ASTM F3409-19
(Practice)Standard Practice for Simplified Aircraft Loads Determination
Standard Practice for Simplified Aircraft Loads Determination
SCOPE
1.1 This practice provides an acceptable, and simplified, means of determining certain design loads criteria and conditions for fixed wing aircraft. In particular, the practice provides overall aircraft flight loads and flight conditions as well as control surface loads, wing loads, gust load factors, and gust loads on stabilizing surfaces.
1.2 This practice is intended to be referenced by other standards that define requirements for comprehensive aircraft loads. This practice does not provide all aircraft loads required for structural compliance. In addition, each load or condition determined through this practice has limitations on its use within the relevant section to which it must adhere.
1.3 Units—The values given in this standard are in SI units and are to be regarded as standard. Any values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to inch-pound (or other) units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents. Where it may not be clear, some equations provide the units of the result directly following the equation.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F3409 −19
Standard Practice for
1
Simplified Aircraft Loads Determination
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3409; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F2245 Specification for Design and Performance of a Light
Sport Airplane
1.1 This practice provides an acceptable, and simplified,
F3060 Terminology for Aircraft
means of determining certain design loads criteria and condi-
F3116/F3116M Specification for Design Loads and Condi-
tions for fixed wing aircraft. In particular, the practice provides
tions
overall aircraft flight loads and flight conditions as well as
control surface loads, wing loads, gust load factors, and gust
3. Terminology
loads on stabilizing surfaces.
3.1 Definitions:
1.2 This practice is intended to be referenced by other
3.1.1 A listing of terms, abbreviations, acronyms, and sym-
standards that define requirements for comprehensive aircraft
bols related to aircraft can be found in Terminology F3060.
loads. This practice does not provide all aircraft loads required
Items listed in 3.2 are more specific to this standard.
for structural compliance. In addition, each load or condition
3.2 Abbreviations:
determined through this practice has limitations on its use
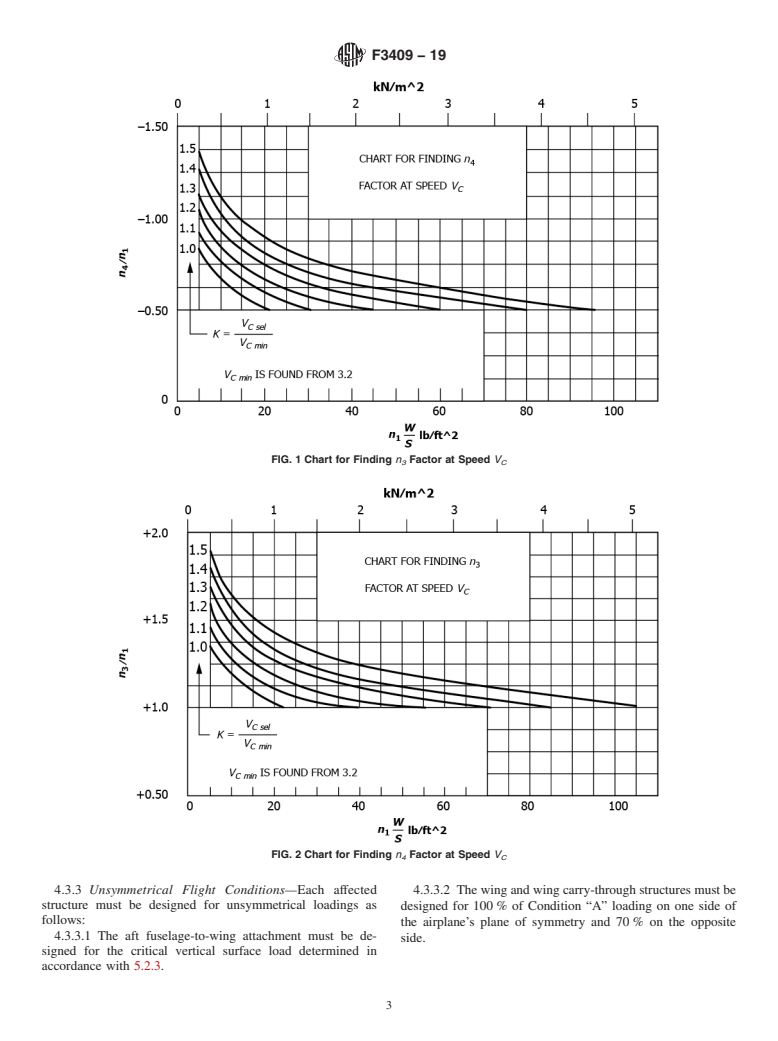
within the relevant section to which it must adhere. n = airplane positive maneuvering limit load factor
1
n = airplane negative maneuvering limit load factor
2
1.3 Units—The values given in this standard are in SI units
n = airplane positive gust limit load factor at V
3 C
and are to be regarded as standard. Any values given in
n = airplane negative gust limit load factor at V
4 C
parentheses are mathematical conversions to inch-pound (or
n = airplane positive limit load factor with flaps fully
flap
other) units that are provided for information only and are not
extended at V
F
considered standard. The values stated in each system may not
V = minimum design flap speed =
Fmin
be exact equivalents. Where it may not be clear, some
=
equations provide the units of the result directly following the 0.818 5 n ~W ⁄ S!
1
equation.
V = design maneuvering speed =
A
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
W
=
V n □where□V 5
S 1 S
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1
S D
ρ C S
! S D
Lmax
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
2
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor- V = minimum design cruising speed
Cmin
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.27 5 =n W ⁄ S
~ !
1
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
but need not exceed 0.9 V
H
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
V = minimum design dive speed
Dmin
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
=
1.79 5 n ~W ⁄ S!
1
2. Referenced Documents
but need not exceed
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
=
1.4□V n ⁄3.8
Cmin 1
See 4.2.5.2.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F37 on Light Sport
V = design cruising speed (if greater than V )
Csel Cmin
Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F37.20 on Airplane.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2019. Published March 2020. DOI: 10.1520/
4. Simplified Design Load Criteria
F3409–19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4.1 Limitations:
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.1.1 Methods provided in this section provide one possible
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. means (but not the only possible means) of compliance. These
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F3409−19
requirements may be applied to airplanes meeting the follow- gated for the most adverse dead weight loading conditions for
ing limitations without further justification. the CG range selected.
4.1.1.1 A main wing located closer to the airplane’s center
4.2.5 The following loads and loading conditions are the
of gravity than to the aft, fuselage-mounted empennage.
minimums for which strength must be provided in the struc-
4.1.1.2 A main wing that contains a quarter chord sweep
ture:
angle of not more than 15° fore or aft.
4.2.5.1 Airplane Equilibrium—The aerodynamic wing loads
4.1.1.3 A main wing that is equipped with trailing-edge
may be cons
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.