ASTM D6576-00
(Specification)Standard Specification for Flexible Cellular Rubber Chemically Blown
Standard Specification for Flexible Cellular Rubber Chemically Blown
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for chemically blown cellular rubber.
1.2 In the case of conflict between the provisions of this specification and those of detailed specifications or test methods for a particular product, the latter shall take precedence.
1.3 Unless specifically stated otherwise, by agreement between the purchaser and the supplier, all test methods shall be performed in accordance with the test methods specified in this specification.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This specification and ISO 6916 are not equivalent.
Note 1--This specification was revised using the updated test methods and specification in Specification D1056 - 98.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 6576 – 00
Standard Specification for
Flexible Cellular Rubber Chemically Blown
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6576; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense. Replaces MIL-R-6130.
1. Scope Sponge or Expanded Rubber
D 3575 Test Methods for Flexible Cellular Materials Made
1.1 This specification establishes requirements for chemi-
from Olefin Polymers
cally blown cellular rubber.
2.2 SAE Standard:
1.2 In the case of conflict between the provisions of this
SAE J 1351-1993 Hot Odor Test for Insulation Materials
specification and those of detailed specifications or test meth-
2.3 Military Standards/Specifications:
ods for a particular product, the latter shall take precedence.
MIL STD 105 Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspec-
1.3 Unless specifically stated otherwise, by agreement be-
tion by Attributes
tween the purchaser and the supplier, all test methods shall be
MIL STD 129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
performed in accordance with the test methods specified in this
MIL STD 293 Visual Inspection Guide for Cellular Rubber
specification.
Items
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
MIL R 6130 C Standard Specification for Flexible Cellular
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
Rubber Chemically Blown
information only.
2.4 Federal Standards/Specifications:
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
PPP-B576 Box, Wood, Cleated, Veneer, Paper Overlaid
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
PPP-B591 Box, Fiberboard, Wood-Cleated
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
PPP-B601 Box, Wood, Cleated Plywood
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
PPP-B621 Box, Wood, Nailed and Lock-Corner
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
PPP-B636 Box, Shipping, Fiberboard
1.6 This specification and ISO 6916 are not equivalent.
2.5 ISO Standards:
NOTE 1—This specification was revised using the updated test methods 7
ISO 6916 Flexible Cellular Polymeric Materials
and specification in Specification D 1056 – 98.
3. Terminology
2. Referenced Documents
3.1 For definitions of technical terms pertaining to cellular
2.1 ASTM Standards:
flexible rubber used in this specification, refer to Terminology
D 297 Test Methods for Rubber Products—Chemical
D 883.
Analysis
3.2 Definitions:
D 471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liq-
3.2.1 cellular material—a generic term for materials con-
uids
taining many cells (either open or closed, or both) dispersed
D 635 Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent and
throughout the mass.
Time of Burning of Self-Supporting Plastics in a Horizon-
3.2.2 closed cell—aproductwhosecellsaretotallyenclosed
tal Position
by its walls and hence not interconnecting with other cells.
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
3.2.3 open cell—a product whose cells are not totally
D 1055 Specifications for Flexible Cellular Materials—
enclosed by its walls and open to the surface, either directly or
Latex Foam
by interconnecting with other cells.
D 1056 Specification for Flexible Cellular Materials—
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.02.
1 5
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on AvailablefromSAEWorldHeadquarters,400CommonwealthDr.,Warrendale,
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular PA 15096–0001.
Materials—Plastics and Elastomers. AvailablefromStandardizationDocumentsOrderDesk,Bldg.4SectionD,700
Current edition approved July 10, 2000. Published October 2000. Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
2 7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 6576
4. Classification 6.5 Cut or Split Sheets (Type II Only)—When two or more
sheets are derived from one thick sheet, the cut or split sheets
4.1 Types—This specification covers two types of cellular
shall not be required to posses a skin or rind on either major
rubber designated as follows:
surface.
4.1.1 Type I—Open cell (sponge rubber).
6.6 Surfacing—Cellular rubber shall be backed or surfaced
4.1.2 Type II—Closed cell (expanded rubber).
with fabric, adhesive, or other materials, when and as specified
4.2 Grades—Both types are divided into three grades des-
in the contract or order or by applicable drawings.
ignated by the lettersA, B, and C added to the roman numeral
prefix.
7. Physical Properties
4.2.1 Grade A—Oil- and flame-resistant.
7.1 The various types and grades of cellular rubber shall
4.2.2 Grade B—No requirements for oil, flame resistance,
conform to the physical properties listed in Table 1 together
or low temperature.
with any additional requirements indicated by suffix letters in
4.2.3 Grade C—Low-temperature resistant (oil and flame
the grade designations as described in Section 4 and Table 2.
resistance not required).
4.3 Conditions—Each type and class has been divided into
8. Tolerances on Dimensions
three different conditions. Each condition is based on a specific
8.1 Tolerances on dimensions of flexible cellular rubber
range of firmness as expressed by compression deflection as
materials are given in Table 3.
follows:
8.2 Molded Shapes—Tolerance requirements for molded
4.3.4 Condition—Super soft a compression deflec- >0to#14 kPa
shapes shall be as specified in drawings, contracts, or by the
tion range of (>0 to#2 psi)
procuring activity.
4.3.2 Condition—Soft a compression deflec- >14 to#35 kPa
tion range of (>2 to#5 psi) 8.3 Sheets and Rolls—Unless otherwise specified, the tol-
4.3.3 Condition—Soft-medium a compression deflec- >35 to#63 kPa
erance requirements for thickness, lengths and width of sheets
tion range of (>5 to#9 psi)
shall be as specified in Table 3.
4.3.4 Condition—Medium a compression deflec- >63 to#91 kPa
tion range of (>9to#13 psi)
9. Test Methods
4.3.5 Condition—Medium-firm a compression deflec- >91 to#119 kPa
tion range of (>13 to#17 psi)
9.1 Unless specifically stated otherwise, all test methods
4.3.6 Condition—Firm a compression deflec- >119 to#175 kPa
shall be in accordance with the test methods specified in
tion range of (>17 to#25 psi)
Sections 10-18.
5. Significance and Use
9.2 Precision and Bias—The repeatability standard devia-
tions for each test method has been determined. The reproduc-
5.1 This specification is a revision of MIL R 6130C retain-
ibility of these test methods is being determined and will be
ing most of the MIL R 6130C material designations and
available on or before March 2006.
property requirements while conforming to ASTM form and
style. It is intended to establish requirements for chemically
NOTE 2—One laboratory tested one closed-cell, flame-resistant, non-oil
blown cellular rubber used by government and industry, and is
resistant, 96-kg/m , 14-35-kPa product as a representative sample. This
intended as a direct replacement for MIL R 6130C. sample was used for shrinkage, recovery, and oil-resistance testing.
10. Test Conditions
6. Materials and Manufacture
10.1 Standard Conditions—Unless otherwise specified
6.1 Materials—The materials shall be homogeneous. Ex-
herein,conductthetestmethodat23 62°C(73.4 63.6°F)and
cept for the following production allowances:
a relative humidity of 50 65%
6.1.1 Tears and edge cracks that do not interfere with
10.2 Specimen Conditioning—Unless otherwise specified,
specified product yield.
condition all test specimens at standard conditions for at least
6.1.2 Depression and pock marks not exceeding 1 in.
22 h prior to testing.
6.1.3 Splices and butt splices.
6.1.4 Laminating sheets to achieve thickness.
11. Compression Deflection
6.2 The material shall not include the following:
11.1 Test in accordance with Sections 17 to 22 of Specifi-
6.2.1 Cemented, bonded, shredded, or reprocessed cellular
cation D 1056.
rubber.
6.2.2 Grade A cellular rubber shall not contain natural
12. Low-Temperature Flex Resistance
rubber.
12.1 Test in accordance with Sections 56 to 60 of Specifi-
6.3 Form—Chemically blown cellular rubber shall be fur-
cation D 1056. Exposure temperatures shall be in accordance
nished as sheets, rolls, or molded shapes as specified, and shall
with Table 4.
have a uniform cell structure, with thin skin or rind surfaces.
13. Accelerated Aging
Cut or split sheets void of skin or rind surfaces may be
furnished only for Type II material when specified.
13.1 Test in accordance with Sections 34 to 41 of Specifi-
6.4 Skin or Rind—The surface formed by contact with the
cation D 1056.
mold shall be considered a skin or rind. It shall be of the same
14. Recovery
compound, and vulcanized integrally with the cellular struc-
ture. Type I shall have skin or rind. Type II may or may not 14.1 Measure the thickness of each test specimen to 0.0254
have skin or rind. mm (0.001 in.).
D 6576
A
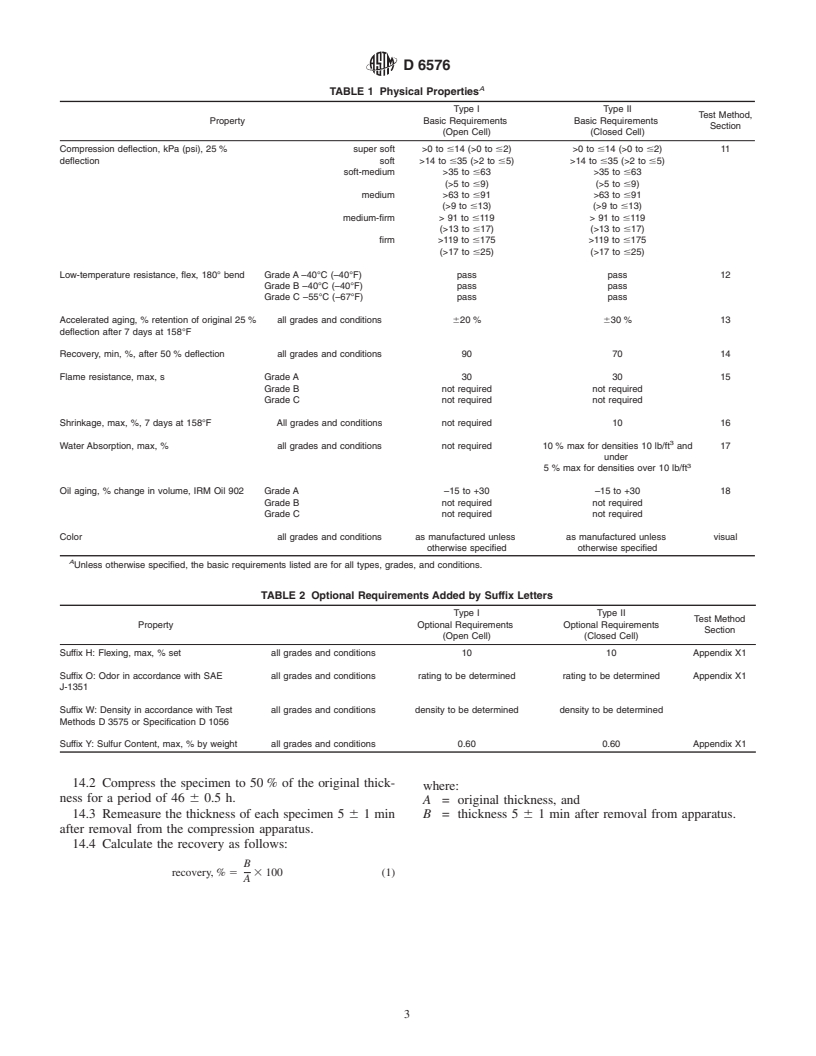
TABLE 1 Physical Properties
Type I Type II
Test Method,
Property Basic Requirements Basic Requirements
Section
(Open Cell) (Closed Cell)
Compression deflection, kPa (psi), 25 % super soft >0 to#14 (>0 to#2) >0 to#14 (>0 to#2) 11
deflection soft >14 to#35 (>2 to#5) >14 to#35 (>2 to#5)
soft-medium >35 to#63 >35 to#63
(>5 to#9) (>5 to#9)
medium >63 to#91 >63 to#91
(>9 to#13) (>9 to#13)
medium-firm > 91 to#119 >91to#119
(>13 to#17) (>13 to#17)
firm >119 to#175 >119 to#175
(>17 to#25) (>17 to#25)
Low-temperature resistance, flex, 180° bend Grade A –40°C (–40°F) pass pass 12
Grade B –40°C (–40°F) pass pass
Grade C –55°C (–67°F) pass pass
Accelerated aging, % retention of original 25 % all grades and conditions 620 % 630 % 13
deflection after 7 days at 158°F
Recovery, min, %, after 50 % deflection all grades and conditions 90 70 14
Flame resistance, max, s Grade A 30 30 15
Grade B not required not required
Grade C not required not required
Shrinkage, max, %, 7 days at 158°F All grades and conditions not required 10 16
Water Absorption, max, % all grades and conditions not required 10 % max for densities 10 lb/ft and 17
under
5 % max for densities over 10 lb/ft
Oil aging, % change in volume, IRM Oil 902 Grade A –15 to +30 –15 to +30 18
Grade B not required not required
Grade C not required not required
Color all grades and conditions as manufactured unless as manufactured unless visual
otherwise specified otherwise specified
A
Unless otherwise specified, the basic requirements listed are for all types, grades, and conditions.
TABLE 2 Optional Requirements Added by Suffix Letters
Type I Type II
Test Method
Property Optional Requirements Optional Requirements
Section
(Open Cell) (Closed Cell)
Suffix H: Flexing, max, % set all grades and conditions 10 10 Appendix X1
Suffix O: Odor in accordance with SAE all grades and conditions rating to be determined rating to be determined Appendix X1
J-1351
Suffix W: Density in accordance with Test all grades and conditions density to be determined density to be determined
Methods D 3575 or Specification D 1056
Suffix Y: Sulfur Content, max, % by weight all grades and conditions 0.60 0.60 Appendix X1
14.2 Compress the specimen to 50 % of the original thick-
where:
ness for a period of 46 6 0.5 h.
A = original thickness, and
14.3 Remeasure the thickness of each specimen 5 6 1 min B = thickness 5 6 1 min after removal from apparatus.
after removal from the compression apparatus.
14.4 Calculate the recovery as follows:
B
recovery, % 5 3 100 (1)
A
D 6576
TABLE 3 Dimensions and Tolerances of Cellular Rubber Products for General Applications
Sponge Rubber
Length and Width
Thickness Dimension, Thickness Tolerance, Length and Width Dimension,
Form Tolerance,
mm (in.) mm (in.) mm (in.)
mm (in.)
Sheet and strip 3.2 (0.125) and under 0.4 (0.016) 152 (6) and under 1.6 (0.063)
over 3.2 (0.125) to 12.7 (0.50), incl 0.8 (0.032) over 152 (6) to 457 (18), incl 3.2 (0.125)
over 12.7 (0.50) 1.2 (0.047) over 457 (18) 0.5 %
Molded or special shapes 6.4 (0.250) and under 0.8 (0.032) 6.4 (0.250) and under 0.8 (0.032)
over 6.4 (0.250) to 76.2 (3), incl 1.6 (0.063) over 6.4 (0.250) to 76 (3), incl 1.6 (0.063)
over 76 (3) to 457 (18), incl 3.2 (0.125)
over 457 (18) 0.5 %
Expanded Rubber
Sheet and strip 12.7 (0.50) and under 1.6 (0.063) 152 (6) and under 6.4 (0.250)
over 12.7 (0.50) 2.4 (0.094) over 152 (6) to 305 (12), incl 9.6 (0.375)
over 305 (12) 3 %
Molded or special shapes 3.2 (0.125) to 12.7 (0.50), incl 1.6 (0.063) 152 (6) and under 6.4 (0.250)
over 12.7 (0.50) to 38.1 (1.50), incl 2.4 (0.094) over 152 (6) to 305 (12), incl 9.6 (0.375)
over 38.1 (1.50) to 76.2 (3), incl 3.2 (0.125) over 305 (12) 3 %
TABLE 4 Low-Temperature Flex-Resistance Temperatures
15.7 Remove the flame after 60 6 1 s and record the
Type Grade Temperature average propagation time in seconds.
I A and B –40 6 1°C (–40 6 2°F)
I C –55 6 1°C (–676 2°F) 16. Shrinkage
II A and B –40 6 1°C (–40 6 2°F)
16.1 Scope—This test method covers the evaluation of
II C –55 6 1°C (–676 2°F)
shrinkage of flexible cellular elastomeric materials.
16.2 Significance and Use—This test method provides a
relatively simple and short-term evaluation of in-use perfor-
14.5 The repeatability standard deviation has been deter-
mance with regard to shrinkage.
mined to be 0.0029 %. The reproducibility of this test method
16.3 Apparatus—Air-circulating oven equipped with a con-
is being determined and will be available on or before March
trol to maintain a temperature of 70 6 1°C (158 6 2°F) during
2006.
the test and having an expanded metal shelf, and a steel rule,
Recovery, %
1 88.80 graduated in millimetres (inches), capable of measuring to
2 89.70
increments of 1.0 mm (0.05 in.).
3 89.50
16.4 Test Specimen—Use three specimens approximately
4 89.60
5 89.40 300 by 75 mm (12 by 3 in.) cut from each of the test samples.
6 89.30
16.5 Procedure—At each of two points, approximately 250
7 89.80
mm (10 in.) apart on the centerline of each specimen, place a
8 89.70
9 89.70
benchmark.Conditionthespecimen24hatatemperatureof23
10 89.60
6 2°C (73 6 3.6°F) and measure the distance between the
benchmarks to the nearest 1.0 mm (0.05 in.). Place the
Average 89.51 %
Standard Deviation 0.00292309 % specimens on an expanded metal shelf in an oven operating at
a temperature of 70 6 1°C (158 6 2°F). After 7 days 6 2
15. Flame Resi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.