ASTM E618-07
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Evaluating Machining Performance of Ferrous Metals Using an Automatic Screw/Bar Machine
Standard Test Method for Evaluating Machining Performance of Ferrous Metals Using an Automatic Screw/Bar Machine
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method can be used to evaluate the machining performance of a single grade or type of metal or to compare one grade or type with another.
5.1.1 The machining performance of the test metal is measured by the maximum rate at which test pieces can be produced within specified surface roughness and dimensional limits for a specified length of time and also by the cutting speed and tool feed employed to attain that rate.
5.1.2 The relative machining performance of the various metals tested using this test method may be evaluated only at operating conditions that produce test pieces of like quality with respect to surface roughness and dimensional limits for comparable periods of machining time.
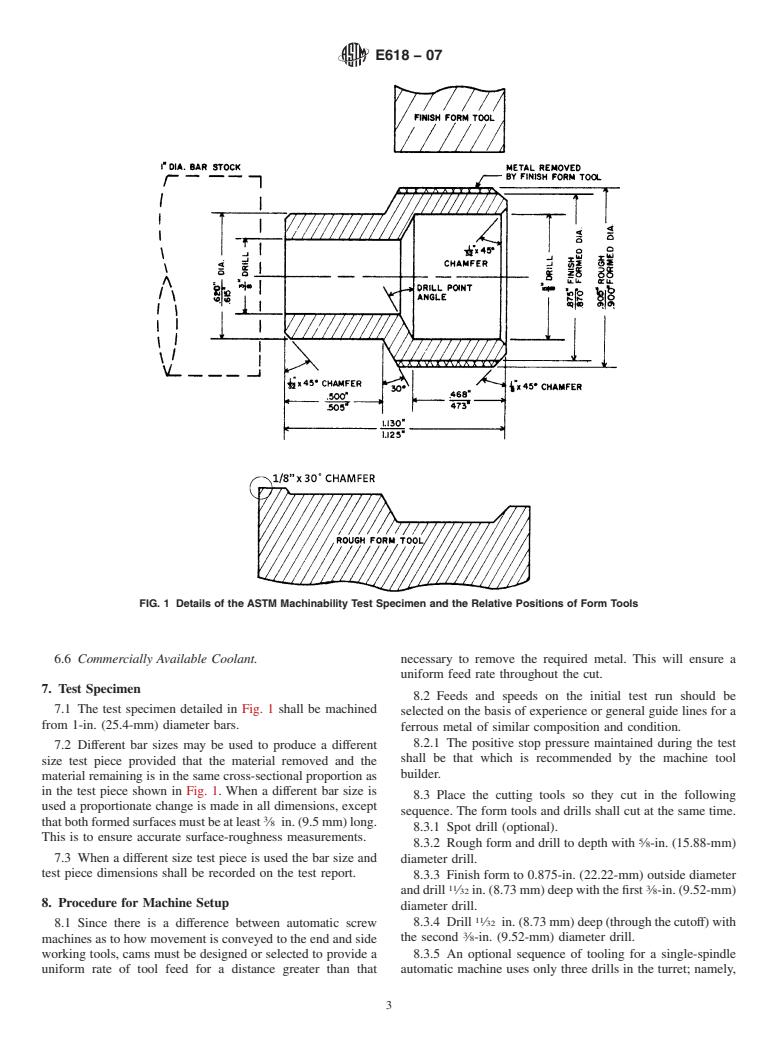
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a production-type test for evaluating the machining performance of ferrous metals as they are used in single-spindle or multiple-spindle automatic screw machines. It is based on producing parts of a standard design in such machines to uniform levels of quality with respect to surface roughness and size variation. The standard test piece, designed for this test, is machined from bars using a specified number of tools in a specified sequence. Nothing in this test method should be construed as defining or establishing limits of acceptability for any grade or type of metal.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E618 − 07
StandardTest Method for
Evaluating Machining Performance of Ferrous Metals Using
1
an Automatic Screw/Bar Machine
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E618; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This test method was written to fill a requirement for a standard test for determining the
machinability of ferrous metals using automatic screw/bar machines. (Hereafter, these machines will
be referred to as automatic screw machines.) Although a variety of short-time laboratory tests have
demonstrated different machining characteristics among ferrous metals, it has been difficult to apply
the resulting data to commercial automatic screw machine practice.
In this test method a standard test piece is machined using tools and machining operations typical
of automatic screw machine practice.
Throughtheuseofthistestmethod,therelativemachiningperformanceofametalcanbeevaluated
even though different automatic screw machines are used. Further, comparisons can be made among
different lots of the same grade or different grades to determine relative machining performance.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This test method covers a production-type test for 2.1 American National Standard:
2
evaluating the machining performance of ferrous metals as B46.1 Surface Texture
they are used in single-spindle or multiple-spindle automatic
3. Terminology
screw machines. It is based on producing parts of a standard
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
design in such machines to uniform levels of quality with
respect to surface roughness and size variation. The standard 3.1.1 average surface roughness (per set of samples)—for
each surface (the major and minor diameter formed surfaces)
test piece, designed for this test, is machined from bars using
a specified number of tools in a specified sequence. Nothing in the surface roughness per set of samples is the average of the
roughnesses recorded as in 3.1.5.1 for the six test pieces per
this test method should be construed as defining or establishing
limits of acceptability for any grade or type of metal. set. A test set is described in 9.3.
3.1.2 calculated hourly production rate (in pieces per
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
hour)—3600s/hdividedbythecycletimeinsecondsperpiece.
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
(Unit: pieces per hour.)
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
and are not considered standard.
3.1.3 cycle time—the time in seconds per piece from bar
feed-out to bar feed-out, or from cutoff to cutoff, during
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
uninterrupted operation of the machine. It includes all stock,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
machine, and tool movements.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.4 surface speed—the product of the original bar circum-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ference (in feet or metres) and the spindle speed in revolutions
per minute. (Unit: ft/min or m/min.)
1
3.1.5 surface-roughness average value (R )—the surface-
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
a
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
roughness average value is the mean reading around which the
A01.15 on Bars.
Current edition approved May 1, 2007. Published May 2007. Originally
2
approved in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as E618 – 81 (2001). Available from American National Standards Institutes, 25 W. 43rd Street, 4th
DOI: 10.1520/E0618-07. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E618 − 07
needle tends to dwell or fluctuate under small amplitude when 5. Significance and Use
a continuously averaging meter is used. (Refer to 3.8.1.1 in
5.1 This test method can be used to evaluate the machining
ANSI B46.1). The surface-roughness value obtained by a
performance of a single grade or type of metal or to compare
continuously averaging digital readout meter is acceptable.
one grade or type with another.
3.1.5.1 The surface-roughness recorded for each surface on
5.1.1 The machining performance of the test metal is
thetestpieceisthemaximumofthesurface-roughnessaverage
mea
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.