ASTM D8378/D8378M-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Potential Expansion of Steel Slag from Hydration Reactions by Autoclave
Standard Test Method for Potential Expansion of Steel Slag from Hydration Reactions by Autoclave
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method provides a procedure for determining the compliance of steel slags and other materials with specifications or applications that limit permissible expansion of base and subbase aggregates containing components subject to hydration.
4.2 This test method can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of aging or other treatments for reducing the expansive potential of such materials.
4.3 This test method is utilized for dense graded materials passing a 25.0 mm (1 in.) sieve. If it is desired to investigate materials larger than a 25.0 mm (1 in.) sieve, Indiana Test Method ITM 219 should be considered.
4.4 Test results have not been correlated with field performance, and values obtained do not necessarily indicate expansion that may occur in service conditions. The various methods will provide different numerical results due to differences in severity of the procedures.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of potential volume expansion of steel slags that contain components susceptible to hydration and consequent volume increase, such as the free calcium and magnesium oxides.
1.1.1 This method is based upon the Cement Autoclave procedure, Test Method C151/C151M, and the California Bearing Ratio procedure, Test Method D1883. This is an aggressive test that can detect both calcium and magnesium expansion potentials. The procedure is also a rapid method typically completed within 24 h.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the standard.
Note 1: Sieve size is identified by its standard designation in Specification E11. The alternative designation given in parentheses is for information only and does not represent a different standard sieve size.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D8378/D8378M − 21
Standard Test Method for
Potential Expansion of Steel Slag from Hydration Reactions
1
by Autoclave
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D8378/D8378M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of potential
volume expansion of steel slags that contain components C29/C29M Test Method for Bulk Density (“Unit Weight”)
and Voids in Aggregate
susceptible to hydration and consequent volume increase, such
as the free calcium and magnesium oxides. C151/C151M Test Method for Autoclave Expansion of Hy-
draulic Cement
1.1.1 This method is based upon the Cement Autoclave
procedure, Test Method C151/C151M, and the California C702/C702M Practice for Reducing Samples of Aggregate
to Testing Size
Bearing Ratio procedure, Test Method D1883. This is an
aggressive test that can detect both calcium and magnesium C1005 Specification for Reference Masses and Devices for
DeterminingMassandVolumeforUseinPhysicalTesting
expansion potentials. The procedure is also a rapid method
typically completed within 24 h. of Hydraulic Cements
D75/D75M Practice for Sampling Aggregates
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
D1883 Test Method for California Bearing Ratio (CBR) of
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
Laboratory-Compacted Soils
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
D4792/D4792M Test Method for Potential Expansion of
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
Aggregates from Hydration Reactions
values from the two systems may result in nonconformance
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test
with the standard.
Sieves
3
NOTE 1—Sieve size is identified by its standard designation in Speci-
2.2 Other Standard:
fication E11. The alternative designation given in parentheses is for
Indiana Test Method ITM 219 Acceptance Procedures of
information only and does not represent a different standard sieve size.
Steel Furnace Slag for Deleterious Materials
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 3. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
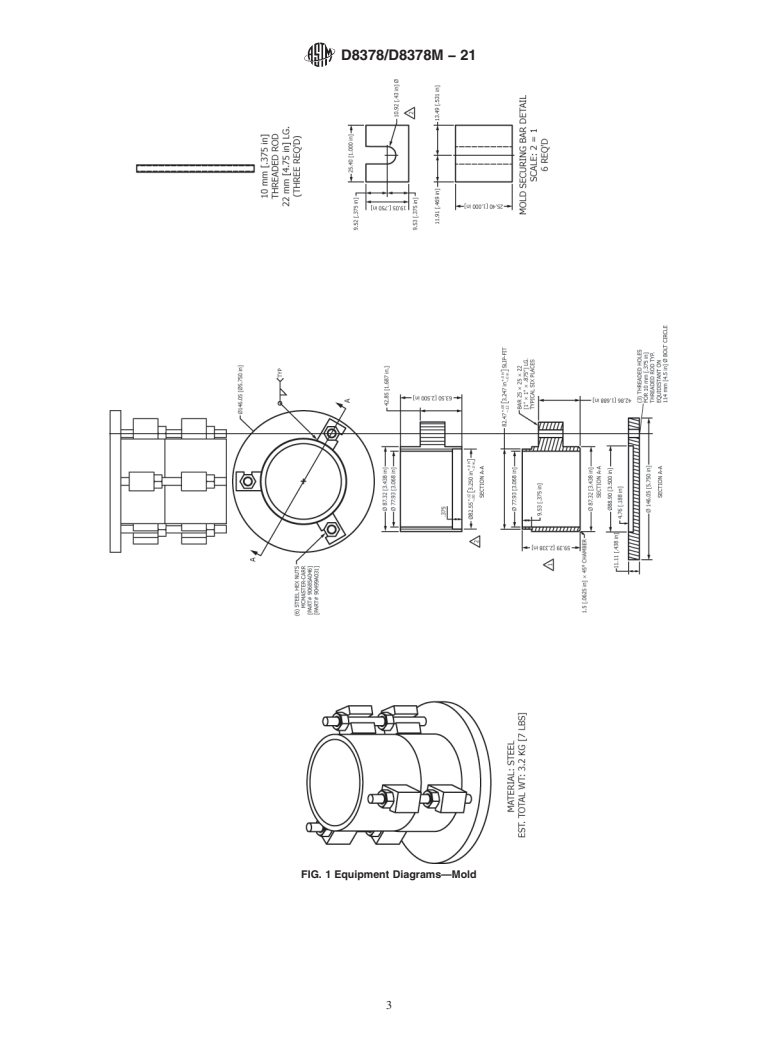
3.1 This test method consists of measuring the volume
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
expansion of compacted specimens following the autoclave
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
procedures of Test Method C151/C151M. The method utilizes
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
a mold similar to the one used in Test Method D1883, with the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
exceptionofitbeingproportionallysmallerinordertofitinthe
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
autoclave. This method is severe due to the high temperatures
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
and pressure. This method detects periclase (MgO) hydration
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
reactions that may not appear during some water bath
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
procedures, such as Test Method D4792/D4792M. As a result,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.51 on Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Aggregate Tests. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2021. Published January 2021. DOI: 10.1520/ Available from Indiana Department of Transportation, https://www.in.gov/
D8378_D8378M-21. indot/div/mt/itm/pubs/219_testing.pdf.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D8378/D8378M − 21
the numerical results obtained by this method tend to be higher [295 psi] to less than 0.07 MPa [10 psi] in 1.5 h after the heat
than those obtained by other methods. When used for supply has been shut off.
acceptance/rejection, this method should be correlated to the
5.5 Rupture Disk—The rupture disk shall be made of a
spe
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.