ASTM F377-03(2009)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Calibration of Braking/Tractive Measuring Devices for Testing Tires
Standard Practice for Calibration of Braking/Tractive Measuring Devices for Testing Tires
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Calibration is essential in the use of various test platforms and devices to insure that the test results generated by these test devices are accurate, repeatable and meaningful. This standard gives the necessary instructions for the calibration of all of the test devices cited in the Scope.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice gives procedures for the calibration of:
reference load cells
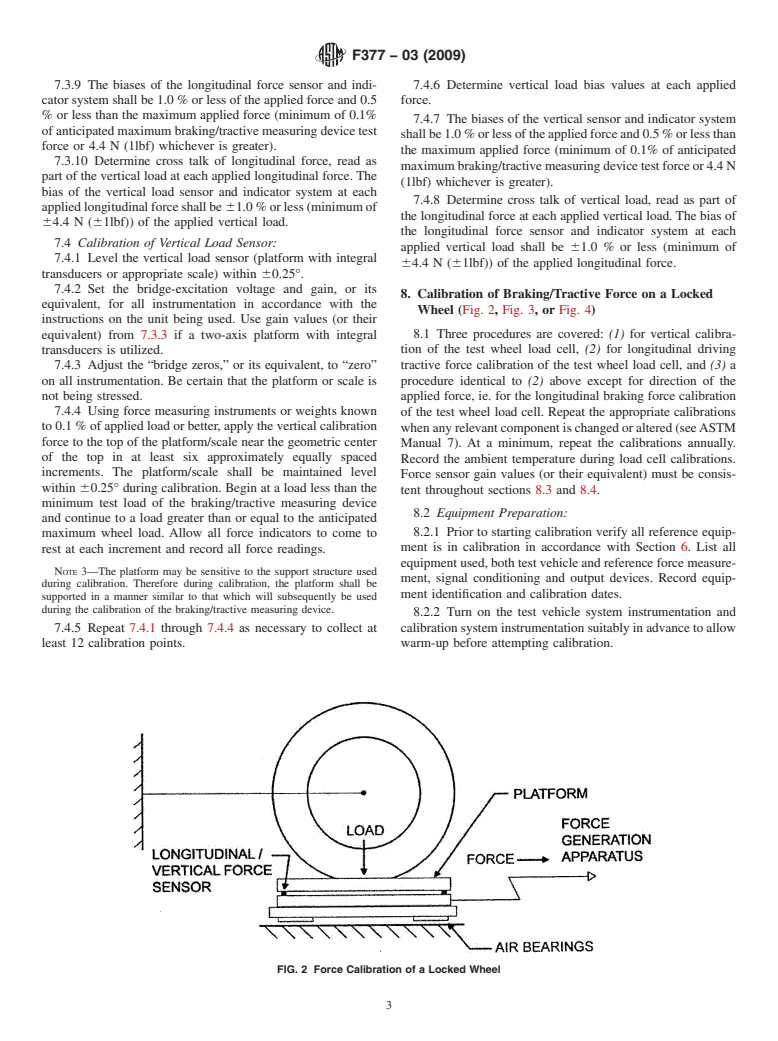
calibration platform systems by using a reference load cell
static calibration of braking/tractive force on locked wheels of tire test trailers, instrumented vehicles, and laboratory tire testing machines by using the calibration platform system as a calibration fixture.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F377 − 03(Reapproved 2009)
Standard Practice for
Calibration of Braking/Tractive Measuring Devices for
Testing Tires
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF377;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Practice
1.1 This practice gives procedures for the calibration of: 4.1 Reference-load cells shall be calibrated using proce-
reference load cells dures and equipment traceable to the National Institute of
calibration platform systems by using a reference load cell Standards and Technology (NIST), or appropriate national
staticcalibrationofbraking/tractiveforceonlockedwheels standards organization.
of tire test trailers, instrumented vehicles, and laboratory tire
NOTE 1—Practice E74 may be used as an alternative method for
testing machines by using the calibration platform system as a
load-cell calibration.
calibration fixture.
4.2 Thecalibratedreference-loadcellisusedtocalibratethe
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
calibration-platform systems or used as the longitudinal force
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
sensor. The tire test trailer, instrumented vehicle, or laboratory
tire testing machine is calibrated with the platform.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5. Significance and Use
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 5.1 Calibration is essential in the use of various test plat-
forms and devices to insure that the test results generated by
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
thesetestdevicesareaccurate,repeatableandmeaningful.This
2. Referenced Documents
standard gives the necessary instructions for the calibration of
all of the test devices cited in the Scope.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E74 Practice of Calibration of Force-Measuring Instruments
6. Apparatus
for Verifying the Force Indication of Testing Machines
6.1 The calibration system consists of the following basic
F538 Terminology Relating to the Characteristics and Per-
formance of Tires components:
6.1.1 Platform—The platform on which the test wheel is
3. Terminology
placed shall have a flat high friction top surface. The platform
shall be of sufficient dimensions to support the entire tire
3.1 Definitions:
contact patch throughout the calibration process.Alow friction
3.1.1 bias, n—the difference between the average measured
bearing (an air bearing is recommended) permitting free
test result and the accepted reference value; it measures in an
horizontal motion and capable of sustaining a vertical load
inverse manner the accuracy of a test.
equal to the largest anticipated wheel load shall support the
3.1.2 longitudinal force, [F], of a tire, n—the component of
platform. The longitudinal movement shall be sufficient to
the tire force vector in the X’ direction.
obtain the necessary required force levels. The platform may
3.1.3 vertical load, n—the normal reaction of the tire on the
also be instrumented with integrated transducers (Force Sen-
road which is equal to the negative of normal force.
sors) to measure vertical and longitudinal forces.
6.1.2 Force Generation Apparatus—A system, capable of
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F09 on Tires and is
developing a longitudinal force sufficient for the calibration of
the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F09.10 on Equipment, Facilities and
the operating range of the device, shall be used.The force shall
Calibration.
be applied along the longitudinal centerline of the platform.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2009. Published March 2010. Originally
6.1.3 Force Sensors—Sensors to measure applied forces in
approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as F377 – 03. DOI:
10.1520/F0377-03R09.
the vertical and longitudinal directions that shall be used to
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
calibrate braking/tractive measuring devices. These sensors
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
can be integrated force transducers located in the platform,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. scales or tension load cells. Sensors shall have sufficient
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F377 − 03 (2009)
measurement range to cover the maximum anticipated test least 8 appropriately spaced increments to a maximum of not
wheel forces. Sensors shall be mounted in a manner such that less than the anticipated maximum force seen in use.Allow all
cross-axis forces will not adversely affect the accuracy. The force indicators to come to rest at each increment and record
force sensor instrumentation shall have the capability to allow the force readings.
for the recording of data, such as a chart recorder, data logger, 7.2.5 Determine bias values at each applied force.
or visual output that allows for manual logging of data. 7.2.6 The biases of the reference-load cell and indicator
6.1.4 Reference Load Cell—The force standard that pro- system shall be 0.25% or less of the known applied force
vides direct traceability to NIST or appropriate national stan- (minimum of 62.2N(60.5lbf)).
dards organization that shall be used to certify other force
7.3 Calibration of Longitudinal Force Sensor Fig. 1:
sensors or weights used within this standard. If integrated
Section 7.3 does not apply when the reference load cell is
platform transducers are not used, the reference load cell may
used as the longitudinal force sensor during calibration of the
be used as the longitudinal force sensor during calibration of
braking/tractive measuring device.
the braking/tractive measuring device. The reference load cell
7.3.1 Mount the reference-load cell such that its longitudi-
shall have sufficient measurement range to cover the maximum
nal axis is parallel to the direction of motion of the platform
anticipated forces.
within 62° and in line with the applied force. If necessary,
place a tension spring in the longitudinal force application
7. Calibration of the Reference Load Cell and Force
system to allow for longitudinal motion.
Sensors
7.3.2 Apply sufficient force to both channels of the system
7.1 Three procedures are covered: (1) calibration of the
throughthefullrangeofexpectedcalibrationforcestoexercise
reference-load cell, (2) calibration of the longitudinal force
to platform. Release all forces.
sensor, and (3) calibration of the vertical load sensor. Repeat
7.3.3 Set the bridge-excitation voltage and gain, or its
the appropriate calibrations when any relevant component is
equivalent, for all instrumentation in accordance with the
changed or altered (see ASTM Manual 7). Repeat the calibra-
instructions on the unit being used.
tions annually unless the changes between the most recent
7.3.4 Adjust the “bridge zeros,” or its equivalent, to “zero”
calibration equation values and those from the previous cali-
on all instrumentation. Be certain that the reference load cell
bration do not exceed 0.1%. Calibration intervals may be
and platform are not being stressed.
lengthened to a maximum of 2 years provided that these
7.3.5 Using weights known to 0.1% of applied load or
changes do not exceed 0.1% of the value. Record the ambient
better, apply a test load, representative of a load which will be
temperature during load cell calibrations. Force sensor gain
encounteredonthebraking/tractivetestdevicetobecalibrated,
values (or their equivalent) shall be consistent throughout
to the top of the platform near the geometric center of the top.
sections 7.3 and 7.4.
The platform must be maintained level within 60.25° during
calibration. Record all force readings.
7.2 Reference Load Calibration:
7.2.1 Set up the reference load cell, indicator and required
NOTE 2—The platform may be sensitive to the support structure used
equipment to perform the calibration. List all equipment used,
during calibration. Therefore during calibration, the platform shall be
supported in a manner similar to that which will subsequently be used
including signal conditioning and output devices. Record
during the calibration of the braking/tractive measuring device.
equipment identification and calibration dates.
7.2.2 Set the bridge-excitation voltage and gain, or its 7.3.6 Apply the longitudinal calibration force in at least 6
equivalent, in accordance with the instructions on the unit approximately equally spaced increments to a maximum of not
being used. less than the anticipated maximum longitudinal wheel force
7.2.3 Adjust the "bridge zero," or its equivalent, to "zero." seen in use. Allow all force indicators to come to rest at each
Be certain that the reference load cell is not being stressed. increment and record the force readings.
7.2.4 Using force measuring instruments or weights known 7.3.7 Repeat 7.3.3 and 7.3.6 as necessary to collect at least
to0.01%orbetterofappliedforce,performacalibrationonthe
12 calibration points.
reference load cell. Class F weights of 8.9N (2 lb) or greater 7.3.8 Determine longitudinal force bias values at each
have a tolerance of 0.01%. Apply the calibration forces in at
applied force.
FIG. 1 Force Calibration of a Platform Force Transducer
F377 − 03 (2009)
7.3.9 The biases of the longitudinal force sensor and indi- 7.4.6 Determine vertical load bias values at each applied
cator system shall be 1.0 % or less of the applied force and 0.5 force.
% or less than the maximum applied force (minimum of 0.1%
7.4.7 The biases of the vertical sensor and indicator system
of anticipated maximum braking/tractive measuring device test
shallbe1.0%orlessoftheappliedforceand0.5%orlessthan
force or 4.4 N (1lbf) whichever is greater).
the maximum applied force (minimum of 0.1% of anticipated
7.3.10 Determine cross talk of longitudinal force, read as
maximumbraking/tractivemeasuringdevicetestforceor4.4N
part of the vertical load at e
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.