ASTM D6774-02(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Crimp and Shrinkage Properties for Textured Yarns Using a Dynamic Textured Yarn Tester (Withdrawn 2019)
Standard Test Method for Crimp and Shrinkage Properties for Textured Yarns Using a Dynamic Textured Yarn Tester (Withdrawn 2019)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Test Method D6774, for determining maximum total contraction, crimp, and residual fiber shrinkage in textured filament yarns is suitable for acceptance testing of commercial shipments.
If there are differences of practical significance between reported test results for two laboratories (or more), comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical assistance. As a minimum, use the samples for such a comparative tests that are as homogeneous as possible, drawn from the same lot of material as the samples that resulted in disparate results during initial testing and randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory. The test results from the laboratories involved should be compared using a statistical test for unpaired data, a probability level chosen prior to the testing series. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected, or future test results for that material must be adjusted in consideration of the known bias.
The properties and their variability as measured by this method relate to bulk appearance, stretch and recovery of fabrics and dyeability of yarns.
For some yarns, elapsed time between processing and testing has a marked effect on the results, of this test, especially during the first 72 h. The effect is caused by stress decay which is known to be minimal beyond the seventh day and after which time the yarn remains relatively stable. Therefore, specimens should only be compared if tested after the same elapsed time. Samples can be tested at-line, thus having little to no elapsed time between processing and testing.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of crimp contraction, residual fiber shrinkage and their variability of all types of filament yarns (partially oriented yarn (POY), fully oriented yarn (FOY), flat yarns, textured and bulked continuous filament (BCF) carpet yarns) using an automated tester.
Note 1—For another method of testing crimp in textured yarns, refer to Test Method D4031.
1.1.1 This method may also be used for non-textured yarns.
1.2 This test method is limited to crimped, multi-filament yarns ranging from 22.0 to 890 dtex (15 to 800 denier) and for BCF yarns from 890 to 4200 dtex (800 to 3800 denier).
1.3 The values stated in either SI or US customary units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the U.S. customary units are in parentheses. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the method.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6774 − 02 (Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
Crimp and Shrinkage Properties for Textured Yarns Using a
1
Dynamic Textured Yarn Tester
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6774; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of textile terms in this test method, refer
1.1 This test method covers the determination of crimp
to Terminology D4849. For other textile terms used in this test
contraction, residual fiber shrinkage and their variability of all
method, refer to Terminology D123.
types of filament yarns (partially oriented yarn (POY), fully
oriented yarn (FOY), flat yarns, textured and bulked continu-
4. Summary of Test Method
ous filament (BCF) carpet yarns) using an automated tester.
4.1 The specimen passes through a pretension device to
NOTE1—Foranothermethodoftestingcrimpintexturedyarns,referto
remove crimp. The specimen then passes, at a constant speed,
Test Method D4031.
around an input roller, to a calibrated sensor which maintains a
1.1.1 This method may also be used for non-textured yarns.
specific tension.
1.2 This test method is limited to crimped, multi-filament
4.1.1 Subsequently, the specimen passes through a heating
yarns ranging from 22.0 to 890 dtex (15 to 800 denier) and for element, at a low tension, where the specimen shrinks and
BCF yarns from 890 to 4200 dtex (800 to 3800 denier).
again is crimped.
4.1.2 The crimped specimen then goes to an intermediate
1.3 The values stated in either SI or US customary units are
roll, at a low tension.
to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the U.S.
4.1.3 The specimen then travels to a second sensor, which
customary units are in parentheses. The values stated in each
maintains a tension equal to the pretension applied, to remove
system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall
developed crimp.
be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in nonconformance with the method.
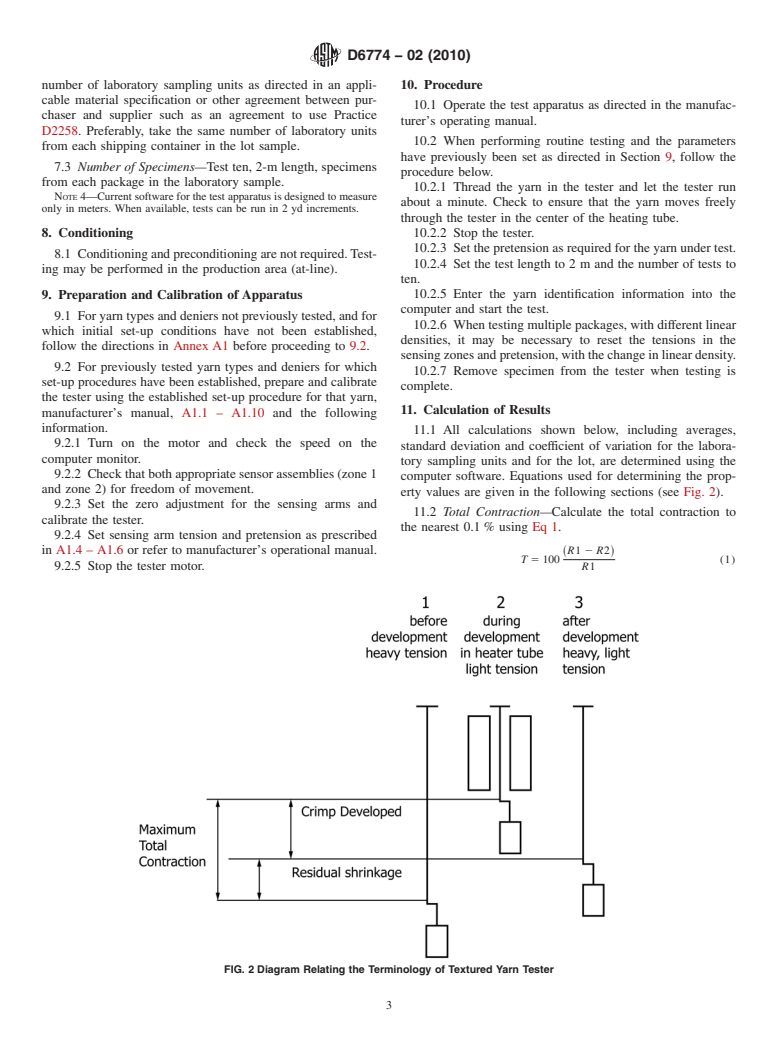
4.2 Residual fiber shrinkage, crimp developed, and maxi-
mum total contraction are calculated by the computer software
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
using speeds of the input, intermediate and output rolls.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Significance and Use
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.1 Test Method D6774, for determining maximum total
contraction, crimp, and residual fiber shrinkage in textured
2. Referenced Documents
filament yarns is suitable for acceptance testing of commercial
2 shipments.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1.1 If there are differences of practical significance be-
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
tween reported test results for two laboratories (or more),
D2258 Practice for Sampling Yarn for Testing
comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is
D4031 Test Method for Bulk Properties of Textured Yarns
a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical
D4849 Terminology Related to Yarns and Fibers
assistance. As a minimum, use the samples for such a com-
parative tests that are as homogeneous as possible, drawn from
thesamelotofmaterialasthesamplesthatresultedindisparate
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
results during initial testing and randomly assigned in equal
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.58 on Yarns and Fibers.
numbers to each laboratory. The test results from the labora-
Current edition approved June 1, 2010. Published September 2010. Originally
tories involved should be compared using a statistical test for
approved in 2002. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D6774-02. DOI:
10.1520/D6774-02R10.
unpaired data, a probability level chosen prior to the testing
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
series. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
corrected, or future test results for that material must be
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. adjusted in consideration of the known bias.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6774 − 02 (2010)
5.2 The properties and their variability as measured by th
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.