ASTM F543-98
(Specification)Standard Specification and Test Methods for Metallic Medical Bone Screws
Standard Specification and Test Methods for Metallic Medical Bone Screws
SCOPE
1.1 This specification provides requirements for materials, finish and marking, care and handling, and the acceptable dimensions and tolerances for metallic bone screws that are implanted into bone. The dimensions and tolerances in this specification are applicable only to metallic bone screws described in this specification.
1.2 This specification provides performance considerations and standard test methods for measuring mechanical properties in torsion of metallic bone screws that are implanted into bone. These test methods may also be applicable to other screws besides those whose dimensions and tolerances are specified here. The following annexes are included:
1.2.1 Annex A1—Test Method for Determining the Torsional Properties of Metallic Bone Screws.
1.2.2 Annex A2—Test Method for Driving Torque of Medical Bone Screws.
1.2.3 Annex A3—Test Method for Determining the Axial Pullout Strength of Medical Bone Screws.
1.2.4 Annex A4—Specifications for Type HA and Type HB Metallic Bone Screws.
1.2.5 Annex A5—Specifications for Type HC and Type HD Metallic Bone Screws.
1.2.6 Annex A6—Specifications for Metallic Bone Screw Drive Connections.
1.3 This specification is based, in part, upon ISO 5835, ISO 6475, and ISO 9268.
1.4 Unless otherwise indicated, the values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are given for information only.
1.5 This standard may involve the use of hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 543 – 98
Standard Specification for
Metallic Medical Bone Screws
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 543; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope plants and Instruments
F 620 Specification for Titanium 6Al-4V ELl Alloy Forg-
1.1 This specification provides requirements for materials,
ings for Surgical Implants
finish and marking, care and handling, and some dimensions
F 799 Specification for Cobalt-28 Chromium-6 Molybde-
and tolerances for metallic bone screws which are implanted
num Alloy Forgings for Surgical Implants
into bone. The dimensions and tolerances in this specification
F 983 Practice for Permanent Marking of Orthopedic Im-
are applicable only to metallic bone screws with a spherical
plant Components
head, hexagonal driving slot, and a solid core.
F 1295 Specification for Wrought Titanium-6 Aluminum-7
1.2 This specification is based, in part, upon ISO 5835.
Niobium Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications [UNS
1.3 Unless otherwise indicated, the values stated in SI units
R56700]
are to be regarded as standard. The values in parentheses are
F 1314 Specification for Wrought Nitrogen Strengthened-2
given for information only.
Chromium-12.5 Nickel-5 Manganese-2.5 Molybdenum
1.4 This standard may involve the use of hazardous mate-
Stainless Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical Implants
rials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not
F 1472 Specification for Wrought Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Sur-
purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated
gical Implant Applications
with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard
F 1537 Specification for Wrought Cobalt-28 Chromium-6
to establish appropriate safety and health practices and
Molybdenum Alloy for Surgical Implants
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to
F 1586 Specification for Wrought Nitrogen
use.
Strengthened-21 Chromium-10 Nickel-3 Manganese-2.5
2. Referenced Documents Molybdenum Stainless Steel Bar for Surgical Implants
F 1622 Test Method for Measuring the Torsional Properties
2.1 ASTM Standards:
in Metallic Bone Screws
F 67 Specification for Unalloyed Titanium for Surgical
F 1691 Test Method for Determining the Axial Pull-Out
Implant Applications
Strength of Medical Bone Screws
F 116 Specification for Medical Screwdriver Bits
F 1713 Specification for Wrought Titanium 13 Niobium-13
F 117 Test Method for Driving Torque of Medical Bone
Zirconium Alloy for Surgical Implant Applications
Screws
F 1813 Specification for Wrought Titanium-12
F 86 Practice for Surface Preparation and Marking of Me-
Molybdenum-6 Zirconium-2 Iron Alloy for Surgical Im-
tallic Surgical Implants
plant Applications
F 136 Specification for Wrought Titanium 6 Aluminum-4
2.2 ISO Standard:
Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) Alloy (R56401) for
5835 Implants for Surgery–Metal Bone Screws with Hex-
Surgical Implant Applications
agonal Driver Connection, Spherical Under Surface of
F 138 Specification for Wrought 18 Chromium-14 Nickel-
Head, Asymmetrical Thread–Dimensions
2.5 Molybdenum Stainless Steel Bar and Wire for Surgical
Implants (UNS S31673)
3. Terminology
F 543 Specification for Cortical Bone Screws
3.1 Definitions—Some of the terms defined in this section
F 544 Reference Chart for Pictorial Cortical Bone Screw
are shown in Fig. 1.
Classification
3.1.1 buttress thread—an asymmetrical thread profile char-
F 565 Practice for Care and Handling of Orthopedic Im-
acterized by a pressure flank which is nearly perpendicular to
the screw axis.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-4 on Medical
3.1.2 cancellous screw—a screw designed primarily to gain
and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F04.21 on Osteosynthesis.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1998. Published March 1999. Originally
published as F 543 – 77. Last previous edition F 543 – 92. Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 W. 42nd St., 13th
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 13.01. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 543
form compatible with the screw’s thread form upon the screw’s
insertion into the bone.
3.1.16 size—an identification of a screw based on its nomi-
nal thread diameter. For HA and HB screws whose dimensions
are included in this specification, the size is provided in Section
3.1.17 solid core—a screw which does not contain a can-
nulation along its longitudinal axis.
3.1.18 spherical head screw—a screw whose head has a
constant radius along its undersurface which makes contact
with the bone or a plate. This is shown as the bottom head
radius, r , Fig. 2 and Fig. 4. All screws whose dimensions are
FIG. 1 Schematic of Screw Terms
defined in this specification (Type HA and HB) have a screw
head with a spherical undersurface.
purchase into cancellous bone. A class of cancellous screws
3.1.19 thread diameter—the largest diameter of the
included in this specification are the HB-type screws given in
threaded portion of the screw measured over the thread crests.
4.1.2. Cancellous screws may or may not be fully threaded.
This is also known as the major diameter.
3.1.3 cannulated screw—a screw which has a through hole
3.1.20 thread length—the length of the threaded portion of
drilled along the entire length of its longitudinal axis. Cannu-
the screw, measured from the thread runout to the screw tip.
lated screws are often inserted into the bone over a guide pin.
3.1.21 thread runout—the intersection of the screw thread
3.1.4 conical head screw—a screw whose head has a
with either the screw shaft or screw head.
conical undersurface which makes contact with the bone or a
4. Classification
plate.
4.1 There are a large variety of medical bone screws
3.1.5 core diameter—the smallest diameter of the threaded
currently in use. They may be classified by the definitions
portion of the screw measured at the thread root. This is also
provided in Section 3. This specification provides dimensions
known as the minor diameter or root diameter.
and tolerances for the following types of screws:
3.1.6 cortical screw—a screw designed primarily to gain
4.1.1 Type HA—Shallow, asymmetrical buttress thread and
bicortical purchase into cortical bone. A class of cortical screws
deep screw head.
included in this specification are the HA-type screws given in
4.1.2 Type HB—Deep, asymmetrical buttress thread and
4.1.1. Cortical screws typically are fully threaded.
shallow screw head.
3.1.7 non-tapping screw—a screw which does not contain
any design features that act to produce the screw’s thread form
5. Dimensions and Tolerances
in the bone upon insertion. Non-tapping screws, by design,
5.1 There are many types of metallic bone screw designs
usually require a pre-tapped pilot hole for screw insertion.
available, so a complete list of dimensions and tolerances for
3.1.8 partially threaded screw—a screw whose threaded
all screws covered by this specification is unfeasible. However,
portion does not extend fully from the screw point to the screw
this specification does provide required dimensions and toler-
head, but instead has a smooth shaft running between the head
ances for 2 types of screws as classified in 4.1. Screws
and threads.
conforming to this specification, and designated as HA or HB
3.1.9 pilot hole—the hole drilled into the bone into which
screws, shall be fabricated in accordance with the dimensions
the screw tip is inserted. The pilot hole is normally slightly
and tolerances described as follows:
larger than the screw’s core diameter. However, if the screw is
5.1.1 Type HA:
to be used to provide compression across a fracture, a portion
5.1.1.1 Screw Dimensions—The dimensions of HA screws
of the pilot hole may be larger to allow for a clearance fit.
are given in Table 1 and Fig. 2.
3.1.10 pitch—the length between the thread crests.
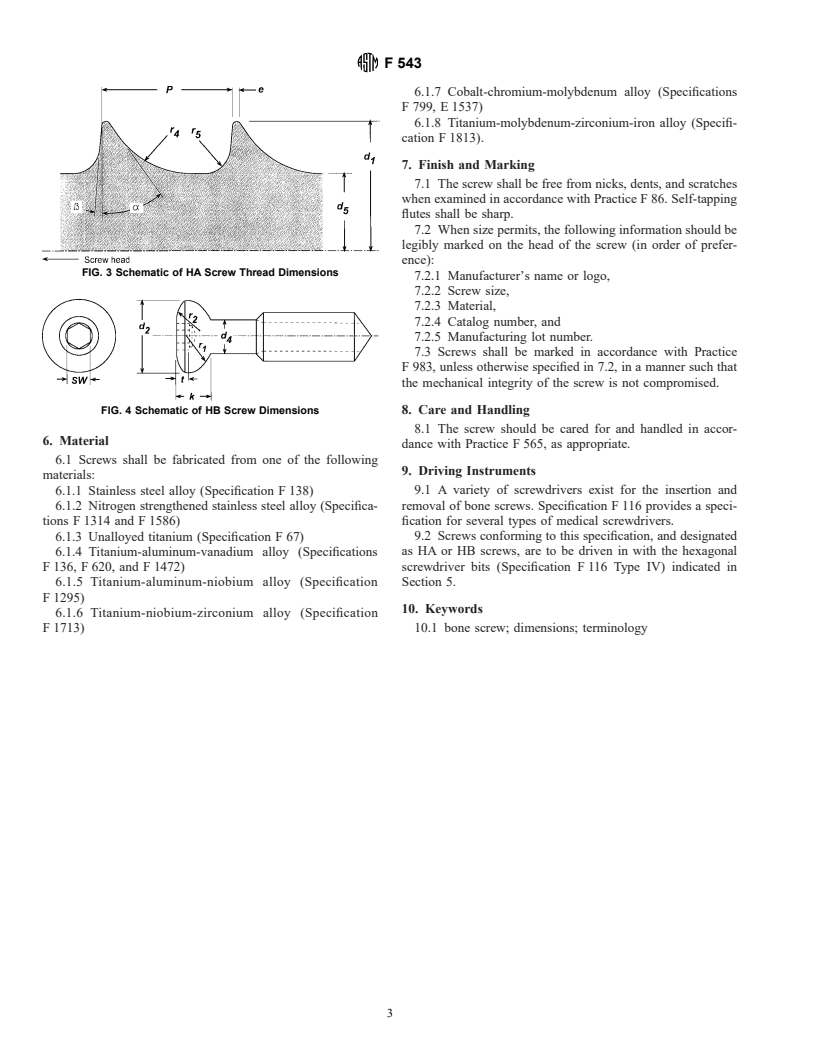
5.1.1.2 Screw Thread—The dimensions of the threads of
3.1.11 screw head—the end of the screw which is opposite
HA screws are given in Table 2 and Fig. 3.
of the tip, and from which the means of inserting the screw is
5.2 Type HB:
coupled.
5.2.1 Screw Dimensions—The dimensions of HB screws are
3.1.12 screw length—the overall length of t
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.