ASTM A1000-99
(Specification)Standard Specification for Steel Wire, Carbon and Alloy Specialty Spring Quality
Standard Specification for Steel Wire, Carbon and Alloy Specialty Spring Quality
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers a quality of round and shaped plain carbon and alloy steel spring wire, uniform in quality and temper, intended for the manufacture of mechanical springs that can withstand moderate fatigue stresses over some relatively low number of cycles. The quality level is between the commercial quality grades of wire such as Specifications A401, A231, and A229 and the valve spring quality grades such Specifications as A230, A232, A877 and A878. It is similar to the grade TD (referenced in EN 10270-2) intended for medium fatigue levels, such as required for clutch springs. This wire shall be either in the annealed and cold-drawn or oil-tempered condition as specified by purchaser.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in parentheses. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independent of the other.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: A 1000 – 99
Standard Specification for
Steel Wire, Carbon and Alloy Specialty Spring Quality
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 1000; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope A 878 Specification for Steel Wire, Modified Chrome-
Vanadium Valve Spring Quality
1.1 This specification covers a quality of round and shaped
A 941 Terminology Relating to Steel, Stainless Steel, Re-
plain carbon and alloy steel spring wire, uniform in quality and
lated Alloys, and Ferroalloys
temper, intended for the manufacture of mechanical springs
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
that can withstand moderate fatigue stresses over some rela-
Determine Conformance with Specifications
tively low number of cycles. The quality level is between the
E 45 Practice for Determining the Inclusion Content of
commercial quality grades of wire such as Specifications
Steel
A 401, A 231 and A 229 and the valve spring quality grades
2.2 Federal Standard:
such Specifications as A 230, A 232, A 877 and A 878. It is
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
similar to the grade TD (referenced in EN 10270-2) intended
2.3 Military Standard:
for medium fatigue levels, such as required for clutch springs.
MIL-STD-163 Steel Mill Products, Preparation for Ship-
This wire shall be either in the annealed and cold-drawn or
ment and Storage
oil-tempered condition as specified by purchaser.
2.4 AIAG Standard:
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
AIAG B-5 02.00 Primary Metals Identification Tag Appli-
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
cation Standard
inch-pound units are shown in parentheses. The values stated
2.5 European Standard:
in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each
EN 10270-2 Steel Wire for Mechanical Springs Part 2:
system must be used independent of the other.
Oil-Hardened and Tempered Springsteel Wire of Unal-
2. Referenced Documents loyed and Alloyed Steels
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3. Terminology
A 229 Specification for Steel Wire, Oil-Tempered for Me-
3.1 Definitions:
chanical Springs
3.1.1 For definition of terms used in this practice, see
A 230 Specification for Steel Wire, Oil-Tempered Carbon
Terminology A 941.
Valve Spring Quality
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
A 231 Specification for Chrome-Vanadium Alloy Steel
3.2.1 commercial quality wire—a grade of wire that is fairly
Spring Quality Wire
common quality and intended for applications that are prima-
A 232 Specification for Chrome-Vanadium Alloy Steel
rily static in nature, not involving significant fatigue loading.
Valve Spring Quality
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for MechanicalTesting
4. Ordering Information
of Steel Products
2 4.1 It shall be the responsibility of the purchaser to specify
A 401 Specification for Steel Wire, Chrome-Silicon Alloy
all requirements that are necessary for material under this
A 700 Practices for Packaging, Marking, and Loading
3 specification. Such requirements may include, but are not
Methods for Steel Products for Domestic Shipment
limited to the following,
A 751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for
4.1.1 Quantity (mass),
Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
A 877 Specification for Steel Wire, Chrome-Silicon Alloy
Valve Spring Quality
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
1 7
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A-1 on Steel, Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg 4 Section D. 700
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS
A01.03 on Steel Rod and Wire. Available from the Automotive Industry Action Group, 26200 Lasher, Suite
Current edition approved March 10, 1999. Published May 1999. 200, Southfield, MI 48034.
2 9
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03. Available from European Committee for Standardization, rue de Stassart
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.05. 36,B-1050 Brussels
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
A1000–99
4.1.2 Name of material (chromium-silicon alloy steel spe- 6.4 For referee purposes, Test Methods, Practices, and
cialty spring quality wire), Terminology A 751 shall be used.
4.1.3 Dimensions (Table 1 and Section 9)
7. Mechanical Properties
4.1.4 Condition (Section 7),
7.1 Annealed and Cold Drawn—When purchased in the
4.1.5 Packaging (Section 15),
annealed and cold-drawn condition, the wire shall have been
4.1.6 Heat analysis report, if requested (6.2),
given a sufficient amount of cold working to meet the purchas-
4.1.7 Certification or test report, or both, if specified (Sec-
er’s coiling requirements and shall be in a suitable condition to
tion 14), and
respond properly to heat treatment. In special cases the
4.1.8 ASTM designation and year of issue.
hardness, if desired, shall be stated in the purchase order.
NOTE 1—A typical ordering description is as follows: 20 000-kg
7.2 Oil Tempered:
oil-tempered chromium-silicon alloy steel specialty spring quality wire,
7.2.1 Tensile Strength and %RA, Round Wire—When pur-
size 6.00 mm in 1500-kg coils toASTM ___ dated ___, or for inch-pound
chased in the oil-tempered condition, the tensile strength and
units, 40 000-lb. oil-tempered chromium-silicon alloy steel specialty
minimum percent reduction in area of round wire, sizes 2.50
spring quality wire, size 0.250 in. in 3000-lb coils toASTM___dated ___.
mm (0.105 in.) and larger shall conform to the requirements
5. Materials and Manufacture
prescribed in Tables 3-6.
5.1 The steel may be made by any commercially accepted 7.2.2 Tensile Strength, Shaped and Flat Wire—Tensile
steel making process. The steel may be either ingot cast or strength of shaped and flat rolled wires shall conform to these
strand cast. tablesbasedontheconversiontoequivalentrounddimensions.
5.2 The finished wire shall be free from detrimental pipe Percent reduction of area is not applicable to shaped and flat
and undue segregation. rolled wires.
7.2.3 Tensile Strength Variation—In addition, the maximum
6. Chemical Composition
tensile variation in a coil shall be 70 Mpa (10 KSI).
6.1 Thesteelshallconformtotherequirementsforchemical
NOTE 2—Any specimen breaking in the tensile grips shall be discarded
composition specified in Table 2.
and a new specimen tested if the specified mechanical properties are not
6.2 Heat Analysis—Each heat of steel shall be analyzed by
achieved. If breakage in the tensile grips prevents conformance to percent
the manufacturer to determine the percentage of elements reductioninarearequirements,conformancetothewraptest(see7.3)shall
suffice.
prescribed in Table 2. This analysis shall be made from a test
specimen preferably taken during the pouring of the heat.
7.2.4 NumberofTests—Onetestspecimenshallbetakenfor
When requested, this shall be reported to the purchaser and
eachfivecoils,orfractionthereof,inalot.Eachheatinagiven
shall conform to the requirements of Table 2.
lot shall be tested.
6.3 Product Analysis—An analysis may be made by the
7.2.5 Location of Tests—Test specimens shall be taken for
purchaser from finished wire representing each heat of steel.
eachfivecoils,orfractionthereof,inalot.Eachheatinagiven
The average of all the separate determinations made shall be
lot shall be tested.
within the limits specified in the analysis column.
7.2.6 Test Method—The tension test shall be made in
accordance with Test Methods and Definitions A 370.
7.3 Wrap Test:
TABLE 1 Permissible Variations in Wire Dimensions (Round and
A
Shapes) 7.3.1 Round oil tempered wire 4.00 mm (0.156 in.) or
smaller in diameter shall wrap on itself as an arbor without
SI Units
Permissible Varia- Permissible Out-Of-
breakage. Larger diameter wire up to and including 8.00 mm
Dimension, mm
tions, 6 mm Round, mm
(0.312 in.) shall wrap without breakage on a mandrel twice the
0.5 to 2.0, incl 0.02 0.02
wire diameter.The wrap test is not applicable to wire over 8.00
Over 2.0 to 4.0, incl 0.03 0.03
Over 4.0 to 9.5, incl 0.04 0.04
mm (0.312 in.) in diameter or to shaped and flat rolled wires.
Over 9.5 0.05 0.05
7.3.2 The special high tensile chrome silicon vanadium
Inch-Pound Units
Permissible Varia- Permissible Out-Of- grade of round oil tempered wire 4.00 mm (0.156 in.) or
Dimension, in.
tions, 6 in. Round, in.
smaller in diameter shall wrap on a mandrel twice the diameter
0.020 to 0.075, incl 0.0008 0.0008
without breakage. Larger diameter wire up to and including
Over 0.075 to 0.148, incl 0.001 0.001
8.00 mm (0.312 in.) shall wrap without breakage on a mandrel
Over 0.148 to 0.375, incl 0.0015 0.0015
Over 0.375 0.002 0.002
threetimesthewirediameter.Thewraptestisnotapplicableto
A
Permissible Variations in Wire Dimensions (Flat Rolled)
wire over 8.00 mm (0.312 in.) in diameter or to shaped and flat
SI Units
rolled wires.
Thickness Width
Dimension, mm Permissible Varia- Permissible Varia-
7.3.3 Test Method—The wrap test shall be made in accor-
tions, 6 mm tions, mm
dance with Test Methods and Definitions A 370.
All 0.05 0.120
Inch-Pound Units
8. Metallurgical Requirements
Thickness Width
Dimension, in. Permissible Varia- Permissible Varia-
8.1 Surface Condition:
tions, 6 in. tions, in.
8.1.1 The surface of the wire as received shall be free of
All 0.002 0.005
A imperfections such as seams, pits, die marks, scratches, and
For purposes of determining conformance with this specification, all specified
limits are absolute as defined in Practice E 29. other surface defects that are deeper than 1 % of the wire
A1000–99
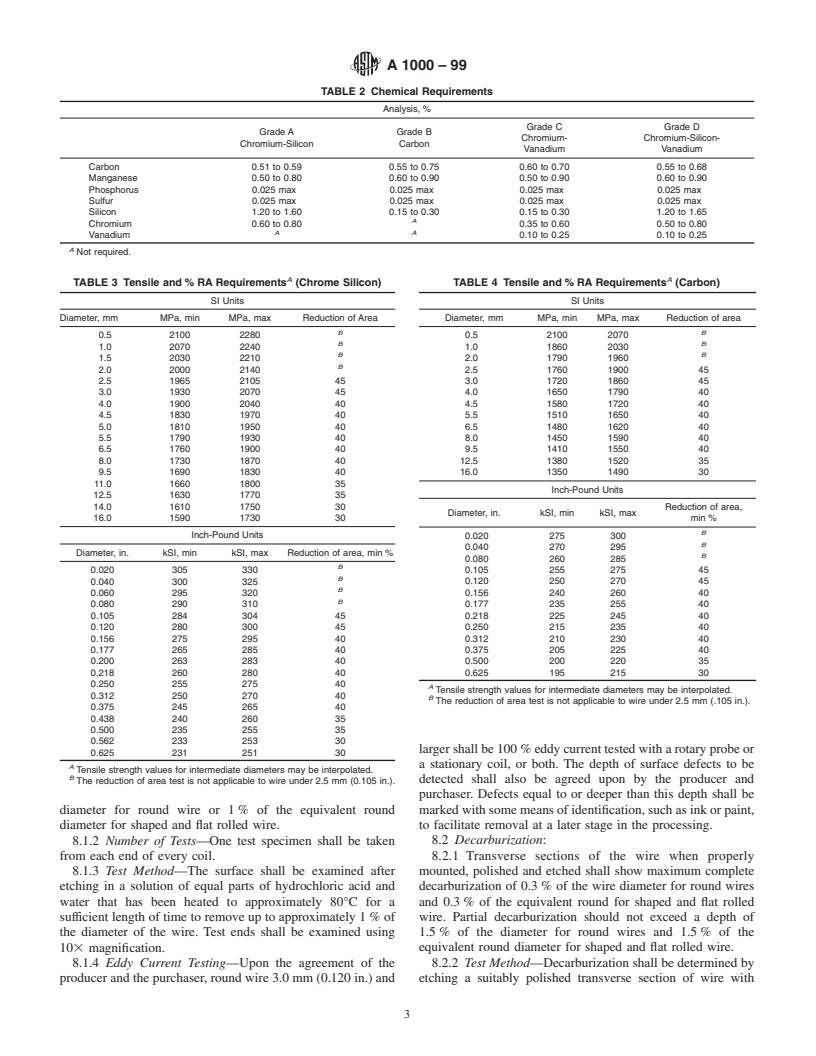
TABLE 2 Chemical Requirements
Analysis, %
Grade C Grade D
Grade A Grade B
Chromium- Chromium-Silicon-
Chromium-Silicon Carbon
Vanadium Vanadium
Carbon 0.51 to 0.59 0.55 to 0.75 0.60 to 0.70 0.55 to 0.68
Manganese 0.50 to 0.80 0.60 to 0.90 0.50 to 0.90 0.60 to 0.90
Phosphorus 0.025 max 0.025 max 0.025 max 0.025 max
Sulfur 0.025 max 0.025 max 0.025 max 0.025 max
Silicon 1.20 to 1.60 0.15 to 0.30 0.15 to 0.30 1.20 to 1.65
A
Chromium 0.60 to 0.80 0.35 to 0.60 0.50 to 0.80
AA
Vanadium 0.10 to 0.25 0.10 to 0.25
A
Not required.
A A
TABLE 3 Tensile and % RA Requirements (Chrome Silicon) TABLE 4 Tensile and % RA Requirements (Carbon)
SI Units SI Units
Diameter, mm MPa, min MPa, max Reduction of Area Diameter, mm MPa, min MPa, max Reduction of area
B B
0.5 2100 2280 0.5 2100 2070
B B
1.0 2070 2240 1.0 1860 2030
B B
1.5 2030 2210 2.0 1790 1960
B
2.0 2000 2140 2.5 1760 1900 45
2.5 1965 2105 45 3.0 1720 1860 45
3.0 1930 2070 45 4.0 1650 1790 40
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.