ASTM D4124-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Separation of Asphalt into Four Fractions
Standard Test Method for Separation of Asphalt into Four Fractions
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
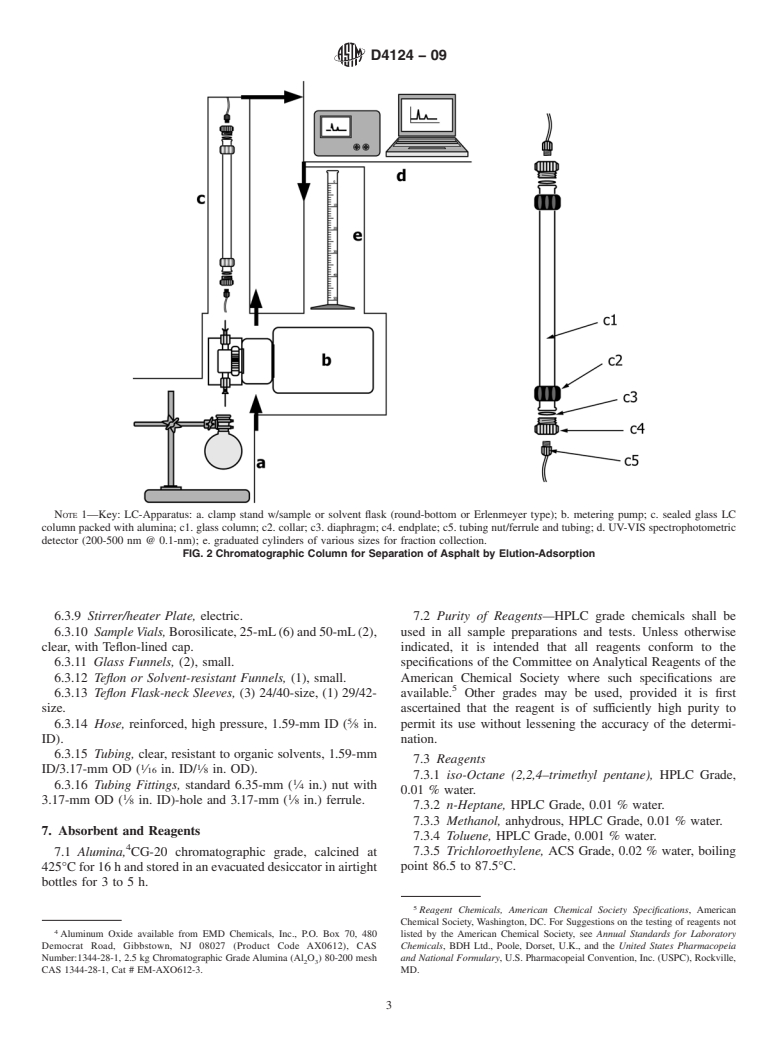
This test method separates asphalts into four well-defined fractions. Analysis of these fractions can be used to evaluate asphalt composition (1, 2). For example, one can compare the ratios of the fractions with other asphalt systems to evaluate processing and aging parameters that relate to performance properties of the asphalt.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the separation of four defined fractions from petroleum asphalts. The four fractions are defined as saturates, naphthene aromatics, polar aromatics, and iso-octane insoluble asphaltenes. This method can also be used to isolate saturates, naphthene aromatics, and polar aromatics from distillate products such as vacuum gas oils, lubricating oils, and cycle stocks. These distillate products usually do not contain asphaltenes.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 8.
1.4 Since a precision estimate for this standard has not been developed, this test method is to be used for research or informational purposes only. Therefore, this standard should not be used for acceptance or rejection of a material for purchasing purposes.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4124 − 09
Standard Test Method for
1
Separation of Asphalt into Four Fractions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4124; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope asphalt in n-alkane (and in some cases, branched alkanes)
under the specified conditions in this test method.
1.1 This test method covers the separation of four defined
3.1.2 naphthene—any of a group of hydrocarbon ring com-
fractions from petroleum asphalts. The four fractions are
pounds of the general formula, C H , derivatives of cyclopen-
defined as saturates, naphthene aromatics, polar aromatics, and
n 2n
tane and cyclohexane, found in certain petroleum stocks.
iso-octane insoluble asphaltenes.This method can also be used
to isolate saturates, naphthene aromatics, and polar aromatics
3.1.3 naphthene aromatics—material that is adsorbed on
from distillate products such as vacuum gas oils, lubricating
calcined CG-20 alumina in the presence of n-heptane, and
oils, and cycle stocks. These distillate products usually do not
desorbed by toluene, after removal of saturates under the
contain asphaltenes.
conditions specified.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1.4 petrolenes (also referred to as maltenes) —(1) any of
standard.
the constituents of a bitumen, as asphalt, that are soluble in
n-alkanes (and in some cases, branched alkanes), which
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
generally range in carbon number between n-C to n-C
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 5 10
alkanes, n-heptane being the most common solvent used; (2)
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the low molecular weight alkane-soluble matter recovered
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
following separation of asphaltenes from the digested mixture
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
under the specified conditions described in this and similar test
tionary statements are given in Section 8.
methods.
1.4 Since a precision estimate for this standard has not been
developed, this test method is to be used for research or
3.1.5 polar aromatics (resins)—material desorbed from cal-
informational purposes only. Therefore, this standard should
cinedCG-20aluminaabsorbent,afterthesaturatesfractionand
not be used for acceptance or rejection of a material for
naphthenic aromatics fraction have been removed, using tolu-
purchasing purposes.
ene:methanol (50:50, vol:vol) and trichloroethylene eluate
under the conditions specified.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.6 saturates—material that, on percolation in an alkane
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
eluate, is not absorbed on calcined CG-20 alumina absorbent
D140 Practice for Sampling Bituminous Materials
under the conditions specified.
2.2 Other Documents:
3
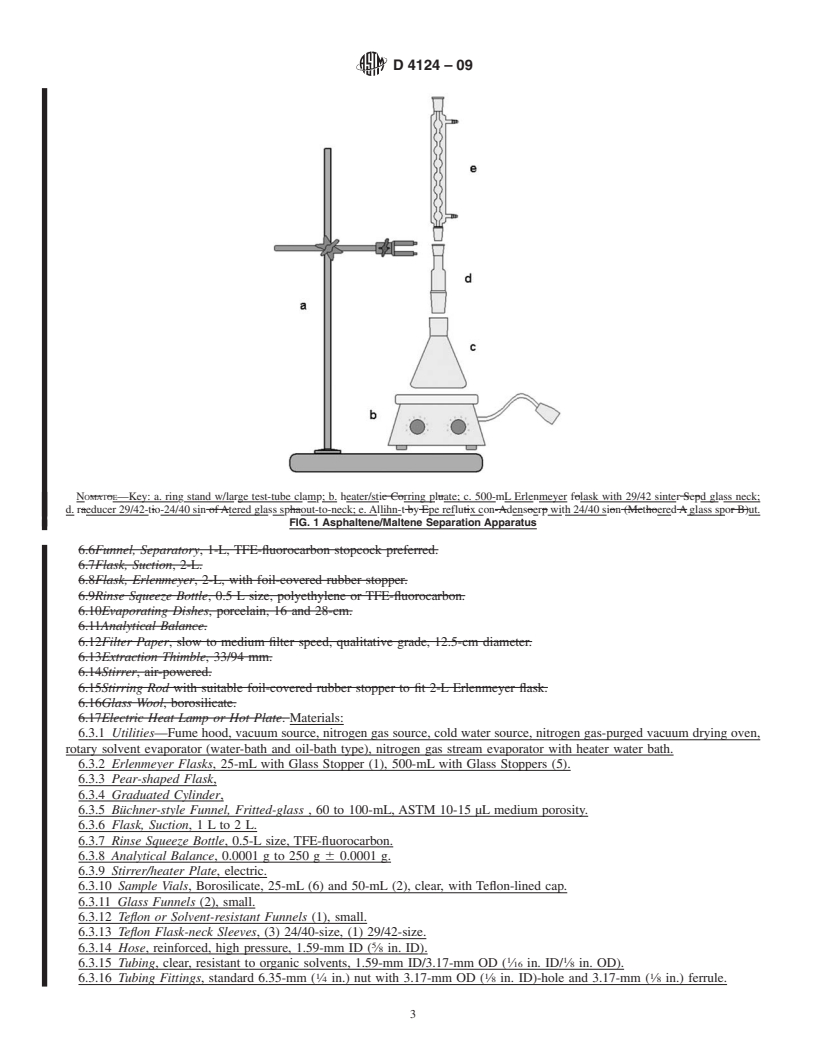
4. Summary of Test Method
Manual on Hydrocarbon Analysis
4.1 The sample containing the four defined fractions is first
3. Terminology
separated into alkane-insoluble asphaltenes and alkane-soluble
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
petrolenes. Petrolenes are then adsorbed onto calcined CG-20
3.1.1 asphaltenes or alkane insolubles—insoluble matter
alumina and further fractionated into saturate, naphthene
that can be separated from asphalt following digestion of the
aromatic, and polar aromatic fractions by pumping an eluo-
tropic series of elution solvents upwards through a glass
1 chromatographiccolumnpackedwithcalcinedalumina.Eluted
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road
and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.47 in
fractions are recovered by solvent removal prior to final
Miscellaneous Asphalt Tests.
weighing. The three eluted fractions plus the alkane-
Current edition approved July 1, 2009. Published August 2009. Originally
precipitated asphaltenes comprise the four fractions as defined
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D4124 – 01. DOI:
in Section 3.
10.1520/D4124-09.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 5. Significance and Use
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
5.1 This test method separates asphalts into four well-
the ASTM website.
3
Available from ASTM as PCN 03-332030-12. defined fractions. Analysis of these fractions can be used to
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
----
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D4124–01
Standard Test Methods for Designation: D 4124 – 09
Standard Test Method for
1
Separation of Asphalt into Four Fractions
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4124; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1These1.1 This test methods covers the separation of four defined fractions from petroleum asphalts. The four fractions are
defined as saturates, naphthene aromatics, polar aromatics, and nC -asphaltenes. These methods iso-octane insoluble asphaltenes.
7
Thismethodcanalsobeusedtoisolatesaturates,naphthenearomatics,andpolararomaticsfromdistillateproductssuchasvacuum
gas oils, lubricating oils, and cycle stocks. These distillate products usually do not contain asphaltenes.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 8and 15.
1.4 Since a precision estimate for this standard has not been developed, this test method is to be used for research or
informational purposes only. Therefore, this standard should not be used for acceptance or rejection of a material for purchasing
purposes.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:C670Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements for Test Methods for Construction Materials
C802Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Test Program to Determine the Precision of Test Methods for Construction
2 2
Materials
D 140 Practice for Sampling Bituminous Materials
3
D3279Test Method for n-Heptane Insolubles Practice for Sampling Bituminous Materials
2.2 Other Documents:
3
Manual on Hydrocarbon Analysis
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 asphaltenes or n-heptane alkane insolubles—insoluble matter that can be separated from asphalt following digestion of
the asphalt in n-heptane n-alkane (and in some cases, branched alkanes) under the specified conditions in thesethis test methods.
method.
3.1.2 naphthene—any of a group of hydrocarbon ring compounds of the general formula, C H , derivatives of cyclopentane
n 2n
and cyclohexane, found in certain petroleum stocks.
3.1.3 naphthene aromatics—material that is adsorbed on calcined CG-20 alumina in the presence of n-heptane, and desorbed
by toluene, after removal of the saturates under the conditions specified.
3.1.3petrolenes—the n-heptane-soluble matter recovered following separation of the asphaltenes from the digested mixture
under the specified conditions in these test methods. -heptane, and desorbed by toluene, after removal of saturates under the
conditions specified.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.47 in
Miscellaneous Asphalt Tests.
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 2001. Published October 2001. Originally published as D4124–82. Last previous edition D4124–97.
Current edition approved July 1, 2009. Published August 2009. Originally approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D 4124 – 01.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 04.02.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.03.
3
Available from ASTM as PCN 03-332030-12.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4124–09
3.1.4 polar aromatics—material desorbed from calcined CG-20 alumina absorbent, after the saturates and naphthene aromatics
have been removed, using toluene and trichloroethylene eluants under the conditions specified.
3.1.5saturates—material that, on percolation in a petrolenes (also referred to as maltenes) —(1) any of the constituents of a
bitumen,asasphalt,thataresolublein n-heptaneeluant,isnotabsorbedoncalcinedCG-20aluminaabsorbentundertheconditions
specified.
METHOD
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.