ASTM C1135-00
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Tensile Adhesion Properties of Structural Sealants
Standard Test Method for Determining Tensile Adhesion Properties of Structural Sealants
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure for quantitatively measuring the tensile adhesion properties of structural sealants, hereinafter referred to as the "sealant".
1.2 The values stated in SI (metric) units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound values given in parentheses are provided for information only.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.Note 1
Two ISO standards are known that develop similar information to C 1135; ISO 8339 and ISO 8340.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:C1135–00
Standard Test Method for
Determining Tensile Adhesion Properties of Structural
Sealants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1135; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Thesealantsusedfortheseapplicationsaredesignedtoprovide
a structural link between the glazing or panel and the framing
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure for
system.
quantitatively measuring the tensile adhesion properties of
4.2 Althoughthistestmethodisconductedatoneprescribed
structural sealants, hereinafter referred to as the “sealant”.
environmental condition, other environmental conditions and
1.2 The values stated in SI (metric) units are to be regarded
duration cycles can be employed.
asthestandard.Theinch-poundvaluesgiveninparenthesesare
provided for information only.
5. Apparatus and Materials
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.1 Tensile Testing Machine, capable of producing a tensile
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
load on the specimen at the rate of 50.8 6 5.1 mm (2.0 6 0.20
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
in.) per minute.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1.1 Fixed Member—A fixed or essentially stationary
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
member carrying one grip.
NOTE 1—Two ISO standards are known that develop similar informa-
5.1.2 Movable Member—A movable member carrying a
tion to C 1135; ISO 8339 and ISO 8340.
second grip.
5.1.3 Grips—The grips should be suitable to firmly grasp
2. Referenced Documents
the test fixture that holds the test specimen and should be
2.1 ASTM Standards:
designed to eliminate eccentric specimen loading. Specimen
C 717 Terminology of Building Seals and Sealants
loading should be perpendicular to the substrate/sealant inter-
2.2 ISO Standards:
faces. For alignment purposes, each grip shall have a swivel or
ISO 8339 Determination of Tensile Properties
universal joint at the end nearest to the specimen.
ISO8340 DeterminationofTensilePropertiesatMaintained
5.1.4 Grip Fixture—A fixture capable of being held by the
Extension
grips and furnishing a tensile force to the sealant specimen.
5.2 Spatulas, for use in applying sealant.
3. Terminology
5.3 Caulking Gun, for extruding sealant from cartridges
3.1 Definitions—RefertoTerminologyC 717fordefinitions
when applicable.
of the following terms used in this test method: cohesive
5.4 Substrate Panels—Two substrates of the same finish are
failure,primer,sealant,spacer,structuralsealant,andsubstrate.
required for each test specimen.
4. Significance and Use
NOTE 2—This test method is based on identical substrates of
6.3 3 25.4 3 76.2 mm (0.25 3 1.0 3 3.0 in.) clear float glass. Other
4.1 Frequently, glass or other glazing or panel materials are
substrates may be tested; however, consideration needs to be given to
structurally adhered with a sealant to a metal framing system.
maintaining adequate rigidity of the substrates during testing.
5.5 Spacer—One piece spacer made from polytetrafluoreth-
ylene (PTFE) or a suitable rigid material shall be used to which
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC24onBuilding
the test sealant will not bond.
Seals and Sealants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C24.30 on
5.6 Substrate Cleaning Materials.
Adhesion.
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 2000. Published April 2000. Originally
5.7 Primer (if needed).
published as C 1135 – 90. Last previous edition C 1135 – 90 (1995).
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.07.
6. Test Specimen
Available from American National Standards, Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Floor, New York, NY 10036. 6.1 Assembly:
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C1135–00
6.1.1 Prior to assembly, wipe the substrates with a clean, 7.2 Remove all spacer sections from the specimens. If
dry, lint-free cloth, then thoroughly clean with a solution desired, spacers may be removed prior to the end of the 21 day
appropriate for the substrate material. Prior to evaporation of cure. If removed early, note this in the report.
the cleaning solution, wipe the substrates dry with a clean,
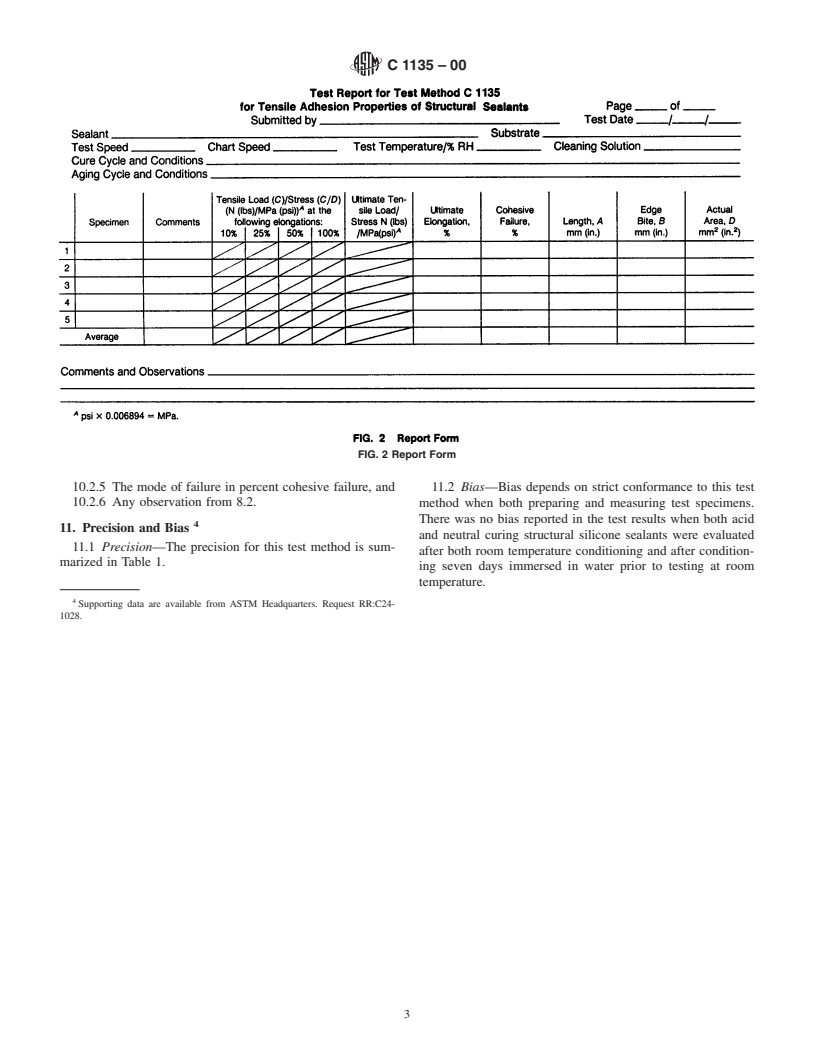
8. Procedure
lint-free cloth.
8.1 Testing:
NOTE 3—The precision and bias statement is based on glass substrates
8.1.1 Pull all specimens on the tensile test machine at
with a recommended cleaning solution of a 50 to 50 ratio isopropanol and
standard conditions at a rate of 50.8 mm (2.0 in.) per minute.
water.
If an analog chart recording device is being used, the chart
6.1.2 Apply recommended primer, if required. Then, con-
speed should be a minimum of 127 mm (5.0 in.) per minute
struct the test specimen assemblies by forming a sealant cavity
(508 mm (20.0 in.) per minute is preferred) to allow for a more
12.7 by 12.7 by 50.8 mm (0.50 by 0.50 by 2.0 in.) between two
accurate reading of force at specific elongations.
substratepanels(seeFig.1)withtheaidofappropriatespacers.
8.1.2 Measure and record to the nearest 0.8 mm (0.03125
6.2 Preparation of Test Assemblies:
in.) the actual minimum length (Dimension A) and minimum
6.2.1 Prepare a set of five test specimen assemblies for each
width (Dimension B), in millimetres (inches) as shown in Fig.
sealant and substrate combi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.