ASTM D4974/D4974M-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Hot Air Thermal Shrinkage of Yarn and Cord Using a Thermal Shrinkage Oven
Standard Test Method for Hot Air Thermal Shrinkage of Yarn and Cord Using a Thermal Shrinkage Oven
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
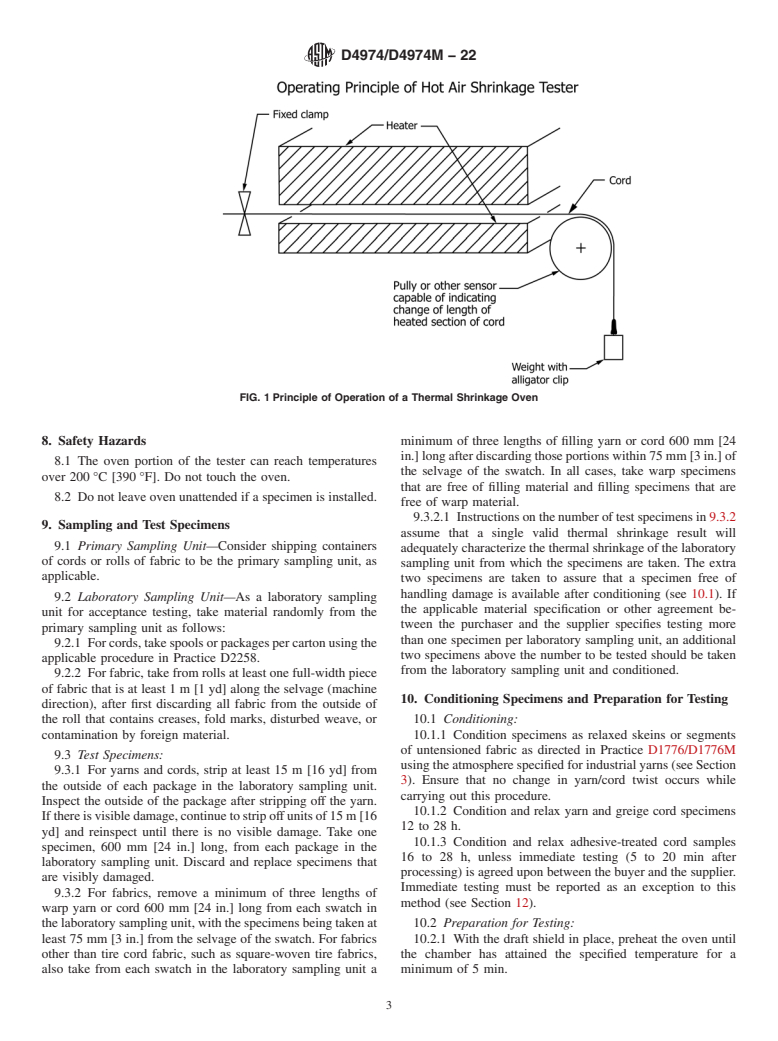
5.1 This test method may be used for the acceptance testing of commercial shipments of yarns and cords. Caution is advised because yarn and cord may contract in length over a period of time due to room temperature retraction. Thermal shrinkage values are reduced proportionately by the amount of room temperature retraction.
Note 1: Experience, especially with nylon, shows that yarn retraction, which may be observed directly as shortening of length (or indirectly as denier increase), will occur in unrestrained yarn or cord that is not at equilibrium (equilibrium in this case being defined as essentially zero thermal shrinkage yarn or fully relaxed yarn). Normally, retractive forces are present in most wound packages of yarn and cord; thus, unrestrained yarn near the surface is likely, with time, to undergo some retraction. After retraction, such yarns exhibit lower thermal shrinkage values than yarn or cord deeper within the package. The opposite condition of yarn on the surface exists with yarn or cord wound against or near a rigid package core, such as a metal or hardwood wind-up spool. Such core yarn or cord cannot move against this restraint, and thus, will exhibit thermal shrinkage values even several weeks later near to those which were measured immediately from the surface of the freshly wound package. Elevated humidity will accelerate retraction of unrestrained yarn, but moisture content in itself will have little influence on thermal shrinkage. Exposure of untensioned skeins of yarn or cord to 95 to 100 % relative humidity at room temperature for two days and reconditioning under standard laboratory conditions will cause most of the room temperature retraction that is possible within a sample to occur.
5.1.1 In case of differences of practical significance in reported test results from two or more laboratories conduct comparative tests to determine if there is a statistical bias between them. Competent statistical assistance is recommended for the invest...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of shrinkage of yarns and cords when exposed in a thermal shrinkage oven.
1.2 This test method is applicable to yarns and cords made of nylon, polyester, and other polymers not detrimentally affected by the temperature used and with linear densities in the range from 20 to 700 tex [180 to 6300 denier].
1.2.1 Yarns or cords for testing may be taken from yarn or cord packages or from fabrics.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined. Referee decisions are to use SI units.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 8.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4974/D4974M − 22
Standard Test Method for
Hot Air Thermal Shrinkage of Yarn and Cord Using a
1
Thermal Shrinkage Oven
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4974/D4974M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D885/D885M Test Methods for Tire Cords, Tire Cord
Fabrics, and Industrial Filament Yarns Made from Manu-
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of shrinkage
factured Organic-Base Fibers
of yarns and cords when exposed in a thermal shrinkage oven.
D1776/D1776M Practice for Conditioning and Testing Tex-
1.2 This test method is applicable to yarns and cords made
tiles
of nylon, polyester, and other polymers not detrimentally
D6477 Terminology Relating to Tire Cord, Bead Wire, Hose
affectedbythetemperatureusedandwithlineardensitiesinthe 3
Reinforcing Wire, and Fabrics (Withdrawn 2022)
range from 20 to 700 tex [180 to 6300 denier].
1.2.1 Yarns or cords for testing may be taken from yarn or
3. Terminology
cord packages or from fabrics.
3.1 Definitions:
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3.2 For definitions of terms relating to tire cord, bead wire,
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
hose wire, and tire cord fabrics, refer to Terminology D6477.
each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to
3.2.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be
greige cord, in tire cords; standard atmosphere for testing
used independently of the other, and values from the two
textiles; thermal shrinkage; tire cord.
systems shall not be combined. Referee decisions are to use SI
3.3 For definitions of other terms related to textiles, refer to
units.
Terminology D123.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.3.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
yarn.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4. Summary of Test Method
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 A relaxed, conditioned specimen of yarn or cord is
Specific hazard statements are given in Section 8.
subjected to dry heat for a specified time while under a
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
specified tension. The percent shrinkage is read directly from a
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
scale or display on the instrument while the specimen is still
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
under tension and exposed to heat.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5. Significance and Use
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 This test method may be used for the acceptance testing
of commercial shipments of yarns and cords. Caution is
2. Referenced Documents
advised because yarn and cord may contract in length over a
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
period of time due to room temperature retraction. Thermal
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
shrinkage values are reduced proportionately by the amount of
room temperature retraction.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
NOTE 1—Experience, especially with nylon, shows that yarn retraction,
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.19 on Industrial Fibers and
which may be observed directly as shortening of length (or indirectly as
Metallic Reinforcements.
denier increase), will occur in unrestrained yarn or cord that is not at
Current edition approved June 1, 2022. Published June 2022. Originally
equilibrium (equilibrium in this case being defined as essentially zero
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D4974–04(2016).
thermal shrinkage yarn or fully relaxed yarn). Normally, retractive forces
DOI: 10.1520/D4974_D4974M-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4974 − 04 (Reapproved 2016) D4974/D4974M − 22
Standard Test Method for
Hot Air Thermal Shrinkage of Yarn and Cord Using a
1
Thermal Shrinkage Oven
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4974;D4974/D4974M; the number immediately following the designation indicates
the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of shrinkage of yarns and cords when exposed in a thermal shrinkage oven.
1.2 This test method is applicable to yarns and cords made of nylon, polyester, and other polymers not detrimentally affected by
the temperature used and with linear densities in the range from 20 to 700 tex (180[180 to 6300 denier).denier].
1.2.1 Yarns or cords for testing may be taken from yarn or cord packages or from fabrics.
1.3 This test method shows values in both SI and inch-pound units. SI is the technically correct name for the system of units
known as the International System of Units. Inch-pound units is the technically correct name for the customary units used in the
United States. The values stated in either acceptable metric SI units or otherinch-pound units shall are to be regarded separately
as standard. The values expressedstated in each system mayare not benecessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure
conformance with the standard, each system mustshall be used independently of eachthe other, without combining values in any
way. and values from the two systems shall not be combined. Referee decisions are to use SI units.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 8.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
D885D885/D885M Test Methods for Tire Cords, Tire Cord Fabrics, and Industrial Filament Yarns Made from Manufactured
Organic-Base Fibers
D1776D1776/D1776M Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
3
D6477 Terminology Relating to Tire Cord, Bead Wire, Hose Reinforcing Wire, and Fabrics (Withdrawn 2022)
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.19 on Industrial Fibers and Metallic
Reinforcements.
Current edition approved July 1, 2016June 1, 2022. Published August 2016June 2022. Originally approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 20112016 as
D4974–04(2011).D4974–04(2016). DOI: 10.1520/D4974-04R16.10.1520/D4974_D4974M-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4974/D4974M − 22
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.2 For definitions of terms relating to tire cord, bead wire, hose wire, and tire cord fabrics, refer to Terminology D6477.
3.2.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard: greige cord, in tire cords,cords; standard atmosphere for testing
textiles,textiles; thermal shrinkage,shrinkage; tire cord.
3.3 For definitions of other terms related to textiles, refer to Terminology D123.
3.3.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard: yarn.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A relaxed, conditioned specimen of yarn or cord is subjected to dry heat for a specified time while under a specified tension.
The percent shrinkage is read directly from a scale or display on the instrument while the specimen is still under tension and
exposed to heat.
5. Significance and Use
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.