ASTM F955-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Evaluating Heat Transfer through Materials for Protective Clothing Upon Contact with Molten Substances
Standard Test Method for Evaluating Heat Transfer through Materials for Protective Clothing Upon Contact with Molten Substances
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of materials' thermal resistance to molten substance pour by describing means of measuring heat transfer.
Note 1—As used in this test method, the term molten substance refers to the three compositions (aluminum, brass, and iron) for which the procedure was validated. The test design may be adapted for use with other substances not validated as part of the test method.
1.2 This test method is applicable to materials from which finished protective apparel articles are made.
1.3 This test method does not measure the flammability of materials, nor is it intended for use in evaluating materials exposed to any other thermal exposure exclusive of the molten substance itself (see ).
1.4 This test method should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response to molten substance pour under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the thermal hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual conditions. However, results of this test may be used as elements of a thermal risk assessment which takes into account all the factors that are pertinent to an assessment of the thermal hazard of a particular end use.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F955–03
Standard Test Method for
Evaluating Heat Transfer through Materials for Protective
1
Clothing Upon Contact with Molten Substances
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 955; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E 457 TestMethodforMeasuringHeat-TransferRateUsing
a Thermal Capacitance (Slug) Calorimeter
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of materials’
F 1494 Terminology Relating to Protective Clothing
thermal resistance to molten substance pour by describing
means of measuring heat transfer.
3. Terminology
NOTE 1—As used in this test method, the term molten substance refers
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
to the three compositions (aluminum, brass, and iron) for which the
3.1.1 break-open—in testing thermal protective material, a
procedure was validated. The test design may be adapted for use with
response evidenced by the formation of a hole in the material
other substances not validated as part of the test method.
which allows the molten substance to pass through the mate-
1.2 This test method is applicable to materials from which
rial.
finished protective apparel articles are made.
3.1.2 charring—the formation of carbonaceous residue as
1.3 This test method does not measure the flammability of
the result of pyrolysis or incomplete combustion.
materials, nor is it intended for use in evaluating materials
3.1.3 dripping—in testing thermal protective material, a
exposed to any other thermal exposure exclusive of the molten
response evidenced by flowing of the fiber polymer.
substance itself (see Note 1).
3.1.4 embrittlement—the formation of a brittle residue as
1.4 Thistestmethodshouldbeusedtomeasureanddescribe
the result of pyrolysis or incomplete combustion.
the properties of materials, products, or assemblies in response
3.1.5 heat flux—the thermal intensity indicated by the
to molten substance pour under controlled laboratory condi-
amount of energy transmitted divided by area and time,
tionsandshouldnotbeusedtodescribeorappraisethethermal 2 2
W/m (cal/cm s).
hazard or fire risk of materials, products, or assemblies under
3.1.6 human tissue burn tolerance—in the testing of ther-
actual conditions. However, results of this test may be used as
mal protective materials, the amount of thermal energy pre-
elements of a thermal risk assessment which takes into account
dicted to cause a second-degree burn in human tissue.
all the factors that are pertinent to an assessment of the thermal
3.1.7 ignition—the initiation of combustion.
hazard of a particular end use.
3.1.8 melting—in testing thermal protective material, a
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
response evidenced by softening of the material, resulting in a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
nonreversible change.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.9 response to molten substance pour—intestingthermal
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
protective material, the observed effect of molten substance
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
contact on textile properties or deterioration of the material.
statements are given in Section 8.
3.1.10 shrinkage—a decrease in one or more dimensions of
an object or material.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.11 thermal end point—in testing of thermal protective
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
materials,thepointofwherethecopperslugcalorimetersensor
D 123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
response (heat energy measured) intersects with a predicted
skin burn injury model.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F23 on 3.2 For definitions of other textile terms used in this test
Protective Clothing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F23.80 on
method, refer to Terminology D 123.
Molten Substances.
Current edition approved August 10, 2003. Published October 2003. Originally
4. Summary of Test Method
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 1996 as F 955 – 96.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 4.1 Amaterialspecimenismountedonaverticalinclineand
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
is exposed to a molten substance pour of prescribed minimum
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
temperature, volume, pour rate, and vertical height.
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
------
...







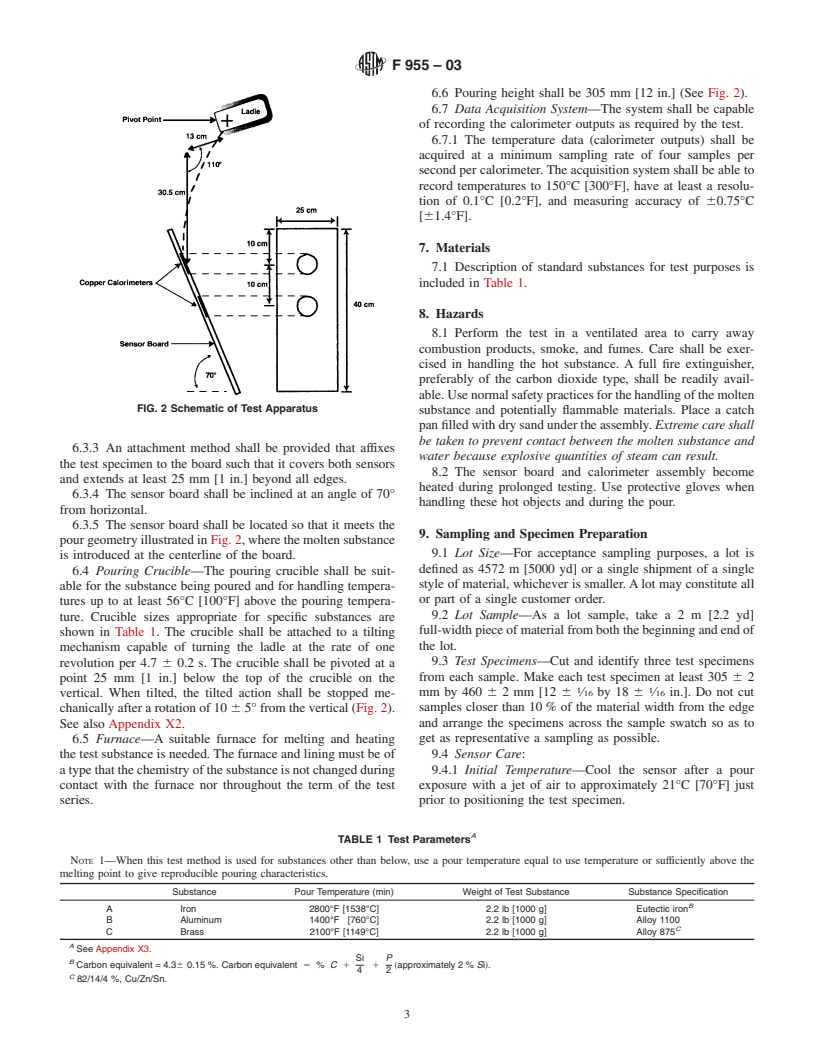
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.