ASTM G48-00
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steels and Related Alloys by Use of Ferric Chloride Solution
Standard Test Methods for Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steels and Related Alloys by Use of Ferric Chloride Solution
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for the determination of the resistance of stainless steels and related alloys to pitting and crevice corrosion (see Terminology G 15) when exposed to oxidizing chloride environments. Four procedures are described and identified as Methods A, B, C, and D.
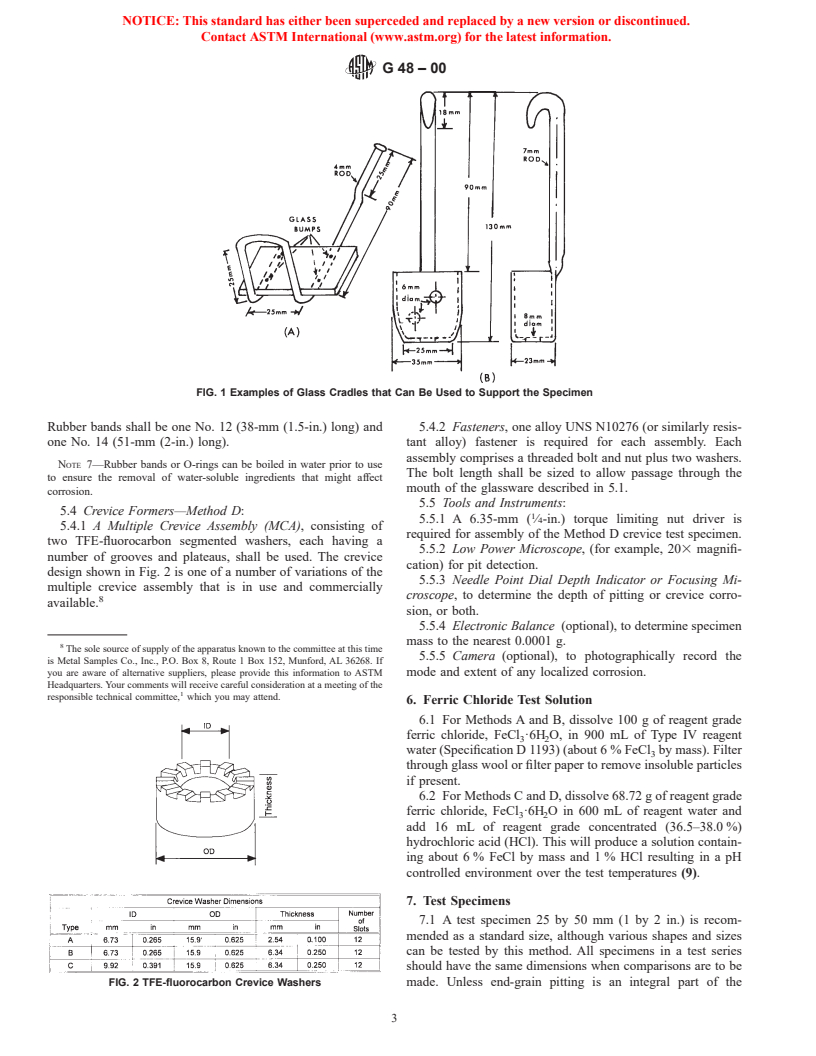
1.1.1 Method A- Ferric chloride pitting test.
1.1.2 Method B- Ferric chloride crevice test.
1.1.3 Method C- Critical pitting temperature test.
1.1.4 Method D- Critical crevice temperature test.
1.2 Method A is designed to determine the relative pitting resistance of stainless steels and nickel-base, chromium-bearing alloys, whereas Method B can be used for determining both the pitting and crevice corrosion resistance of these alloys. Methods C and D allow for a ranking of alloys by minimum (critical) temperature to cause initiation of pitting corrosion and crevice corrosion, respectively, of stainless steels and nickel-base, chromium-bearing alloys in a standard ferritic chloride solution.
1.3 These tests may be used to determine the effects of alloying additives, heat treatment, and surface finishes on pitting and crevice corrosion resistance.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. Other units are given in parentheses for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: G 48 – 00
Standard Test Methods for
Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance of Stainless
Steels and Related Alloys by Use of Ferric Chloride
1
Solution
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G 48; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
2
1. Scope lar Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
3
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
1.1 These test methods cover procedures for the determina-
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
tion of the resistance of stainless steels and related alloys to
4
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
pitting and crevice corrosion (see Terminology G 15) when
E 1338 Guide for the Identification of Metals and Alloys in
exposed to oxidizing chloride environments. Four procedures
5
Computerized Material Property Databases
are described and identified as Methods A, B, C, and D.
G 1 Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Cor-
1.1.1 Method A—Ferric chloride pitting test.
6
rosion Test Specimens
1.1.2 Method B—Ferric chloride crevice test.
G 15 Terminology Relating to Corrosion and Corrosion
1.1.3 Method C—Critical pitting temperature test.
6
Testing
1.1.4 Method D—Critical crevice temperature test.
G 46 Guide for Examination and Evaluation of Pitting
1.2 Method A is designed to determine the relative pitting
6
Corrosion
resistance of stainless steels and nickel-base, chromium-
G 107 Guide for Formats for Collection and Compilation of
bearing alloys, whereas Method B can be used for determining
Corrosion Data for Metals for Computerized Database
both the pitting and crevice corrosion resistance of these alloys.
6
Input
Methods C and D allow for a ranking of alloys by minimum
(critical) temperature to cause initiation of pitting corrosion
3. Terminology
and crevice corrosion, respectively, of stainless steels and
3.1 Definition of Terms Specific to This Standard:
nickel-base, chromium-bearing alloys in a standard ferric
3.1.1 critical crevice temperature, n—the minimum tem-
chloride solution.
perature (°C) to produce crevice attack at least 0.025-mm
1.3 These tests may be used to determine the effects of
(0.001-in.) deep on the bold surface of the specimen beneath
alloying additives, heat treatment, and surface finishes on
the crevice washer, edge attack ignored.
pitting and crevice corrosion resistance.
3.1.2 critical pitting temperature, n— the minimum tem-
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
perature (°C) to produce pitting attack at least 0.025-mm
standard. Other units are given in parentheses for information
(0.001-in.) deep on the bold surface of the specimen, edge
only.
attack ignored.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2 The terminology used herein, if not specifically defined
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
otherwise, shall be in accordance with Terminology G 15.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Definitions provided herein and not given in Terminology G 15
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
are limited only to this standard.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 These test methods describe laboratory tests for com-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
paring the resistance of stainless steels and related alloys to the
A 262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranu-
initiation of pitting and crevice corrosion. The results may be
1 2
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G01 on Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
3
Corrosion of Metals, and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G01.05 on Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01.
4
Laboratory Corrosion Tests. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
5
Current edition approved May 10, 2000. Published June 2000. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.05.
6
published as G 48 – 76. Last previous edition G 48 – 99a. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
G48–00
used for ranking alloys in order of increasing resistance to 5.1.3 Condensers, Vents and Covers:
pitting and crevice corrosion initiation under the specific 5.1.3.1 A variety of condensers may be used in conjunction
conditions of these
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.