ASTM D5070-90(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Synthetic Quaternary Ammonium Salts in Fabric Softeners by Potentiometric Titrations
Standard Test Method for Synthetic Quaternary Ammonium Salts in Fabric Softeners by Potentiometric Titrations
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
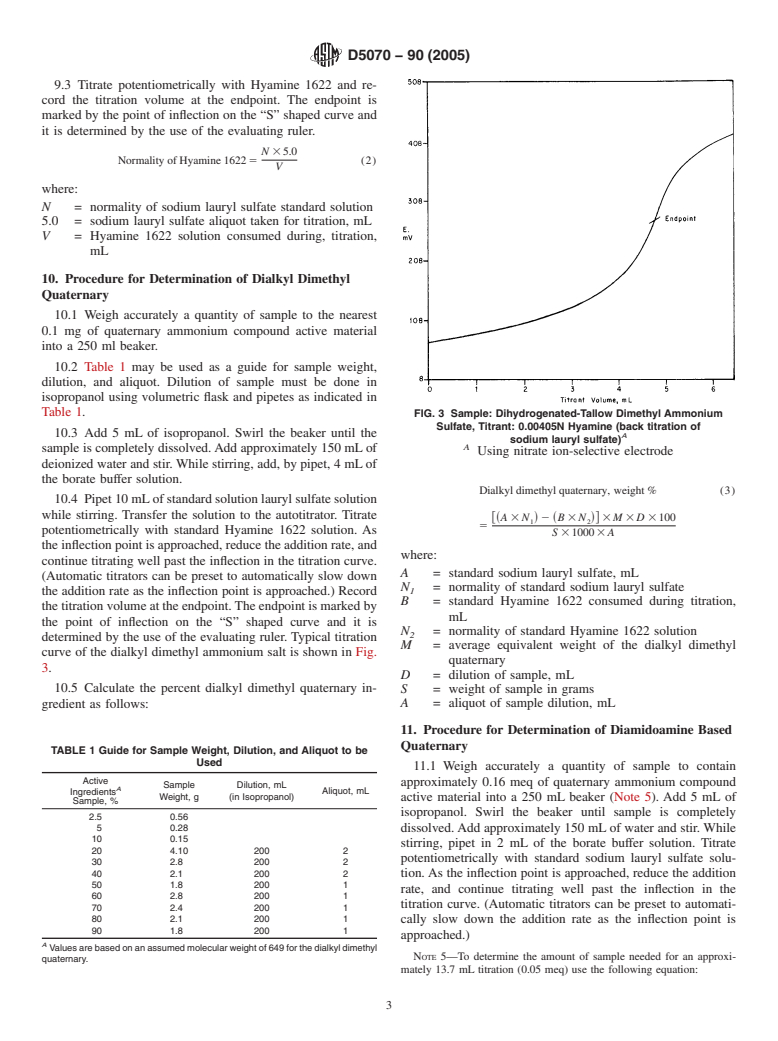
This test method is used to determine the quaternary ammonium salts commonly found in fabric softeners. Quaternary ammonium compounds being the active ingredients in fabric softeners requires accurate determination to assess the cost and performance of such compounds.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a potentiometric titration procedure for the determination of quaternary ammonium salts in fabric softeners. This test method is intended for the analysis of known quaternary ammonium salts such as the dialkyl dimethyl quaternary ammonium compound type and the diamidoamine based quaternary ammonium compound type.
1.2 The quaternary ammonium salts conform to the structures shown in Fig.1 and Fig. 2.
1.3 The analytical procedure appears in the following order:SectionApparatus5Reagents6Preparation of standard reagents7Standardization of hyamine solution9Safety precautions8Procedure for determination of dialkyl dimethyl quaternaries10Procedure for determination of diamidoamine based quaternaries11
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 6.4, 6.6, 6.7 and Section 8 for specific warning statements.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5070 − 90 (Reapproved2005)
Standard Test Method for
Synthetic Quaternary Ammonium Salts in Fabric Softeners
by Potentiometric Titrations
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5070; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope in an aqueous medium with a standard solution of sodium
lauryl sulfate using a nitrate ion-selective electrode. In this
1.1 This test method describes a potentiometric titration
potentiometric titration, the reaction involves the formation of
procedureforthedeterminationofquaternaryammoniumsalts
a complex between the quaternary ammonium compound and
infabricsofteners.Thistestmethodisintendedfortheanalysis
theanionicsurfactantwhichthenprecipitates.Attheendpoint,
of known quaternary ammonium salts such as the dialkyl
the nitrate ion electrode appears to respond to an excess of
dimethyl quaternary ammonium compound type and the di-
titrant with a potential change large enough to give a well
amidoamine based quaternary ammonium compound type.
defined inflection in the titration curve. Alternatively the
1.2 The quaternary ammonium salts conform to the struc-
quaternary ammonium compound can be first complexed with
tures shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
an excess of standard sodium lauryl sulfate; the excess sodium
1.3 Theanalyticalprocedureappearsinthefollowingorder: lauryl sulfate is titrated potentiometrically with standard
Hyamine 1622.
Section
Apparatus 5
Reagents 6
4. Significance and Use
Preparation of standard reagents 7
Standardization of hyamine solution 9
4.1 This test method is used to determine the quaternary
Safety precautions 8
ammonium salts commonly found in fabric softeners. Quater-
Procedure for determination of dialkyl dimethyl quaternaries 10
nary ammonium compounds being the active ingredients in
Procedure for determination of diamidoamine based quaternaries 11
fabric softeners requires accurate determination to assess the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
cost and performance of such compounds.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 6.4, 6.6, 6.7
5.1 AutotitrationSystem—buretwith10or20mLcapacity;
5 6
and Section 8 for specific warning statements.
magnetic stirrer; evaluating ruler.
2. Referenced Documents 5.2 Electrodes—(1) nitrate specific ion electrode; (2) sur-
8 9
factant electrode; (3) Ag/AgCl reference electrode.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
D3049Test Method for Synthetic Anionic Ingredient by
Cationic Titration
The sole source of supply of Hyamine 1622 known to the committee at this
time is Gallard Schlesinger Manufacturing Corp., 584 Mineola Ave., Carle Place,
NY11514.Ifyouareawareofalternativesuppliers,pleaseprovidethisinformation
3. Summary of Test Method
to ASTM Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a
3.1 Quaternary ammonium compounds present in fabric
meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Metrohm-Brinkman E-536, or equivalent, has been found satisfactory. Avail-
softeners,astheactivematerials,aretitratedpotentiometrically
able from Brinkman Instruments Inc., Cantiague Rd., Westbury, NY 11590.
Potentiograph/E-535 and Dosimat/E-459, or equivalent, have been found
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D12 on Soaps satisfactory. Available from Brinkman Instruments Inc., Cantiague Rd., Westbury,
and Other Detergents and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D12.12 on NY 11590.
AnalysisandSpecificationsofSoaps,Synthetics,DetergentsandtheirComponents. Evaluating Ruler EA-893, or equivalent, has been found satisfactory.Available
Current edition approved May 1, 2005. Published June 2005. Originally from Brinkman Instruments Inc., Cantiague Rd., Westbury, NY 11590.
approvedin1990.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin1997asD5070-90(1997).DOI: Orion Model 93.07, or equivalent, has been found satisfactory.Available from
10.1520/D5070-90R05. Orion Research Inc., 529 Main St., Boston, MA 02129.
2 8
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Orion Model 93.42, or equivalent, has been found satisfactory.Available from
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Orion Research Inc., 529 Main St., Boston, MA 02129.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Metrohm Model EA-440, or equivalent, has been found satisfactory.Available
the ASTM website. from Brinkman Instruments Inc., Cantiague Rd., Westbury, NY 11590.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5070 − 90 (2005)
6.4 Isopropanol, reagent grade. (Warning—Highly flam-
mable.)
6.5 Sodium Borate Decahydrate—(Na B O 10H O), re-
2 4 7 2
agent grade.
6.6 BoricAcid(H BO ),reagentgrade.(Warning—Causes
3 3
irritation.)
−
X = chloride or methyl sulfate 6.7 Sulfuric Acid (H SO ), reagent grade. (Warning
2 4
R = fatty alkyl groups saturated or unsaturated, normal or branched C −C
8 22
—Causes severe burns on contact with skin. See Section 8.)
FIG. 1 Dialkyl Dimethyl Quaternaries
6.8 Five percent (V/V) Sulfuric Acid Solution—Using a
graduated cylinder, transfer 80 mL of deionized water to a
100-mL volumetric flask. Slowly, carefully, and with stirring,
add5mLofconcentratedsulfuricacid.Cooltoroomtempera-
ture and dilute to the mark with water.
6.9 Borate Buffer Solution pH 6.00—In a 500 mL beaker,
dissolve 5.0 g 6 0.02 g of sodium borate decahydrate and 7.0
g 6 0.02 g of boric acid in approximately 300 mLwater, with
stirring; adjust pH to 6.00 with 5% sulfuric acid solution.
Transfer to a 500-mL volumetric flask, mix, and dilute to
volume with water.
7. Preparation of Standard Reagents
−
X = usually methyl sulfate
−3
R = fatty alkyl groups, saturated or unsaturated, normal or branched C −C
12 18
7.1 Sodium Lauryl Sulfate Solution, 4×10 N—Weigh
R = 2-hydroxyethyl,
accurately 1.15 6 0.01 g of sodium lauryl sulfate to 0.1 mg;
2-hydroxypropyl
dissolve in water and dilute to a final volume of 1 L. Calculate
FIG. 2 Diamidoamine Based Quarternaries
the normality of the solution with the following equation:
W 3P
Normalityofsodiumlaurylsulfate 5 (1)
288.38 100
~ !~ !
5.3 Adaptors—(1) coaxial adaptor, required for indicator
electrode, (2) banana plug adaptor, required for reference
where:
electrode.
P = purity of the sodium lauryl sulfate, weight %
W = weight of sodium lauryl sulfate, g
NOTE 1—To ensure electrical continuity (after assembly) shake down
electrode in the manner of a clinical thermometer.Also, the conditioning
7.2 Keepthesolutionnolongerthan1monthbeforemaking
of the electrode is essential for obtaining a good break in the titration
a fresh solution.
curve.Conditioningnewelectrodesin0.01MKNO ,aqueoussolutionfor
−3
60 min (or more) prior to use is recommended.
7.3 Hyamine 1622 Solution,4×10 N—Dissolve 1.85 6
NOTE 2—Other electrodes (for example, a calomel electrode) are
0.5 g of Hyamine 1622 in deionized water. Transfer toa1L
suitable as the reference electrode provided they give a stable reference
volumetric flask, and dilute to volume with water.
potential during the titration. Reference electrodes having a ceramic or an
asbestos junction tend to clog with use. Therefore, a ground-glass sleeve
8. Hazards
electrode (such as the Metrohm EA 440 or equivalent) is suggested.
8.1 Allreagentsandchemicalsshouldbehandledwithcare.
6. Reagents
Before using any chemical, read and follow all safety precau-
6.1 Hyamine 1622, diisobutylphenoxyethoxyethyl dimethyl
tions and instructions on the manufacturer’s label or MSDS
benzyl ammonium chloride monohydrate.
(Material Safety Data Sheet).
6.2 Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, primary standard (Note 3).
9. Standardization of Hyamine 1622 Solution
NOTE 3—Sodium lauryl sulfate must be analyzed for purity according
9.1 Thisdeterminationmustbedoneintriplicate.Pipet5.00
to the Reagent section of Test Method D3049, before its use as a primary
mL of the standard lauryl sulfate into a 150 mL beaker. Add
standard.
approximately 100 mL of deionized water and while stirring
6.3 Water, type III reagent water conforming to Specifica-
a
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.