ASTM F1575-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Bending Yield Moment of Nails
Standard Test Method for Determining Bending Yield Moment of Nails
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Nails are a common mechanical fastener in wood structures. Engineering design procedures used to determine the capacities of laterally-loaded nailed connections currently use a yield theory to establish the nominal resistance for laterally-loaded nailed connections that are engineered. In order to develop the nominal resistance for laterally-loaded nailed connections, the bending yield moment must be known.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers procedures for determining the bending yield moment of nails when subjected to static loading. It is intended only for nails used in engineered connection applications, in which a required connection capacity is specified by the designer.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1575–03
Standard Test Method for
1
Determining Bending Yield Moment of Nails
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1575; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope * capacity of the connection under each yield mode is deter-
minedbythebearingstrengthofthematerialunderthefastener
1.1 This test method covers procedures for determining the
and the bending strength of the fastener, with the lowest
bending yield moment of nails when subjected to static
capacity calculated for the various modes being taken as the
loading. It is intended only for nails used in engineered
design load for the connection.
connection applications, in which a required connection capac-
ity is specified by the designer.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 Test specimens are evaluated to determine capacity to
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
resist lateral bending loads applied at a constant rate of
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
deformation with a suitable testing machine. The load on the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
test specimen at various intervals of deformation is measured.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Supplementaryphysicalpropertiesofthetestspecimenarealso
2. Referenced Documents determined.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Significance and Use
2
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
5.1 Nails are a common mechanical fastener in wood
F 1470 GuideforFastenerSamplingforSpecifiedMechani-
3
structures. Engineering design procedures used to determine
cal Properties and Performance Inspection
the capacities of laterally-loaded nailed connections currently
F 1667 Specification for Driven Fasteners: Nails, Spikes,
3
use a yield theory to establish the nominal resistance for
and Staples
laterally-loaded nailed connections that are engineered. In
3. Terminology order to develop the nominal resistance for laterally-loaded
nailed connections, the bending yield moment must be known.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
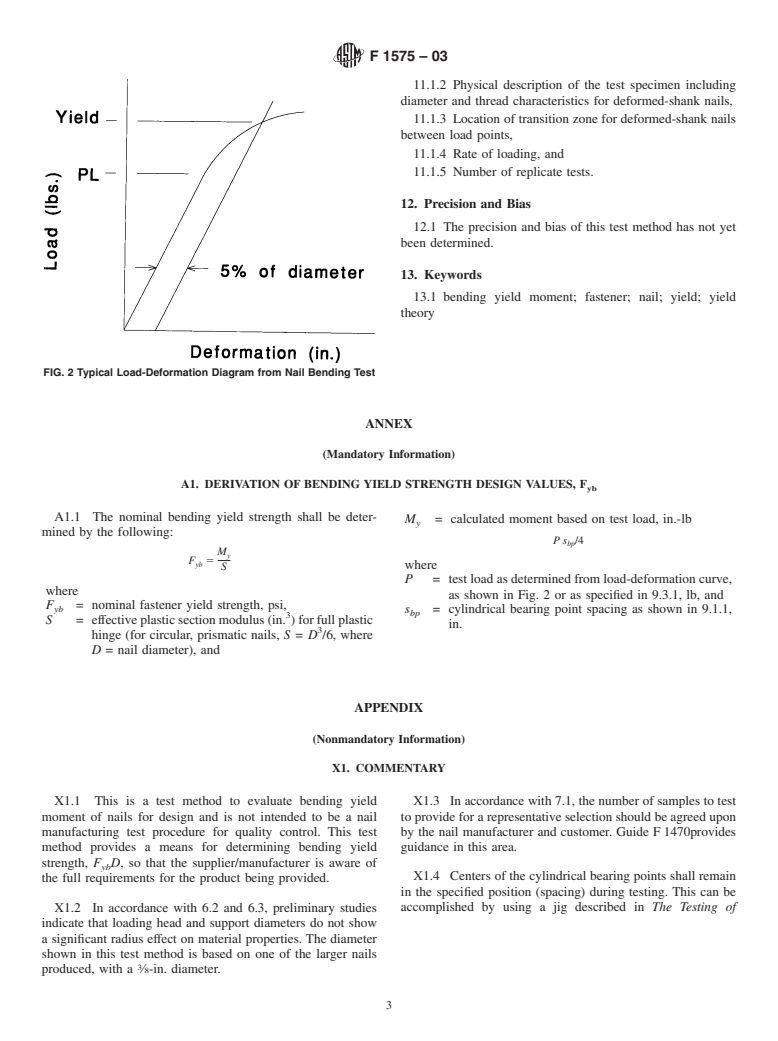
3.1.1 bending yield moment—the moment determined from
6. Apparatus
the load-deformation curve that is intermediate between the
6.1 Testing Machine—Any suitable testing machine capable
proportional limit and maximum load for the nail. It is
of operation at a constant rate of motion of its movable head
calculated by the intersection of the load-deformation curve
and having an accuracy of 61 % when calibrated in accor-
with a line represented by the initial tangent modulus offset
dance with Practice E 4.
5 % of the fastener diameter.
6.2 Cylindrical Bearing Points—Any cylindrical metal
3.1.2 transition zone—the location of the transition from
membercapableofsupportingthetestspecimenduringloading
smooth shank to threaded shank on a deformed-shank nail.
without deforming, as shown in Fig. 1, and having diameter
3.1.3 yield theory—the model for lateral load design values
(D) = 0.375 in.
for dowel-type fasteners that specifically accounts for the
6.2.1 Cylindrical bearing points shall be free to rotate as the
different ways these connections behave under load. The
test specimen deforms.
6.3 Cylindrical Load Point—Any cylindrical metal member
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on
capable of loading the test specimen without deforming, as
Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.05 on Driven and
shown in Fig. 1, and having diameter (D) = 0.375 in.
Other Fasteners.
6.4 Recording Device—Any device with at least a reading
Current edition approved May 10, 2003. Published June 2003. Originally
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as F 1575 – 02.
of 0.001 in. (0.025 mm) and any suitable device for measuring
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
the load on the test specimen during deformation.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.08.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1575–03
9.1.1 Cylindrical bearing point spacing, s , shall be as
bp
indicated in Table 1
9.1.1.1 Ifnailsaretooshorttomeetthisrequirementandthe
nails receive no processing after forming that can affect
fastener bending yield strength, such as heat treating or thread
rolling, the test shall be performed on wire from which the nail
is made.
9.1.1.2 If nails are too shor
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.