ASTM D4161-01(2005)
(Specification)Standard Specification for "Fiberglass" (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting-Resin) Pipe Joints Using Flexible Elastomeric Seals
Standard Specification for "Fiberglass" (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting-Resin) Pipe Joints Using Flexible Elastomeric Seals
ABSTRACT
This specification covers axially unrestrained bell-and-spigot gasket joints including couplings required for machine-made "fiberglass" (glass-fiber-reinforced thermosetting-resin) pipe systems, 8 in. (200 mm) through 144 in. (3700 mm), using flexible elastomeric seals to obtain soundness. The pipe systems may be pressure or nonpressure systems for water or for chemicals or gases that are not deleterious to the materials specified in this specification. The gasket shall be a continuous elastomeric ring of circular or other geometric cross section and shall meet the prescribed specifications. The gasket shall be subject to vacuum or external pressure test and shear loading test.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers axially unrestrained bell-and-spigot gasket joints including couplings required for machine-made "fiberglass" (glass-fiber-reinforced thermosetting-resin) pipe systems, 8 in. (200 mm) through 144 in. (3700 mm), using flexible elastomeric seals to obtain soundness. The pipe systems may be pressure (typically up to 250 psi) or nonpressure systems for water or for chemicals or gases that are not deleterious to the materials specified in this specification. This specification covers materials, dimensions, test requirements, and methods of test.
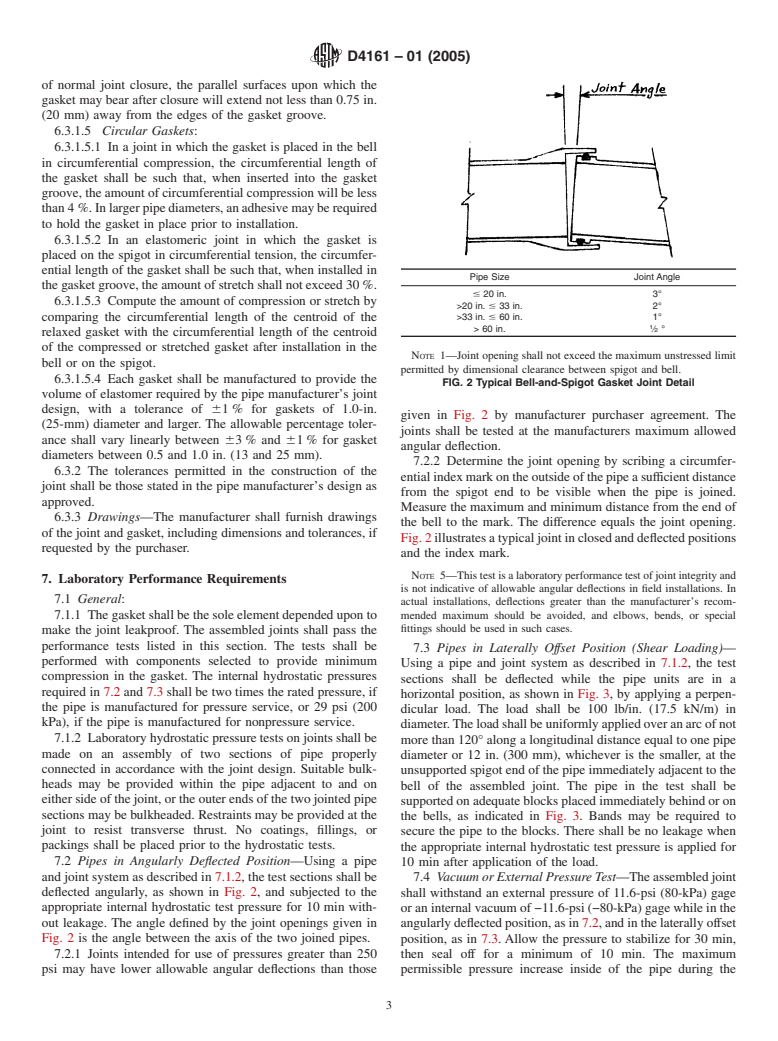
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only. Note 1There is a similar but technically different ISO Standard (ISO 8639).
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D4161 – 01 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Specification for
“Fiberglass” (Glass-Fiber-Reinforced Thermosetting-Resin)
,
1 2
Pipe Joints Using Flexible Elastomeric Seals
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4161; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This specification covers axially unrestrained bell-and- 3.1 Definitions:
spigot gasket joints including couplings required for machine- 3.1.1 General—Definitions and abbreviations are in accor-
made “fiberglass” (glass-fiber-reinforced thermosetting-resin) dance with Terminology D883 or Terminology F412, and
pipesystems,8in.(200mm)through144in.(3700mm),using Terminology D1600 unless otherwise indicated.
flexible elastomeric seals to obtain soundness. The pipe sys-
4. Types of Joints
tems may be pressure (typically up to 250 psi) or nonpressure
systems for water or for chemicals or gases that are not 4.1 This specification covers two types of axially unre-
strained joints based on effecting soundness of the joint
deleterious to the materials specified in this specification. This
specification covers materials, dimensions, test requirements, through compression of an elastomeric seal or ring:
4.1.1 Bell-and-spigot or coupling joint with the gasket
and methods of test.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded placed in the bell in circumferential compression. An elasto-
meric gasket joint design featuring a continuous elastomeric
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
for information purposes only. ring gasket placed in an annular space provided in the bell or
socketofthepipeorfitting.Thespigotendofthepipeorfitting
NOTE 1—ThereisasimilarbuttechnicallydifferentISOStandard(ISO
is forced into the bell, thereby compressing the gasket radially
8639).
to form a positive seal.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1.2 Bell-and-spigot or coupling joint with the gasket
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
placedonthespigotincircumferentialtension:Apushonjoint
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
designfeaturingacontinuouselastomericringgasketplacedin
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
an annular space provided on the spigot end of the pipe or
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
fitting. The spigot is forced into the bell of the pipe or fitting,
therebycompressingthegasketradiallytoformapositiveseal.
2. Referenced Documents
NOTE 2—A coupling joint of these types is a loose double-bell sleeve
2.1 ASTM Standards:
used to connect pipes which have spigots at both ends (see Fig. 1). All
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
references to bells in this specification are applicable to the sleeve
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
coupling as well as to the integral bell of a bell-and-spigot gasket joint.
Plastics
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
5. Materials and Manufacture
F477 SpecificationforElastomericSeals(Gaskets)forJoin-
5.1 The gasket shall be a continuous elastomeric ring of
ing Plastic Pipe
circular or other geometric cross section and shall meet the
requirements of Specification F477, unless otherwise specified
in this specification. When a splice is used in the manufacture
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
of the gasket, no more than two splices shall be made in any
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.23 on Reinforced
one gasket.
Plastic Piping Systems and Chemical Equipment.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2005. Published November 2005. Originally
5.1.1 The chemical composition of the gasket shall be
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D4161–01. DOI:
compatible with the type of environment to which it will be
10.1520/D4161-01R05.
subjected. Selection of the gasket composition shall be in
An ISO equivalency statement was added.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or accordance with a purchaser and seller agreement.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
NOTE 3—Consult the gasket manufacturer for advice as to the suitabil-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. ity of specific rubber compounds for the intended service and joint
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D4161 – 01 (2005)
spigot, shall not be less than the design volume of the gasket
furnished. For a rectangular gasket groove, the cross-sectional
area of annular space shall be calculated for minimum bell
inside diameter, maximum spigot outside diameter, minimum
width of groove at surface of spigot, and minimum depth of
groove. The volume of the annular space shall be calculated at
thecenterlineofthegrooveandconsideringthecentroidofthe
cross-sectional area to be at the midpoint between the surface
of the groove on which the gasket is seated and the surface of
the bell, if the groove is on the spigot, or the surface of the
spigot, if the groove is in the bell.
6.3.1.2 When the design volume of the gasket is less than
75% of the volume of the annular space in which the gasket is
confined,thedimensionsandtolerancesofthegasket,bell,and
spigot shall be such that, when the outer surface of the spigot
and the inner surface of the bell come into contact at some
FIG. 1 Typical Coupling Joint Detail
point in their periphery, the deformation in the gasket shall not
exceed40%atthepointofcontactnorbelessthan15%atany
point.Ifthedesignvolumeofthegasketis75%ormoreofthe
configurations. Items such as cold set when the joint is deflected under
volume of the annular space, the deformation of the gasket, as
low-temperature conditions and maximum and minimum stretch in the
prescribedabove,shallnotexceed50%norbelessthan15%.
gasket may be dependent upon the specific chemical compounds used.
The cross-sectional area of annular space shall be calculated
5.2 Materials in the bell and spigot of the joint shall meet
for average bell diameter, average spigot diameter, average
the requirements of the applicableASTM specification for the
width of groove at surface of spigot, and average depth of
pipe or fitting of which the joint is a part.
groove. The volume of the annular space shall be calculated at
thecenterlineofthegrooveandconsideringthecentroidofthe
6. Requirements Requirements
cross-sectional area to be at the midpoint between the surface
6.1 Joint Surfaces—Allsurfacesofthejointuponoragainst
of the groove on which the gasket is seated and the surface of
which the gasket may bear shall be smooth and free of cracks,
the bell, if the groove is on the spigot, or the surface of the
fractures,orotherimperfectionsthatwouldadverselyaffectthe
spigot, if the groove is in the bell.
performance of the joint.
NOTE 4—It is recognized that a relationship exists between the water-
6.2 Joint Geometry—The design of the joint shall include a
tightnessofajoint,thegasketdeformation,andtheratioofgasketvolume
means to retain the gasket and prevent it from being uninten-
to space volume. For high-pressure applications, it may be necessary to
tionallydisplaced,eitherduringassemblyofthejointorduring
provide a very high-volume ratio to obtain a sound joint. Some manufac-
operation of the completed pipe system. turers also have developed satisfactory joints with very little gasket
deformation, but meet the requirements of Section 6 by utilizing a very
6.3 Dimensions and Tolerances—The provisions of 6.3.1.1
high-volume ratio.
apply only to a joining system utilizing a gasket of circular
cross section retained in a rectangular groove. Manufacturers 6.3.1.3 When determining the maximum percent deforma-
maysubmittothepurchaserdetaileddesignsforjointsutilizing tion of the gasket, the minimum depth of groove and the
gaskets or grooves, or both, of other geometric shape or for stretched gasket diameter shall be used and calculations made
joints not meeting the criteria of 6.3.1. Joints not meeting the at the centerline of the groove. When determining the mini-
requirements of this section shall meet the test requirements of mum percent deformation of the gasket, the maximum bell
Section 7; such joints shall be acceptable, provided the design
diameter,theminimumspigotdiameter,themaximumdepthof
isapprovedbythepurchaserpriortomanufactureandprovided groove, and the stretched gasket diameter shall be used and
thetestpipecomplieswiththespecifiedtestrequirements.Test
calculations made at the centerline of the groove. For gasket
results may be extended to other diameters with the same joint deformation calculations, if the gasket is placed on the spigot
configuration, gasket shape and gasket composition provided in circumferential tension, the stretched gasket diameter shall
substantially similar gasket compressions and gasket hardness be determined as being the design diameter of the gasket
are maint
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.