ASTM D6807-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Operating Performance of Continuous Electrodeionization Systems on Reverse Osmosis Permeates from2 to 100 μS/cm
Standard Test Method for Operating Performance of Continuous Electrodeionization Systems on Reverse Osmosis Permeates from<brk/>2 to 100 μS/cm
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
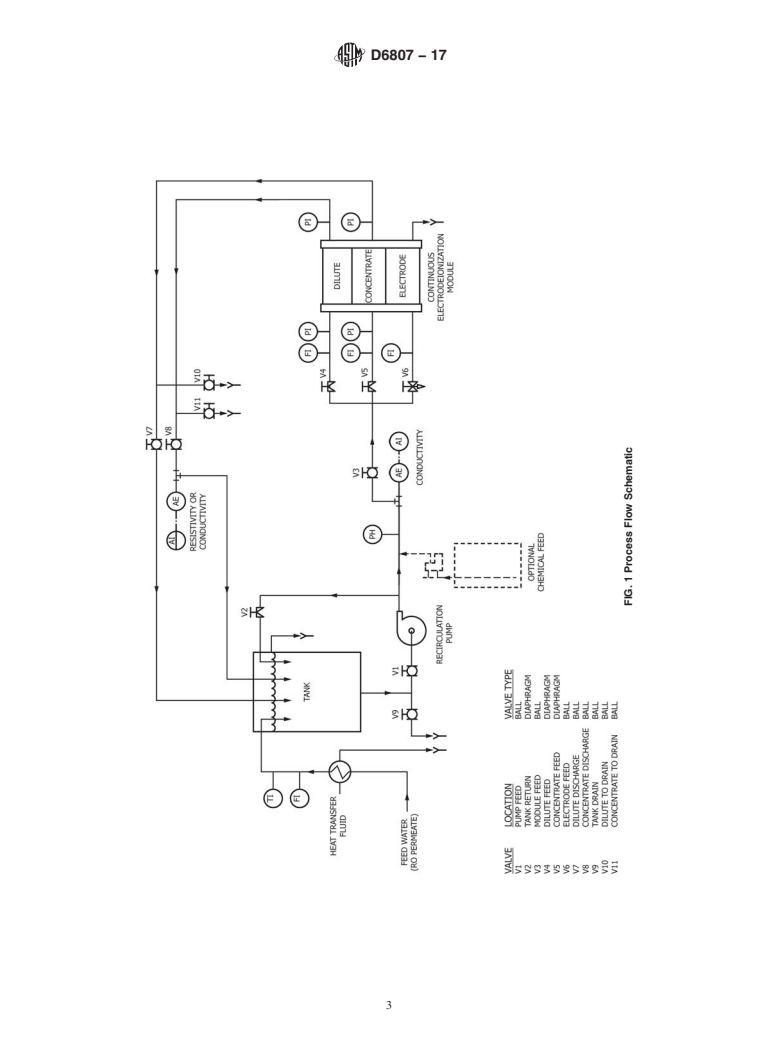
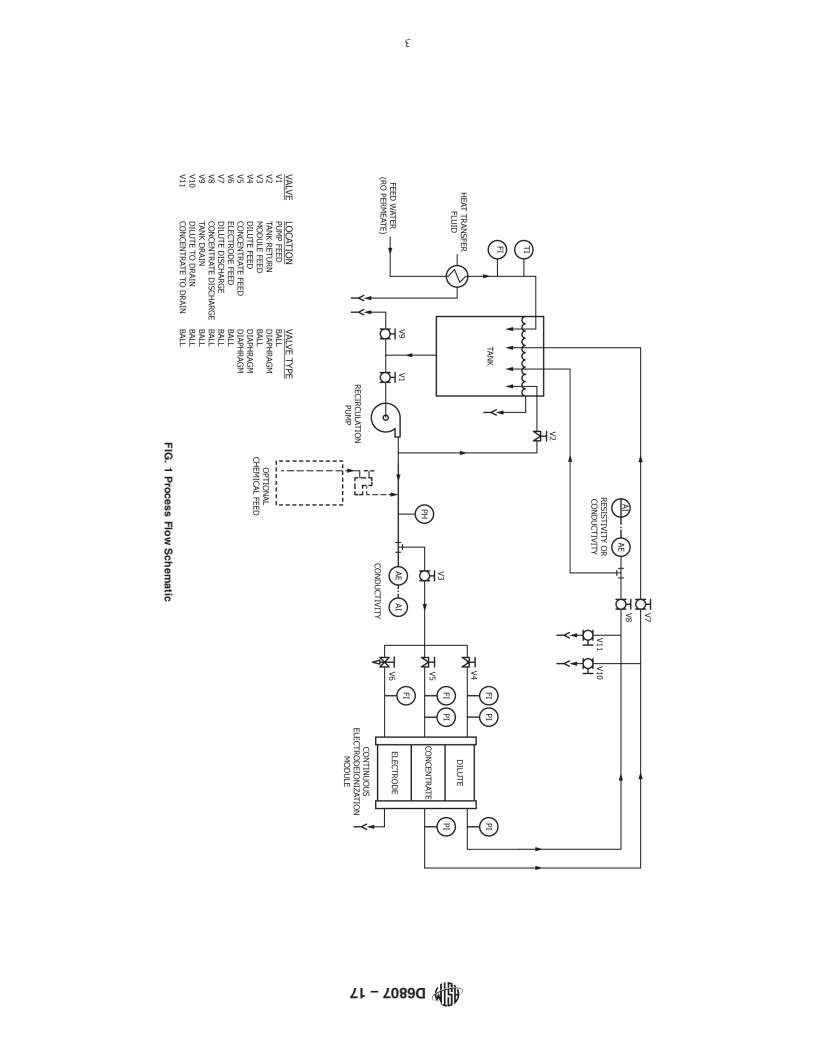
5.1 CEDI devices can be used to produce deionized water from feeds of pretreated water. This test method permits the measurement of key performance capabilities of CEDI devices using a standard set of conditions. The data obtained can be analyzed to provide information on whether changes may have occurred in operating characteristics of the device independently of any variability in feed water characteristics or operating conditions. Under specific circumstances, this test method may also provide sufficient information for plant design.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the operating characteristics of continuous electrodeionization (CEDI) devices, indicative of deionization performance when a device is applied to production of highly deionized water from the product water of a reverse osmosis system. This test method is a procedure applicable to feed waters containing carbonic acid or dissolved silica, or both, and other solutes, with a conductivity range of approximately 2 to 100 microsiemens-cm-1.
1.2 This test method covers the determination of operating characteristics under standard test conditions of CEDI devices where the electrically active transfer media therein is predominantly regenerated.
1.3 This test method is not necessarily indicative of:
1.3.1 Long term performance on feed waters containing foulants or sparingly soluble solutes, or both;
1.3.2 Performance on feeds of brackish water, sea water, or other high salinity feeds;
1.3.3 Performance on synthetic industrial feed solutions, pharmaceuticals, or process solutions of foods and beverages; or
1.3.4 Performance on feed waters less than 2 μS/cm, particularly performance relating to organic solutes, colloidal or particulate matter, or biological or microbial matter.
1.4 This test method, subject to the limitations described, can be applied as either an aid to predict expected deionization performance for a given feed water quality, or as a method to determine whether performance of a given device has changed over some period of time. It is ultimately, however, the user’s responsibility to ensure the validity of this test method for their specific applications.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6807 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Operating Performance of Continuous Electrodeionization
Systems on Reverse Osmosis Permeates from
1
2 to 100 µS/cm
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6807; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the oper-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ating characteristics of continuous electrodeionization (CEDI)
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
devices, indicative of deionization performance when a device
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
is applied to production of highly deionized water from the
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
product water of a reverse osmosis system. This test method is
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
a procedure applicable to feed waters containing carbonic acid
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
or dissolved silica, or both, and other solutes, with a conduc-
-1
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
tivity range of approximately 2 to 100 microsiemens-cm .
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.2 This test method covers the determination of operating
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
characteristics under standard test conditions of CEDI devices
where the electrically active transfer media therein is predomi-
2. Referenced Documents
nantly regenerated.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.3 This test method is not necessarily indicative of:
D513 Test Methods for Total and Dissolved Carbon Dioxide
1.3.1 Long term performance on feed waters containing
in Water
foulants or sparingly soluble solutes, or both;
D859 Test Method for Silica in Water
1.3.2 Performance on feeds of brackish water, sea water, or
D1125 Test Methods for Electrical Conductivity and Resis-
other high salinity feeds;
tivity of Water
1.3.3 Performance on synthetic industrial feed solutions,
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
pharmaceuticals, or process solutions of foods and beverages;
D1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
or
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
1.3.4 Performance on feed waters less than 2 µS/cm, par-
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
ticularly performance relating to organic solutes, colloidal or
D4194 Test Methods for Operating Characteristics of Re-
particulate matter, or biological or microbial matter.
verse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Devices
1.4 This test method, subject to the limitations described,
3. Terminology
can be applied as either an aid to predict expected deionization
performance for a given feed water quality, or as a method to 3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to
determine whether performance of a given device has changed
over some period of time. It is ultimately, however, the user’s Terminology D1129.
3.1.2 For descriptions of terms relating to reverse osmosis,
responsibility to ensure the validity of this test method for their
refer to Test Methods D4194.
specific applications.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 cell, n—an independently fed chamber formed by two
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard. adjacent ion exchange membranes, or by a membrane and an
adjacent electrode.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.08 on Membranes and Ion
2
Exchange Materials. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2017. Published February 2018. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D6807 – 02 (2009). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D6807-17. the ASTM website.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6807 − 17
3.2.2 continuous electrodeionization (CEDI) device, n—a exchanger or othe
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6807 − 02 (Reapproved 2009) D6807 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Operating Performance of Continuous Electrodeionization
Systems on Reverse Osmosis Permeates from
1
2 to 100 μS/cm
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6807; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the operating characteristics of continuous electrodeionization (CEDI) devices,
indicative of deionization performance when a device is applied to production of highly deionized water from the product water
of a reverse osmosis system. This test method is a procedure applicable to feed waters containing carbonic acid and/or dissolved
-1
silica or dissolved silica, or both, and other solutes, with a conductivity range of approximately 2 to 100 microsiemens-cm .
1.2 This test method covers the determination of operating characteristics under standard test conditions of CEDI devices where
the electrically active transfer media therein is predominantly regenerated.
1.3 TheThis test method is not necessarily indicative of:
1.3.1 Long term performance on feed waters containing foulants and/oror sparingly soluble solutes;solutes, or both;
1.3.2 Performance on feeds of brackish water, sea water, or other high salinity feeds;
1.3.3 Performance on synthetic industrial feed solutions, pharmaceuticals, or process solutions of foods and beverages; or,or
1.3.4 Performance on feed waters less than 2 μS/cm, particularly performance relating to organic solutes, colloidal or particulate
matter, or biological or microbial matter.
1.4 TheThis test method, subject to the limitations described, can be applied as either an aid to predict expected deionization
performance for a given feed water quality, or as a method to determine whether performance of a given device has changed over
some period of time. It is ultimately, however, the user’suser’s responsibility to ensure the validity of thethis test method for their
specific applications.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all
of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate
safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D513 Test Methods for Total and Dissolved Carbon Dioxide in Water
D859 Test Method for Silica in Water
D1125 Test Methods for Electrical Conductivity and Resistivity of Water
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
D1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
D4194 Test Methods for Operating Characteristics of Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Devices
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.08 on Membranes and Ion Exchange
Materials.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009Dec. 15, 2017. Published June 2009February 2018. Originally approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 20022009 as
D6807 – 02.D6807 – 02 (2009). DOI: 10.1520/D6807-02R09.10.1520/D6807-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6807 − 17
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of general terms used in these test methods, refer to Terminology D1129.
3.1 For desc
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.