ASTM F2255-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Strength Properties of Tissue Adhesives in Lap-Shear by Tension Loading
Standard Test Method for Strength Properties of Tissue Adhesives in Lap-Shear by Tension Loading
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended to provide a means for comparison of the adhesive strengths of tissue adhesives intended for use as surgical adhesives or sealants, or both, on soft tissue. With the appropriate choice of substrate, it may also be used for purposes of quality control in the manufacture of tissue adhesive based medical devices.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F 2255 – 03
Standard Test Method for
Strength Properties of Tissue Adhesives in Lap-Shear by
Tension Loading
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2255; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.2.2 tissue sealant—a surface coating with adequate adhe-
sive strength to prevent leakage of body fluids.
1.1 This test method is intended to provide a means for
comparison of the adhesive strengths of tissue adhesives
4. Significance and Use
intended for use as surgical adhesives or sealants, or both, on
4.1 Materials and devices that function at least in part by
softtissue.Withtheappropriatechoiceofsubstrate,itmayalso
adhering to living tissues are finding increasing use in surgical
be used for purposes of quality control in the manufacture of
procedures either as adjuncts to sutures and staples, or as frank
tissue adhesive based medical devices.
replacements for those devices in a wide variety of medical
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
procedures. While the nature and magnitude of the forces
standard.
involvedvariesgreatlywithindicationandwithpatientspecific
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
circumstances, all uses involve to some extent the ability of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
material to resist imposed mechanical forces. Therefore, the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
mechanical properties of the materials, and in particular the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
adhesive properties, are important parameters in evaluating
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
their fitness for use. In addition, the mechanical properties of a
2. Referenced Documents given adhesive composition can provide a useful means of
determining product consistency for quality control, or as a
2.1 ASTM Standards:
means for determining the effects of various surface treatments
D 907 Terminology of Adhesives
on the substrate prior to use of the device.
D 1002 Test Method forApparent Shear Strength of Single-
4.2 The complexity and variety of individual applications
Lap-Joint Adhesively Bonded Metal Specimens by Ten-
for tissue adhesive devices, even within a single indicated use
sion Loading (Metal-to-Metal)
3 (surgical procedure) is such that the results of a single-lap-
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
shear test are not suitable for determining allowable design
2.2 American Association of Tissue Banks Standards:
stresses without thorough analysis and understanding of the
Standards for Tissue Banking
application and adhesive behaviors.
3. Terminology 4.3 This test method may be used for comparing adhesives
or bonding processes for susceptibility to fatigue and environ-
3.1 Definitions—Many terms in this test method are defined
mentalchanges,butsuchcomparisonsmustbemadewithgreat
in Terminology D 907.
caution since different adhesives may respond differently to
3.2 Definitions:
varying conditions.
3.2.1 tissue adhesive—for the purposes of this test method,
tissue adhesive is defined as a compound or system intended
5. Apparatus
for use in closing wounds (surgical or traumatic) or for sealing
5.1 Testing Machine, of the constant-rate-of-crosshead-
against leakage of body fluids.
movement type and comprising essentially the following:
5.1.1 Fixed Member, a fixed or essentially stationary mem-
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F04 on Medical
ber carrying one grip.
and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
5.1.2 Movable Member, a movable member carrying a
F04.15 on Material Test Methods.
second grip.
Current edition approved Apr. 10, 2003. Published May 2003.
5.1.3 Grips, for holding the test specimen between the fixed
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.06.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
member and the movable member of the testing machine can
Available from the American Association of Tissue Banks (AATB), 1350
be either the fixed or self-aligning type.
Beverly Rd., Suite 220-A, McLean, VA 22101.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2255–03
5.1.3.1 Fixed Grips are rigidly attached to the fixed and be brought to the test temperature or other prescribed tempera-
movable members of the testing machine. When this type of ture (such as body temperature) prior to application of the
grip is used extreme care should be taken to ensure that the test adhesive.
specimen is inserted and clamped so that the long axis of the 6.2.2 Fixed tissue should not be used since it has been
test specimen coincides with the direction of pull through the demonstrated that fixatives cause large alterations in the
centerline of the grip assembly. mechanical properties of the tissue and it is probable that the
adhesive strength would be affected as well.
5.1.3.2 Self-aligning Grips are attached to the fixed and
6.2.3 Ifthetargetorganisofasizeorgeometry,orboth,that
movable members of the testing machine in such a manner that
they will move freely into alignment as soon as any load is does not allow fabrication of test samples as shown in Fig. 1,
a tissue of similar origin but larger size should be used. For
applied so that the long axis of the test specimen will coincide
example, if the intended indication is for anastomosis of small
with the direction of the applied pull through the center line of
blood vessels, a larger vessel should be substituted.
the grip assembly. The specimens should be aligned as per-
fectly as possible with the direction of pull so that no rotary 6.2.4 The thickness of the tissue sample should be mini-
mized and should not exceed 5 mm. Thicker samples will lead
motion that may induce slippage or damage to the sample will
occur in the grips; there is a limit to the amount of misalign- to distortion of the substrate and mixed loading (shear and
tension). It is also important that the thickness be as uniform as
ment self-aligning grips will accommodate.
possible.
5.1.4 Drive Mechanism, for imparting to the movable mem-
6.3 Substrates for Quality Control Testing:
ber a uniform, controlled velocity with respect to the stationary
6.3.1 For testing that is undertaken as part of a quality
member, with this velocity to be regulated as specified in 9.3.
control process in the manufacturing of a tissue adhesive
5.1.5 Load Indicator, a suitable load-indicating mechanism
device, the use of freshly harvested tissue is highly inconve-
capable of showing the total tensile load carried by the test
nient and may also lead to unacceptable variation in the test
specimen when held by the grips. This mechanism shall be
results, especially if the failure occurs in the adherend (sub-
essentially free of inertia lag at the specified rate of testing and
strate failure). Since the purpose of quality control testing is to
shall indicate the load with an accuracy of 61 % of the
demonstrate consistency in the device, substitution of a model
indicated value, or better. The accuracy of the testing machine
substrate is preferred so long as it is demonstrated that the
shall be verified in accordance with Practices E 4.
adhesive does bond to the adherand. For devices that require
5.2 Temperature-controlling Equipment, capable of main-
contact with tissues to cure, Mediskin XenoGraft should be
taining the test temperature to 62°C. If ambient laboratory
used for quality control testing as well as comparative testing.
conditionsareemployedthesamedegreeofcontrolisrequired.
Awaterbathorenvironmentalchambercapableofmaintaining
7. Test Specimen
37°C is required for testing on tissue substrates.
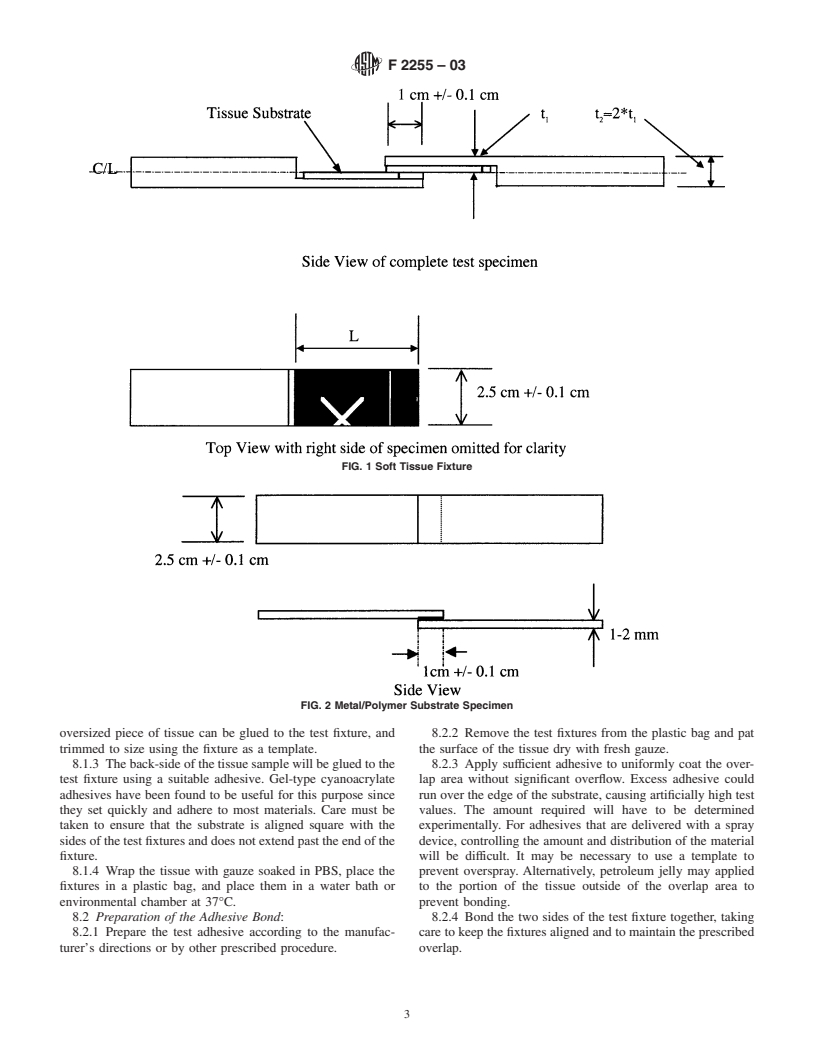
7.1 Specimens with Soft-tissue Substrates shall conform to
6. Test Substrate the form shown in Fig. 1. The length of the tissue substrate (L)
5 attached to each specimen holder should be at least 1.5 times
6.1 For comparative testing: Mediskin Xenograft (Cat
the length of the overlap area in order to ensure that the failure
#102) should be used. It is a split thickness porcine skin graft
occurs at the overlap bond and doesn’t pull the tissue substrate
material. The graft must be thawed according to manufactur-
off of the specimen holder. For very strong adhesives, L may
er’s instructions prior to use. Unused graft may be kept at 2 to
need to be 2 to 3 times the overlap length. The tissue can be
8°C for up to two weeks after thawing.
bonded to the specimen holder with any suitable adhesive.
6.2 Application Specific Testing:
Gel-type cyanoacrylate adhesives have been found to be
6.2.1 The strength of any adhesive is highly dependent on
convenient for this purp
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.