ASTM C900-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Pullout Strength of Hardened Concrete
Standard Test Method for Pullout Strength of Hardened Concrete
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 For a given concrete and a given test apparatus, pullout strengths can be related to compressive strength test results. Such strength relationships are affected by the configuration of the embedded insert, bearing ring dimensions, depth of embedment, and the type of aggregate (lightweight or normal weight). Before use, the relationships must be established for each test system and each new concrete mixture. Such relationships are more reliable if both pullout test specimens and compressive strength test specimens are of similar size, consolidated to similar density, and cured under similar conditions.
Note 1: Published reports (1-17)4 by different researchers present their experiences in the use of pullout test equipment. Refer to ACI 228.1R (14) for guidance on establishing a strength relationship and interpreting test results. The Appendix provides a means for comparing pullout strengths obtained using different configurations.
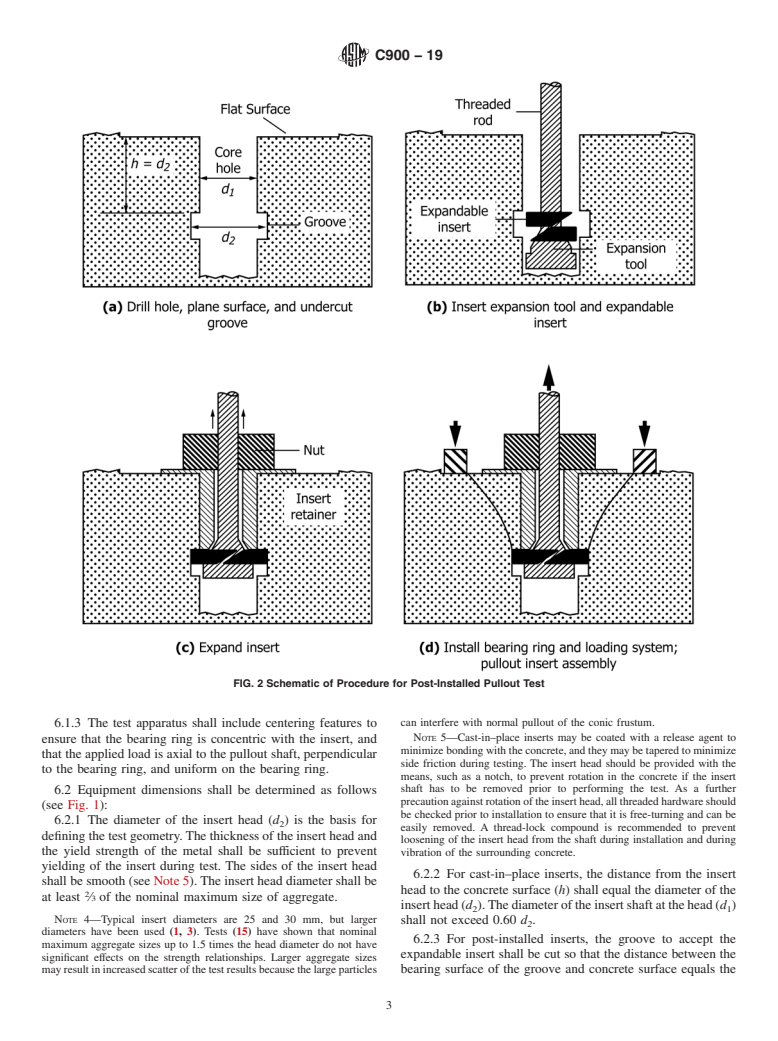
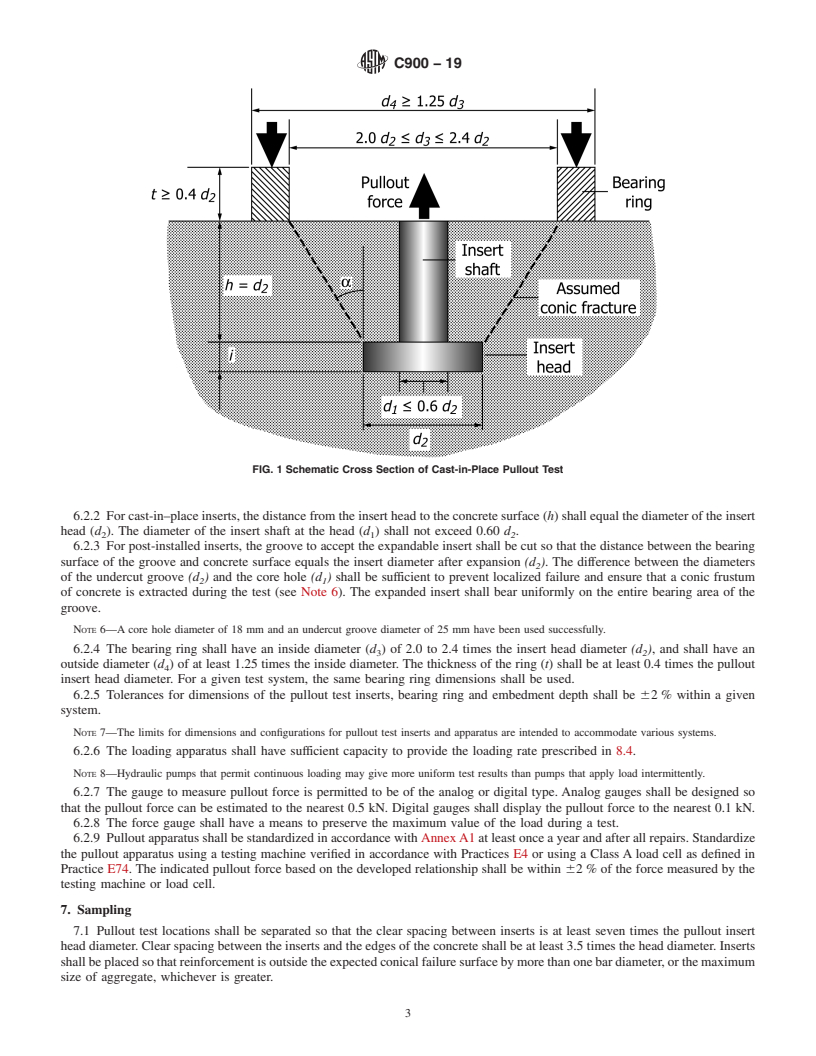
5.2 If a strength relationship has been established experimentally and accepted by the specifier of tests, pullout tests are used to estimate the in-place strength of concrete to establish whether it has reached a specified level so that, for example:
(1) post-tensioning may proceed;
(2) forms and shores may be removed;
(3) structure may be placed into service; or
(4) winter protection and curing may be terminated.
In addition, post-installed pullout tests may be used to estimate the strength of concrete in existing construction.
5.3 When planning pullout tests and analyzing test results, consideration should be given to the normally expected decrease of concrete strength with increasing height within a given concrete placement in a structural element.
5.4 The measured pullout strength is indicative of the strength of concrete within the region represented by the conic frustum defined by the insert head and bearing ring. For typical surface installations, pullout strengths are indicative of the quality of the oute...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determination of the pullout strength of hardened concrete by measuring the force required to pull an embedded metal insert and the attached concrete fragment from a concrete test specimen or structure. The insert is either cast into fresh concrete or installed in hardened concrete. This test method does not provide statistical procedures to estimate other strength properties.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. No other units of measurement are included in this test method.
1.3 The text of this test method refers to notes and footnotes that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this test method.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.2)
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C900 − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
Pullout Strength of Hardened Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C900; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* C125Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Ag-
gregates
1.1 This test method covers determination of the pullout
C670Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
strength of hardened concrete by measuring the force required
for Test Methods for Construction Materials
to pull an embedded metal insert and the attached concrete
E4Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
fragmentfromaconcretetestspecimenorstructure.Theinsert
E74Practices for Calibration and Verification for Force-
is either cast into fresh concrete or installed in hardened
Measuring Instruments
concrete. This test method does not provide statistical proce-
dures to estimate other strength properties.
3. Terminology
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1 Definitions:
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this method, refer to
test method.
Terminology C125.
1.3 Thetextofthistestmethodreferstonotesandfootnotes
that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes
4. Summary of Test Method
(excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered
4.1 A metal insert is either cast into fresh concrete or
as requirements of this test method.
installed into hardened concrete. When a measure of the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
in-place pullout strength is desired, the insert is pulled by
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
means of a jack reacting against a bearing ring. The pullout
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
strength is determined by measuring the maximum force
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
required to pull the insert from the concrete mass.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Alternatively, the insert is loaded to a specified load to verify
(Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic
whether a minimum level of in-place pullout strength has been
and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon
attained.
2
prolonged exposure. )
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
5. Significance and Use
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
5.1 For a given concrete and a given test apparatus, pullout
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
strengths can be related to compressive strength test results.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
Such strength relationships are affected by the configuration of
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
the embedded insert, bearing ring dimensions, depth of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
embedment, and the type of aggregate (lightweight or normal
weight). Before use, the relationships must be established for
2. Referenced Documents
each test system and each new concrete mixture. Such rela-
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tionships are more reliable if both pullout test specimens and
compressive strength test specimens are of similar size, con-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
solidatedtosimilardensity,andcuredundersimilarconditions.
Concrete and ConcreteAggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4
C09.64 on Nondestructive and In-Place Testing. NOTE1—Publishedreports (1-17) bydifferentresearcherspresenttheir
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2019. Published February 2020. Originally experiencesintheuseofpullouttestequipment.RefertoACI228.1R (14)
approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as C900–15. DOI:
for guidance on establishing a strength relationship and interpreting test
10.1520/C0900-19.
results. The Appendix provides a means for comparing pullout strengths
2
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing,
obtained using different configurations.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The boldface numbers refer to the list of references at the end of this test
the ASTM we
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C900 − 15 C900 − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
Pullout Strength of Hardened Concrete
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C900; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers determination of the pullout strength of hardened concrete by measuring the force required to pull
an embedded metal insert and the attached concrete fragment from a concrete test specimen or structure. The insert is either cast
into fresh concrete or installed in hardened concrete. This test method does not provide statistical procedures to estimate other
strength properties.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. No other units of measurement are included in this test
method.
1.3 The text of this test method references refers to notes and footnotes whichthat provide explanatory material. These notes
and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this test method.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause
2
chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure. )
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates
C670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements for Test Methods for Construction Materials
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
E74 Practices for Calibration and Verification for Force-Measuring Instruments
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this practice,method, refer to Terminology C125.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A metal insert is either cast into fresh concrete or installed into hardened concrete. When a measure of the in-place pullout
strength is desired, the insert is pulled by means of a jack reacting against a bearing ring. The pullout strength is determined by
measuring the maximum force required to pull the insert from the concrete mass. Alternatively, the insert is loaded to a specified
load to verify whether a minimum level of in-place pullout strength has been attained.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 For a given concrete and a given test apparatus, pullout strengths can be related to compressive strength test results. Such
strength relationships are affected by the configuration of the embedded insert, bearing ring dimensions, depth of embedment, and
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on Concrete and Concrete Aggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C09.64 on
Nondestructive and In-Place Testing.
Current edition approved May 1, 2015Dec. 15, 2019. Published June 2015February 2020. Originally approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 20142015 as
C900 – 14.C900 – 15. DOI: 10.1520/C0900-15.10.1520/C0900-19.
2
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C900 − 19
the type of aggregate (lightweight or normal weight). Before use, the relationships must be established for each test system and
each new concrete mixture. Such relationships are more reliable if both pullout test specimens and compressive strength tes
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.