ASTM D4127-18a
(Terminology)Standard Terminology Used with Ion-Selective Electrodes
Standard Terminology Used with Ion-Selective Electrodes
SCOPE
1.1 This terminology covers those terms recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC),2 and is intended to provide guidance in the use of ion-selective electrodes for analytical measurement of species in water, wastewater, and brines.
1.2 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4127 − 18a
Standard Terminology Used with
1
Ion-Selective Electrodes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4127; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
concentration. Ionic activity, not concentration, determines both the
1. Scope*
rate and the extent of chemical reactions.
1.1 This terminology covers those terms recommended by
activity coefficient, n—afactor, γ,thatrelatesactivity, A,tothe
the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
2
(IUPAC), and is intended to provide guidance in the use of concentration, C of a species in solution:
ion-selective electrodes for analytical measurement of species
A 5 γC
in water, wastewater, and brines.
DISCUSSION—The activity coefficient is dependent on the ionic
strength of the solution. Ions of similar size and charge have similar
1.2 This international standard was developed in accor-
activity coefficients.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
alkaline error, n—in alkaline solutions, where hydrogen ion
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
activity becomes very small, some glass electrodes respond
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
to other cations, such as sodium.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. DISCUSSION—AnegativeerrorinthepHreadingresults.Bychanging
thecompositionoftheglass,theaffinityoftheglassforsodiumioncan
2. Referenced Documents be reduced. Such electrodes are known as lithium glass, high-pH, or
full-range electrodes.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1129Terminology Relating to Water analate, n—the sample being analyzed; used in the terms
“analate addition” and “analate subtraction.”
3. Terminology
DISCUSSION—This term differs from the term “analyte,” which
describes the chemical species of interest in an analytical test.
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to
asymmetry potential, n—the potential across a glass pH
Terminology D1129.
electrode membrane when the inside and outside of the
membrane are in contact with solutions of identical pH.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Relevant to Ion-Selective Electrode
DISCUSSION—This term has also been used to define the observed
Technology:
potential differences between identical electrode pairs placed in iden-
acid error, n—in very acid solutions, the activity of water is
tical solutions.
reduced (less than unity) causing a non-Nernstian response
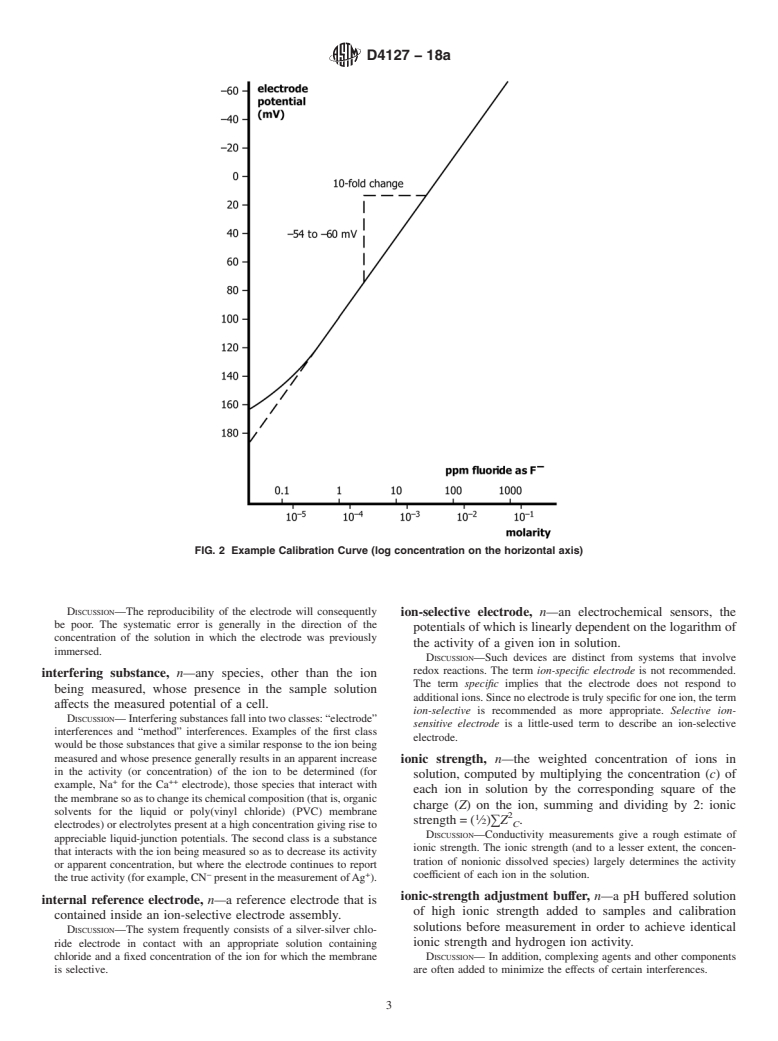
in glass electrodes. calibration curve, n—a plot of the potential (emf or E) of a
DISCUSSION—A positive error in the pH reading results.
given ion-selective electrode cell assembly (ion-selective
electrode combined with an identified reference electrode)
activity, n—the thermodynamically effective concentration of
versus the logarithm of the ionic activity (or concentration)
a free ion in solution.
of a given species.
DISCUSSION—In dilute solutions, ionic activity, and concentration are
DISCUSSION—For uniformity, it is recommended that the potential be
practically identical, but in solutions of high ionic strength, or in the
plotted on the ordinate (vertical axis) with the more positive potentials
presence of complexing agents, activity may differ significantly from
at the top of the graph and that pa (−log activity of the species
A
measured, A)orpc (−log concentration of species measured, A)be
A
1 plotted on the abscissa (horizontal axis) with increasing activity to the
This terminology is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D19 on Water
right. See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. Region I of Fig. 1 represents the segment
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic Constituents
in Water. of the curve where the potential no longer changes in response to
Current edition approved May 1, 2018. Published June 2018. Originally
changes of the measured species activity and the electrode no longer
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as D4127–18. DOI:
demonstrates Nernstian response.
10.1520/D4127-18a.
IUPAC
2
Recommendations for Nomenclature of Ion-Selective Electrodes, IUPAC Com-
mission on Analytical Nomenclature, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1976.
activity standard, n—a standardizing solution whose value is
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
reported in terms of ionic activity.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
DISCUSSI
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4127 − 18 D4127 − 18a
Standard Terminology Used with
1
Ion-Selective Electrodes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4127; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This terminology covers those terms recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC),
and is intended to provide guidance in the use of ion-selective electrodes for analytical measurement of species in water,
wastewater, and brines.
1.2 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to Terminology D1129.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Relevant to Ion-Selective Electrode Technology:
acid error, n—in very acid solutions, the activity of water is reduced (less than unity) causing a non-Nernstian response in glass
electrodes.
DISCUSSION—
A positive error in the pH reading results.
activity, n—the thermodynamically effective concentration of a free ion in solution.
DISCUSSION—
In dilute solutions, ionic activity, and concentration are practically identical, but in solutions of high ionic strength, or in the presence of complexing
agents, activity may differ significantly from concentration. Ionic activity, not concentration, determines both the rate and the extent of chemical
reactions.
activity coefficient, n—a factor, γ, that relates activity, A, to the concentration, C of a species in solution:
A 5 γC
DISCUSSION—
The activity coefficient is dependent on the ionic strength of the solution. Ions of similar size and charge have similar activity coefficients.
1
This terminology is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on Water and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic Constituents in Water.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2018May 1, 2018. Published May 2018June 2018. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 20122018 as
D4127 – 12.D4127 – 18. DOI: 10.1520/D4127-18.10.1520/D4127-18a.
2
Recommendations for Nomenclature of Ion-Selective Electrodes, IUPAC Commission on Analytical Nomenclature, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1976.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4127 − 18a
alkaline error, n—in alkaline solutions, where hydrogen ion activity becomes very small, some glass electrodes respond to other
cations, such as sodium.
DISCUSSION—
A negative error in the pH reading results. By changing the composition of the glass, the affinity of the glass for sodium ion can be reduced. Such
electrodes are known as lithium glass, high-pH, or full-range electrodes.
analate, n—the sample being analyzed; used in the terms “analate addition” and “analate subtraction.”
DISCUSSION—
This term differs from the term “analyte,” which describes the chemical species of interest in an analytical test.
asymmetry potential, n—the potential across a glass pH electrode membrane when the inside and outside of the membrane are
in contact with solutions of identical pH.
DISCUSSION—
This term has also been used to define the observed potential differences between identical electrode pairs placed in identical solutions.
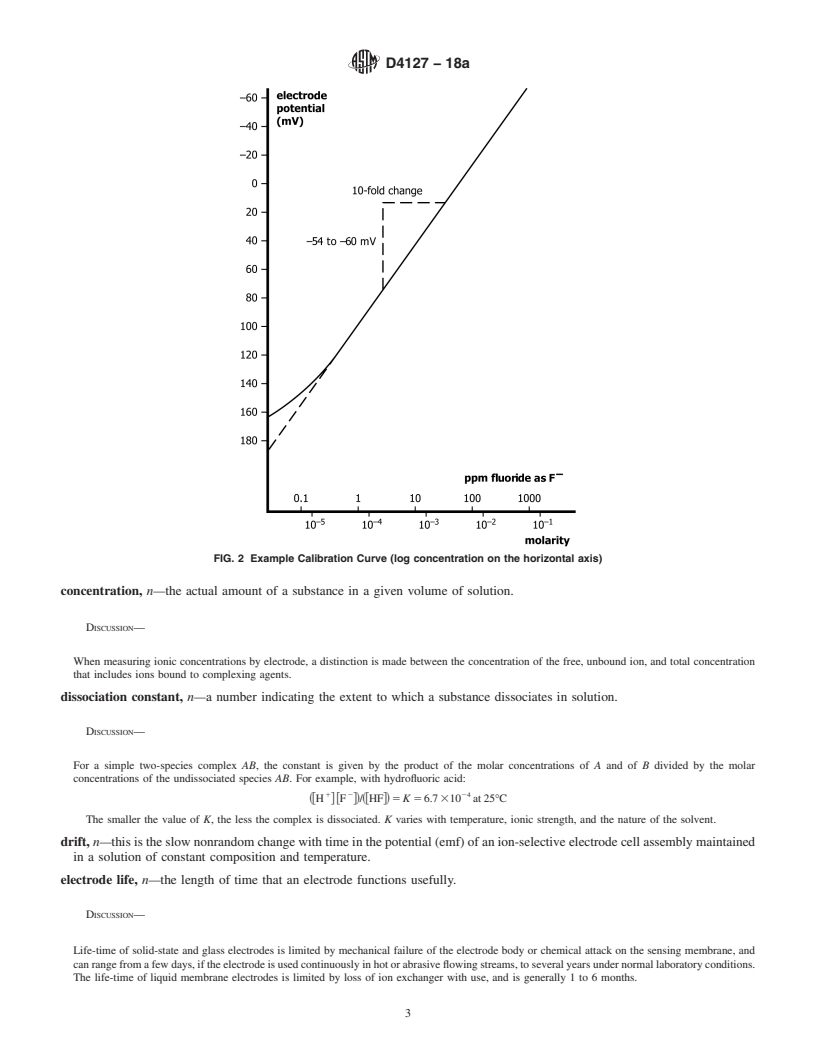
calibration curve, n—a plot of the potential (emf or E) of a given ion-selective electrode cell assembly (ion-selective electrode
combined with an identified reference electrode) versus the logarithm of the ionic activity (or concentration) of a given species.
DISCUSSION—
For uniformity, it is recommended that the potential be plotted on the ordinate (vertical axis) with the more positive po
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.