ASTM D6824-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Filterability of Aviation Turbine Fuel
Standard Test Method for Determining Filterability of Aviation Turbine Fuel
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is intended for use in the laboratory or field in evaluating aviation turbine fuel cleanliness.
5.2 A change in filtration performance after storage, pretreatment, or commingling can be indicative of changes in fuel condition.
5.3 Relative filterability of fuels may vary, depending on filter porosity and structure, and may not always correlate with results from this test method.
5.4 Causes of poor filterability in industrial/refinery filters include fuel degradation products, contaminants picked up during storage or transfer, incompatibility of commingled fuels, or interaction of the fuel with the filter media. Any of these could correlate with orifice or filter system plugging, or both.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the filterability of aviation turbine fuels.Note 1—ASTM specification fuels falling within the scope of this test method are Specifications D1655 and D6615 and the military fuels covered in the military specifications listed in 2.2.
1.2 This test method is not applicable to fuels that contain undissolved water.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6824 − 13 AnAmerican National Standard
Standard Test Method for
1
Determining Filterability of Aviation Turbine Fuel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6824; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D6426 Test Method for Determining Filterability of Middle
Distillate Fuel Oils
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the
D6615 Specification for Jet B Wide-Cut Aviation Turbine
filterability of aviation turbine fuels.
Fuel
NOTE 1—ASTM specification fuels falling within the scope of this test
3
2.2 Military Standards:
method are Specifications D1655 and D6615 and the military fuels
covered in the military specifications listed in 2.2.
MIL-DTL-5624 Turbine Fuel, Aviation, Grades JP-4, JP-5,
and JP-5/JP-8 ST
1.2 This test method is not applicable to fuels that contain
MIL-DTL-25524 Turbine Fuel, Aviation, Thermally Stable
undissolved water.
MIL-DTL-38219 Turbine Fuels, Low Volatility, JP-7
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
MIL-DTL-83133 Turbine Fuels, Aviation, Kerosine Types,
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
NATO F-34 (JP-8), NATO F-35, and JP-8+100
only.
3. Terminology
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 filterability, n—a measure of the rapidity with which a
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
standard filter medium is plugged by insoluble matter in fuel
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
and may be described as a function of pressure or volume:
3.1.1.1 filterability (by pressure), n—the pressure drop
2. Referenced Documents
across a filter medium when 300 mL of fuel is passed at a rate
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of 20 mL/min.
D1655 Specification for Aviation Turbine Fuels
3.1.1.2 filterability (by volume), n—the volume of fuel
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
passed when a pressure of 104 kPa (15 psig) is reached.
Petroleum Products
D4176 Test Method for FreeWater and Particulate Contami-
3.1.1.3 Discussion—Filterability by volume is used when
nation in Distillate Fuels (Visual Inspection Procedures)
less than 300 mL passes the filter at a pressure up to 104 kPa
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
(15 psig).
Petroleum Products
3.1.1.4 filterability quality factor (F-QF), n—a value that
D4860 Test Method for FreeWater and Particulate Contami-
defines the filter plugging tendency of a fuel caused by
nation in Middle Distillate Fuels (Clear and Bright Nu-
particulates.
merical Rating)
3.1.1.5 Discussion—The F-QF value is calculated using the
D5452 Test Method for Particulate Contamination in Avia-
volume and pressure attained at the end of the test cycle,
tion Fuels by Laboratory Filtration
according to one of two equations, depending on the outcome
D6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias
of the test. (See Section 10, Calculations.)
Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and
Lubricants
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A sample is passed at a constant rate (20 mL/min)
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
through a standard porosity filter medium. The pressure drop
Petroleum Products and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
across the filter and the volume of filtrate are monitored. The
D02.J0.01 on Jet Fuel Specifications.
test is concluded either when the pressure drop across the filter
Current edition approved June 15, 2013. Published August 2013. Originally
approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D6824 – 07. DOI: exceeds 104 kPa (15 psig) or when 300 mL have passed
10.1520/D6824-13.
through the filter.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
the ASTM website. Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6824 − 13
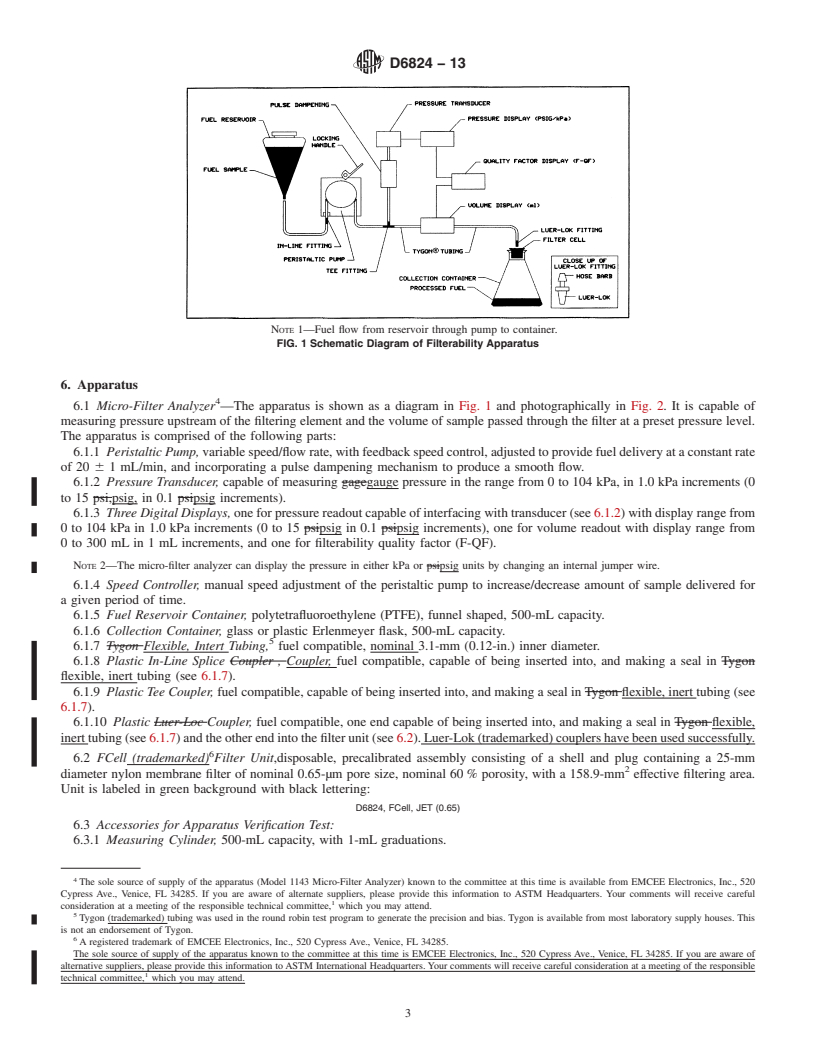
NOTE 1—Fuel flow from reservoir through pump to container.
FIG. 1 Schematic Diagram of Filterability Apparatus
4.2 Results
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6824 − 07 D6824 − 13 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
1
Determining Filterability of Aviation Turbine Fuel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6824; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the filterability of aviation turbine fuels.
NOTE 1—ASTM specification fuels falling within the scope of this test method are Specifications D1655 and D6615 and the military fuels covered in
the military specifications listed in 2.2.
1.2 This test method is not applicable to fuels that contain undissolved water.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1655 Specification for Aviation Turbine Fuels
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4176 Test Method for Free Water and Particulate Contamination in Distillate Fuels (Visual Inspection Procedures)
D4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4860 Test Method for Free Water and Particulate Contamination in Middle Distillate Fuels (Clear and Bright Numerical
Rating)
D5452 Test Method for Particulate Contamination in Aviation Fuels by Laboratory Filtration
D6300 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and Lubricants
D6426 Test Method for Determining Filterability of Middle Distillate Fuel Oils
D6615 Specification for Jet B Wide-Cut Aviation Turbine Fuel
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
3
2.2 Military Standards:
MIL-DTL-5624 Turbine Fuel, Aviation, Grades JP-4, JP-5, and JP-5/JP-8 ST
MIL-DTL-25524 Turbine Fuel, Aviation, Thermally Stable
MIL-DTL-38219 Turbine Fuels, Low Volatility, JP-7
MIL-DTL-83133 Turbine Fuels, Aviation, Kerosine Types, NATO F-34 (JP-8), NATO F-35, and JP-8+100
2.3 ASTM Adjuncts:
4
ADJD6300 D2PP, Version 4.43, Determination of Precision and Bias Data for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 filterability—filterability, n—a measure of the rapidity with which a standard filter medium is plugged by insoluble matter
in fuel and can be described in the following ways:may be described as a function of pressure or volume:
3.1.1.1 filterability (by pressure)—pressure), n—the pressure drop across a filter medium when 300 mL of fuel is passed at a
rate of 20 mL/min.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.J0.01
on Jet Fuel Specifications.
Current edition approved July 1, 2007June 15, 2013. Published August 2007August 2013. Originally approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 20042007 as
D6824D6824 – 07.–04. DOI: 10.1520/D6824-07.10.1520/D6824-13.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6824 − 13
3.1.1.2 filterability (by volume)—volume), n—the volume of fuel passed when a pressure of 104 kPa (15 psi) is reached. This
method of report is used when less than 300 mL passes at that pressure, 104 kPa (15 psi).psig) is reached.
3.1.1.3 Discussion—
Filterability by volume is used when less than 300 mL passes the filter at a pressure up to 104 kPa (15 psig).
3.1.1.4 filterability quality factor (F-QF)—(F-QF), n—a value that defines the filter plugging tendency of
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.