue content.
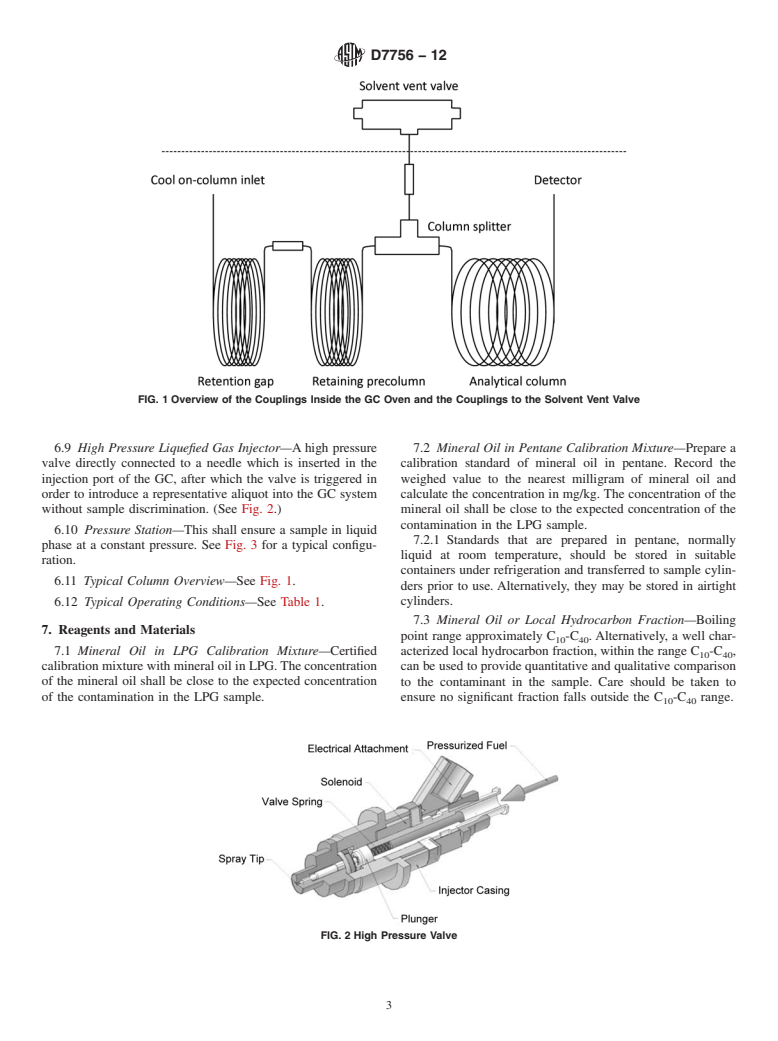
5.3 This test method provides enhanced sensitivity in measurements of heavier (oily) residues, with a quantification limit of 10 mg/kg total residue.
5.4 This test method gives both quantitative results and information about contaminant composition such as boiling point range and fingerprint, which can be very useful in tracing the source of a particular contaminant.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination, by gas chromatography, of soluble hydrocarbon materials, sometimes called “oily residue,” which can be present in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases and which are substantially less volatile than the LPG product.
1.2 This test method quantifies, in the range of 10 to 600 mg/kg (ppm mass), the residue with a boiling point between 174°C and 522°C (C10 to C40) in LPG. Higher boiling materials, or materials that adhere permanently to the chromatographic column, will not be detected.
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7756 −12
StandardTest Method for
Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases by Gas
1
Chromatography with Liquid, On-Column Injection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7756; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Lighter Hydrocarbons to Gas-Volume, Liquid-Volume, or
Mass Basis
1.1 This test method covers the determination, by gas
D2598 Practice for Calculation of Certain Physical Proper-
chromatography, of soluble hydrocarbon materials, sometimes
ties of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases from Composi-
called “oily residue,” which can be present in Liquefied
tional Analysis
Petroleum (LP) Gases and which are substantially less volatile
D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Float-
than the LPG product.
ing Piston Cylinder
1.2 This test method quantifies, in the range of 10 to 600
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance
mg/kg (ppm mass), the residue with a boiling point between
and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical
174°C and 522°C (C to C ) in LPG. Higher boiling
10 40
Measurement System Performance
materials, or materials that adhere permanently to the chro-
D6667 Test Method for Determination of Total Volatile
matographic column, will not be detected.
Sulfur in Gaseous Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded Gases by Ultraviolet Fluorescence
E355 Practice for Gas ChromatographyTerms and Relation-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are for informa-
tion only. ships
E594 Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3. Terminology
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1 Definitions of Terms Concerning Chromatography—
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
This test method makes reference to many common gas
chromatographicprocedures,terms,andrelationships.Detailed
2. Referenced Documents
definitions of these can be found in Practices E355 and E594.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2 Definitions of Terms Concerning Liquefied Petroleum
D1265 Practice for Sampling Liquefied Petroleum (LP)
Gases—This test method makes reference to the definitions of
Gases, Manual Method
liquefied petroleum gases as described in Specification D1835.
D1835 Specification for Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
3.3 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
D2158 Test Method for Residues in Liquefied Petroleum
3.3.1 high pressure liquefied gas injector, n—Sample intro-
(LP) Gases
duction device which injects liquefied gas samples under
D2163 Test Method for Analysis of Liquefied Petroleum
pressure and at room temperature directly onto the chromato-
(LP) Gases and Propene Concentrates by Gas Chromatog-
graphic column thereby maintaining the sample in liquid phase
raphy
during the injection process.
D2421 Practice for Interconversion of Analysis of C and
5
3.3.2 pressure station, n—Device that supplies high pres-
sure nitrogen to a suitable sample cylinder and therefore
1
maintains sample in the liquid phase during the injection
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
procedure.
D02.H0 on Liquefied Petroleum Gas.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2012. Published April 2013. Originally
4. Summary of Test Method
approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D7756–11.
4.1 A sample cylinder of LPG is pressurized to 2500 kPa
DOI:10.1520/D7756-12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
(363 psi) using nitrogen or helium.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.2 TheinjectionsystemisflushedwithLPGinliquidphase
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. at room temperature.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7756−12
4.3 After flushing, the injection device is routed to the GC point range and fingerprint, which can be very useful in tracing
injector port and LPG (25 milliseconds activation time equiva- the source of a particular contaminant.
lent to 30 µL) is introduced via a high pressure valve and
need
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7756 − 11 D7756 − 12
Standard Test Method for
Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases by Gas
1
Chromatography with Liquid, On-Column Injection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7756; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination, by gas chromatography, of soluble hydrocarbon materials, sometimes called
“oily residue,” which can be present in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases and which are substantially less volatile than the LPG
product.
1.2 This test method quantifies, in the range of 10 to 600 mg/kg (ppm mass), the residue with a boiling point between 174°C
and 522°C (C to C ) in LPG. Higher boiling materials, or materials that adhere permanently to the chromatographic column,
10 40
will not be detected.
1.3 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1265 Practice for Sampling Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases, Manual Method
D1835 Specification for Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
D2158 Test Method for Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
D2163 Test Method for Analysis of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases and Propene Concentrates by Gas Chromatography
D2421 Practice for Interconversion of Analysis of C and Lighter Hydrocarbons to Gas-Volume, Liquid-Volume, or Mass Basis
5
D2598 Practice for Calculation of Certain Physical Properties of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases from Compositional Analysis
D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Floating Piston Cylinder
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical Measure-
ment System Performance
D6667 Test Method for Determination of Total Volatile Sulfur in Gaseous Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum Gases by
Ultraviolet Fluorescence
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relationships
E594 Practice for Testing Flame Ionization Detectors Used in Gas or Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Concerning Chromatography—This test method makes reference to many common gas chromato-
graphic procedures, terms, and relationships. Detailed definitions of these can be found in Practices E355 and E594.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Concerning Liquefied Petroleum Gases—This test method makes reference to the definitions of
liquefied petroleum gases as described in Specification D1835.
3.3 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.H0 on
Liquefied Petroleum Gas.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2011Nov. 1, 2012. Published November 2011April 2013. DOI:10.1520/D7756-11Originally approved in 2011. Last previous edition
approved in 2011 as D7756–11. DOI:10.1520/D7756-12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7756 − 12
3.3.1 high pressure liquefied gas injector, n—Sample introduction device which injects liquefied gas samples under pressure and
at room temperature directly onto the chromatographic column thereby maintaining the sample in liquid phase during the injection
process.
3.3.2 pressure station, n—Device that supplies high pressure nitrogen to a suitable sample cylinder and therefore maintains
sample in the liquid phase during the injection procedure.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A sample cylinder of LPG is pressurized to 2500 kPa (363 psi) using nitrogen or helium.
4.2 The injection system is flus
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.