ASTM D1179-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Fluoride Ion in Water
Standard Test Methods for Fluoride Ion in Water
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Simple and complex fluoride ions are found in natural waters. Fluoride forms complexing ions with silicon, aluminum, and boron. These complexes may originate from the use of fluorine compounds by industry.
Fluoridation of drinking water to prevent dental caries is practiced by a large number of communities in this country. Fluoride is monitored to assure that an optimum treatment level of 1.4 to 2.4 mg/L, depending on the corresponding range of ambient temperatures of 32 to 10°C, is maintained.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of fluoride ion in water. The following two test methods are given: SectionsTest Method A-Distillation7 to 13 Test Method B-Ion Selective Electrode14 to 22
1.2 Test Method A covers the accurate measurement of total fluoride in water through isolation of the fluoride by distillation and subsequent measurement in the distillate by use of the ion selective electrode (ISE) method. The procedure covers the range from 0.1 to 2.6 mg/L of fluoride.
1.3 Test Method B covers the accurate measurement of simple fluoride ion in water by means of an ion selective electrode. With this test method, distillation is eliminated because the electrode is not affected by the interferences common to colorimetric procedures. Concentrations of fluoride from 0.1 to 1000 mg/L may be measured.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific precautionary statement, see 12.1.2.
1.5 Former Test Method A, SPADNS Photometric Procedure, was discontinued. Refer to Appendix X1 for historical information.
General Information
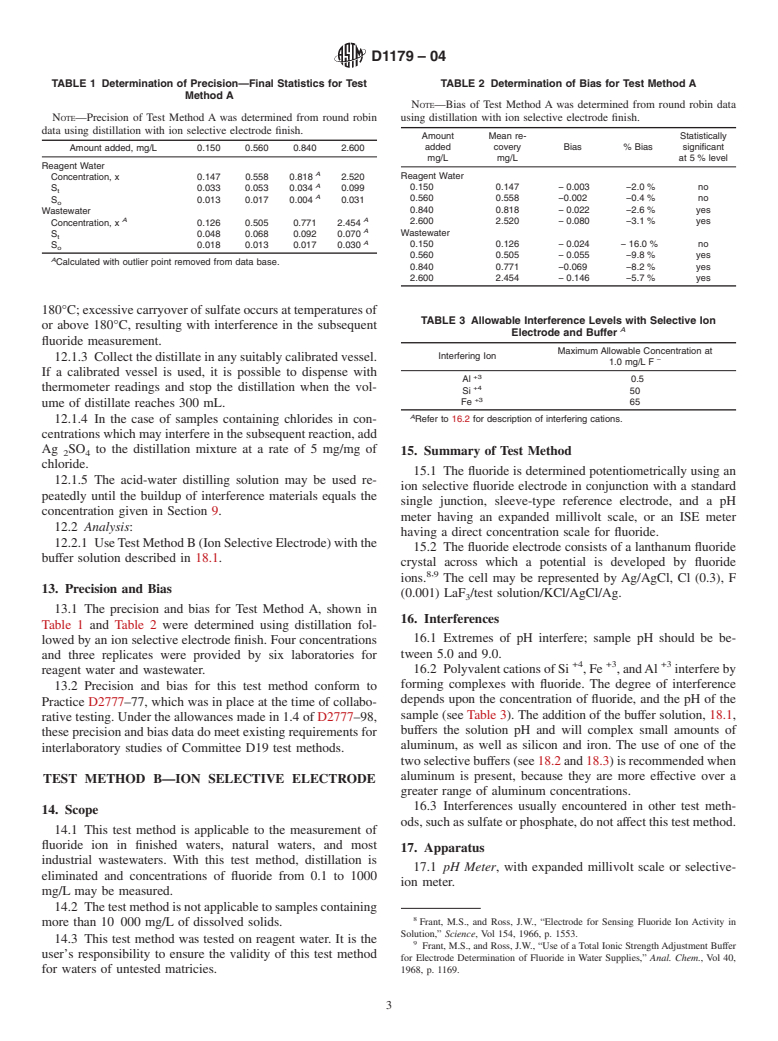
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1179–04
Standard Test Methods for
1
Fluoride Ion in Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1179; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* D1192 Guide for Equipment for SamplingWater and Steam
5
2
in Closed Conduits
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of fluoride
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
ion in water. The following two test methods are given:
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
Sections
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
Test Method A—Distillation 7 to 13
Test Method B—Ion Selective Electrode 14 to 22
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
1.2 Test MethodAcovers the accurate measurement of total
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
fluorideinwaterthroughisolationofthefluoridebydistillation
and subsequent measurement in the distillate by use of the ion
3. Terminology
selective electrode (ISE) method. The procedure covers the
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in these test
range from 0.1 to 2.6 mg/L of fluoride.
methods, refer to Terminology D1129.
1.3 Test Method B covers the accurate measurement of
simple fluoride ion in water by means of an ion selective
4. Significance and Use
electrode. With this test method, distillation is eliminated
4.1 Simple and complex fluoride ions are found in natural
because the electrode is not affected by the interferences
waters. Fluoride forms complexing ions with silicon, alumi-
commontocolorimetricprocedures.Concentrationsoffluoride
num, and boron. These complexes may originate from the use
from 0.1 to 1000 mg/L may be measured.
of fluorine compounds by industry.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.2 Fluoridationofdrinkingwatertopreventdentalcariesis
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
practiced by a large number of communities in this country.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Fluorideismonitoredtoassurethatanoptimumtreatmentlevel
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
of 1.4 to 2.4 mg/L, depending on the corresponding range of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific
ambient temperatures of 32 to 10°C, is maintained.
precautionary statement, see 12.1.2.
1.5 Former Test Method A, SPADNS Photometric Proce-
5. Purity of Reagents
dure, was discontinued. Refer to Appendix X1 for historical
5.1 Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests.
information.
Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all reagents shall
conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical
2. Referenced Documents
3 Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6
specifications are available. Other grades may be used, pro-
D1066 Practice for Sampling Steam
4
vided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
high purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of
the determination.
5.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on
to water shall be understood to mean Type I reagent water
Water and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic
Constituents in Water.
Current edition approved July 1, 2004. Published July 2004. Originally approved
in 1951. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D1179 – 9p. DOI: 10.1520/
5
D1179-04. Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
2
Bellack, E., “Simplified Fluoride Distillation Method,’’ Journal of the Ameri- on www.astm.org.
6
can Water Works Association, Vol 50, 1958, p. 530. Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
the ASTM website. and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
4
Withdrawn. MD.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Dri
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.