ASTM D5575-07
(Specification)Standard Classification System for Copolymers of Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) with Other Fluorinated Monomers
Standard Classification System for Copolymers of Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) with Other Fluorinated Monomers
ABSTRACT
This classification system covers both developing property designations and specifications for thermoplastic compositions consisting of vinylidene fluoride (VDF) polymers modified with other fluoromonomers and property-enhancing additives. Four property codes are presented: code 1 - melt temperature, code 2 - melt-flow rate or melt viscosity, or both, code 3 - tensile strength and modulus, and code 5 - density. The melt temperatures, melt-flow rate, melt viscosity, tensile properties, specific gravity, volume resistivity, dielectric constant, dissipation factor, and limiting oxygen index shall be tested to meet the requirements prescribed.
SCOPE
1.1 This classification system covers both developing property designations and specifications for thermoplastic compositions consisting of vinylidene fluoride (VDF) polymers modified with other fluoromonomers and property-enhancing additives. The other fluoromonomers include one or more of the following: hexafluoropropylene (HFP), tetrafluoroethylene (TFE), and chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE). The additives are those that improve its flame resistance, processing, or physical properties. However, these additives are not normally considered to be reinforcing. This classification system covers thermoplastic compositions supplied in pellet or powder forms.
1.2 A designation or specification applies only to the virgin polymers prepared from vinylidene fluoride (>50 weight %) with one or more of the following comonomers: hexafluoropropylene, tetrafluoroethylene, and chlorotrifluoroethylene. Some polymers contain additives to enhance certain properties.
1.3 This system constitutes a line callout as a means of designating and specifying properties of VDF-based copolymers. At least four of the designated properties are used to define a polymer's specification. Specification criteria from international documents can be used if their criteria match designation properties currently used by this classification system. This classification system is not intended for the selection of materials.
1.4 The manufacturer of the virgin resin shall establish the designation of a resin based on the property value criteria in this classification system.
1.5 The minimum specification properties are established by this classification system. Additional specification properties, based on the designation properties cited, can be established by the resin supplier and customer.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.7 The property tests are intended to provide information for specifications of modified VDF-copolymer compositions. It is not the purpose of this classification system to provide engineering data for design purposes.Note 1
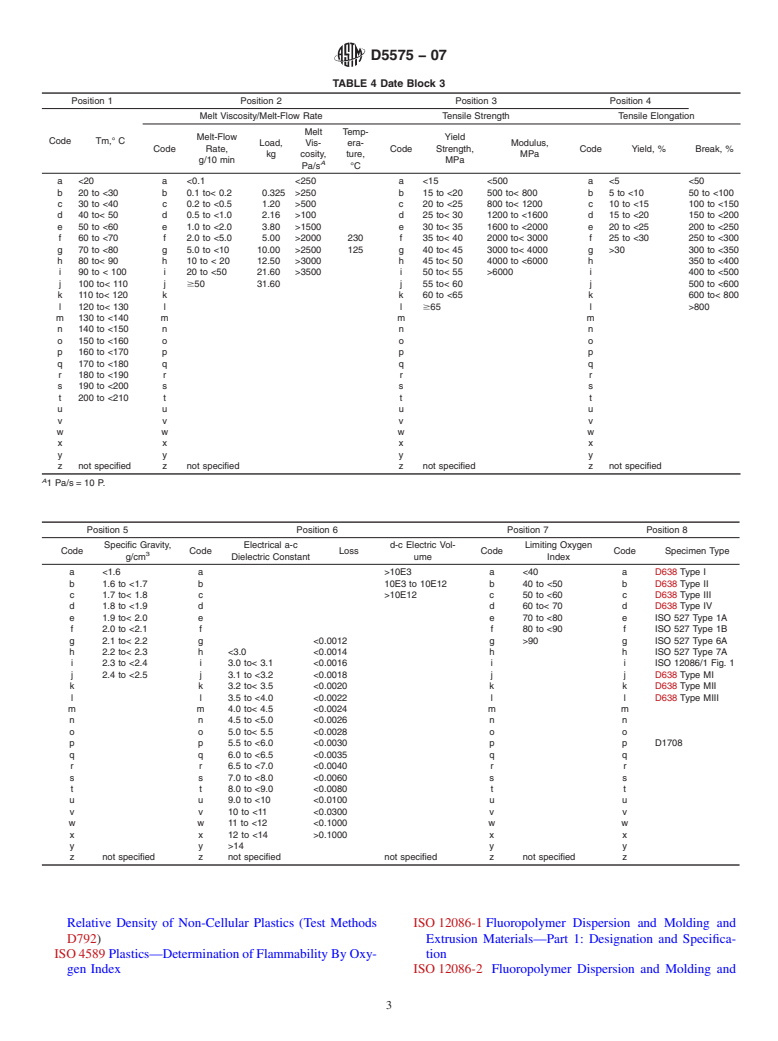
Although the values listed in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 are necessary to include the range of properties available in existing materials, they are not to be interpreted as implying that every possible combination of the properties exists or can be obtained. It is possible for a user or designer, using , to call out property relationships that are physically impossible to occur in a copolymer made using current technology.Note 2
Many of these polymers exhibit polymorphism. The type and extent of crystalline structure will vary with the thermomechanical history of the sample. Properties vary based on the technique used to prepare the specimens.
1.8 Test methods used in this classification system can result in the incidental production of hazardous materials. Modified VDF polymer fluoroplastics melt between 90 and 182°C (194 and 359°F) and are thermally stable up to about 350&%176;C (662°F), or somewhat higher, depending on the composition. (Evolution of corrosive, colorless, and toxic hydrogen fluoride can occur under certain conditions.)
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish ap...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5575 −07
StandardClassification System for
Copolymers of Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) with Other
1
Fluorinated Monomers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5575; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.5 Theminimumspecificationpropertiesareestablishedby
this classification system. Additional specification properties,
1.1 This classification system covers both developing prop-
basedonthedesignationpropertiescited,canbeestablishedby
erty designations and specifications for thermoplastic compo-
the resin supplier and customer.
sitions consisting of vinylidene fluoride (VDF) polymers
modified with other fluoromonomers and property-enhancing 1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
additives. The other fluoromonomers include one or more of standard.
the following: hexafluoropropylene (HFP), tetrafluoroethylene
1.7 The property tests are intended to provide information
(TFE), and chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE). The additives are
forspecificationsofmodifiedVDF-copolymercompositions.It
those that improve its flame resistance, processing, or physical
is not the purpose of this classification system to provide
properties. However, these additives are not normally consid-
engineering data for design purposes.
ered to be reinforcing. This classification system covers ther-
NOTE 1—Although the values listed in Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table
moplastic compositions supplied in pellet or powder forms.
4, and Table are necessary to include the range of properties available in
1.2 Adesignation or specification applies only to the virgin
existing materials, they are not to be interpreted as implying that every
possible combination of the properties exists or can be obtained. It is
polymers prepared from vinylidene fluoride (>50 weight %)
possible for a user or designer, using Tables 1-, to call out property
with one or more of the following comonomers:
relationships that are physically impossible to occur in a copolymer made
hexafluoropropylene, tetrafluoroethylene, and chlorotrifluoro-
using current technology.
ethylene. Some polymers contain additives to enhance certain 3
NOTE2—Manyofthesepolymersexhibitpolymorphism. Thetypeand
properties.
extentofcrystallinestructurewillvarywiththethermomechanicalhistory
of the sample. Properties vary based on the technique used to prepare the
1.3 This system constitutes a line callout as a means of
specimens.
designating and specifying properties of VDF-based copoly-
1.8 Testmethodsusedinthisclassificationsystemcanresult
mers. At least four of the designated properties are used to
in the incidental production of hazardous materials. Modified
define a polymer’s specification. Specification criteria from
VDF polymer fluoroplastics melt between 90 and 182°C (194
international documents can be used if their criteria match
and359°F)andarethermallystableuptoabout350°C(662°F),
designation properties currently used by this classification
2
or somewhat higher, depending on the composition.
system. This classification system is not intended for the
(Warning— Evolution of corrosive, colorless, and toxic hy-
selection of materials.
drogen fluoride can occur under certain conditions.)
1.4 The manufacturer of the virgin resin shall establish the
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
designation of a resin based on the property value criteria in
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
this classification system.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1
ThisclassificationsystemisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20on
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.SeeWarning in1.8
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials.
and Section 10 for specific hazards statements.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2007. Published November 2007. Originally
NOTE 3—Many, but not all of the codes and specifications found in this
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D5575-99(2003).
This standard is needed to cover commercial products outside the scope of classification system are also in ISO12086-1 and ISO12086-2.
Specification D3222. DOI: 10.1520/D5575-07.
2
Fluoropolymer property specification data from international standards can
include properties intentionally excluded from this classification system (for
3
example,composition).Theonlypropertycriteriafromotherdocumentsthatcanbe Lovinger, A. J., “Poly(vinylidene fluoride),” Developments in Crystalline
used are those having similar properties a
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5575–99 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Specification for Designation: D 5575 – 07
Standard Classification System for
Copolymers of Vinylidene Fluoride (VDF) with Other
1
Fluorinated Monomers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5575; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification classification system covers both developing property designations and specifications for thermoplastic
compositions consisting of vinylidene fluoride (VDF) polymers modified with other fluoromonomers and property-enhancing
additives.Theotherfluoromonomersincludeoneormoreofthefollowing:hexafluoropropylene(HFP),tetrafluoroethylene(TFE),
and chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE). The additives are those that improve its flame resistance, processing, or physical properties.
However, these additives are not normally considered to be reinforcing. This specification classification system covers
thermoplastic compositions supplied in pellet or powder forms.
1.2 Adesignation or specification applies only to the virgin polymers prepared from vinylidene fluoride (>50 weight %) with
one or more of the following comonomers: hexafluoropropylene, tetrafluoroethylene, and chlorotrifluoroethylene. TheseSome
polymers may contain additives to enhance certain properties.
1.3 ThissystemconstitutesalinecalloutasameansofdesignatingandspecifyingpropertiesofVDF-basedcopolymers.Atleast
four of the designated properties are used to define a polymer’s specification. Specification criteria from international documents
2
can be used if their criteria match designation properties currently used by this specification.classification system. This
specification classification system is not intended for the selection of materials.
1.4 The manufacturer of the virgin resin shall establish the designation of a resin based on the property value criteria in this
specification. classification system.
1.5 The minimum specification properties are established by this specification. classification system. Additional specification
properties, based on the designation properties cited, can be established by the resin supplier and customer.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard and the practices of IEEE/ASTMSI–10 incorporated herein,
except where common usage or test method specify common units acceptable within IEEE/ASTMSI–10.standard.
1.7 ThepropertytestsareintendedtoprovideinformationforspecificationsofmodifiedVDF-copolymercompositions.Itisnot
the purpose of this specificationclassification system to provide engineering data for design purposes.
NOTE 1—Although the values listed inTable 1,Table 2,Table 3,Table 4,Table 5 are necessary to include the range of properties available in existing
materials, they shouldare not to be interpreted as implying that every possible combination of the properties exists or can be obtained. It is possible for
a user or designer, using Tables 1-5, to call out property relationships that are physically impossible to occur in a copolymer made using current
technology.
3
NOTE 2—Many of these polymers exhibit polymorphism. The type and extent of crystalline structure can vary with the thermomechanical history of
the sample. Specimens prepared by different techniques could have properties that may vary. The type and extent of crystalline structure will vary with
the thermomechanical history of the sample. Properties vary based on the technique used to prepare the specimens.
1.8 Testmethodsusedinthisspecificationmayinvolveclassificationsystemcanresultintheincidentalproductionofhazardous
materials.ModifiedVDFpolymerfluoroplasticsmeltbetween90and182°C(194and359°F)andarethermallystableuptoabout
350°C (662°F), or somewhat higher, depending on the composition. (Warning—Evolution of corrosive, colorless, and toxic
hydrogen fluoride can occur under certain conditions.)
1
This specification classification system is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on
Thermoplastic Materials .
Current edition approved NovemberNov. 1, 2003.2007. Published December 2003.November 2007. Originally approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in
19992003 as D5575-99(2003).
This standard is needed to cover commercial products outside the scope of Specification D3222.
2
Fluoropolymer prop
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.