ASTM C1138M-05(2010)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete (Underwater Method)
Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete (Underwater Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is intended to qualitatively simulate the behavior of swirling water containing suspended and transported solid objects that produce abrasion of concrete and cause potholes and related effects.
This test method should provide a relative evaluation of the resistance of concrete to such action.
The results are expected to be useful in selection of materials, mixtures, and construction practices for use where such action is to be expected.
The test method is not intended to provide a quantitative measurement of the length of service that may be expected from a specific concrete.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the relative resistance of concrete (including concrete overlays and impregnated concrete) to abrasion under water (see Note 1). This procedure simulates the abrasive action of waterborne particles (silt, sand, gravel, and other solids).
Note 1—Other procedures are available for measuring abrasion resistance of concrete surfaces not under water. These include Test Methods C418, C779/C779M, and C944.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (WarningFresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.)
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: C1138M − 05(Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
Abrasion Resistance of Concrete (Underwater Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1138M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
´ NOTE—The units statement in 1.2 was revised editorially October 2010.
1. Scope C779/C779M Test Method forAbrasion Resistance of Hori-
zontal Concrete Surfaces
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the
C944 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete or
relative resistance of concrete (including concrete overlays and
Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating-Cutter Method
impregnated concrete) to abrasion under water (see Note 1).
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Ma-
This procedure simulates the abrasive action of waterborne
terials
particles (silt, sand, gravel, and other solids).
NOTE 1—Other procedures are available for measuring abrasion resis-
3. Significance and Use
tance of concrete surfaces not under water. These include Test Methods
C418, C779/C779M, and C944. 3.1 Thistestmethodisintendedtoqualitativelysimulatethe
behavior of swirling water containing suspended and trans-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
ported solid objects that produce abrasion of concrete and
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
cause potholes and related effects.
standard.
3.2 This test method should provide a relative evaluation of
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the resistance of concrete to such action.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.3 The results are expected to be useful in selection of
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
materials, mixtures, and construction practices for use where
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh
such action is to be expected.
hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause
3.4 The test method is not intended to provide a quantitative
chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.)
measurement of the length of service that may be expected
from a specific concrete.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4. Apparatus
C42/C42M Test Method for Obtaining and Testing Drilled
4.1 Rotating Device—A drill press or similar device with a
Cores and Sawed Beams of Concrete
chuck capable of holding and rotating the agitation paddle
C418 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete by
under test conditions at a speed of 1200 6 100 rpm shall be
Sandblasting
used.
C642 Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in
Hardened Concrete
4.2 TestContainer—Asteelpipe,305 66-mm(12 6 ⁄4-in.)
C670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
inside diameter by 450 6 25-mm (18 6 1-in.) high, fitted with
for Test Methods for Construction Materials
a watertight steel base shall be used (see Fig. 1).
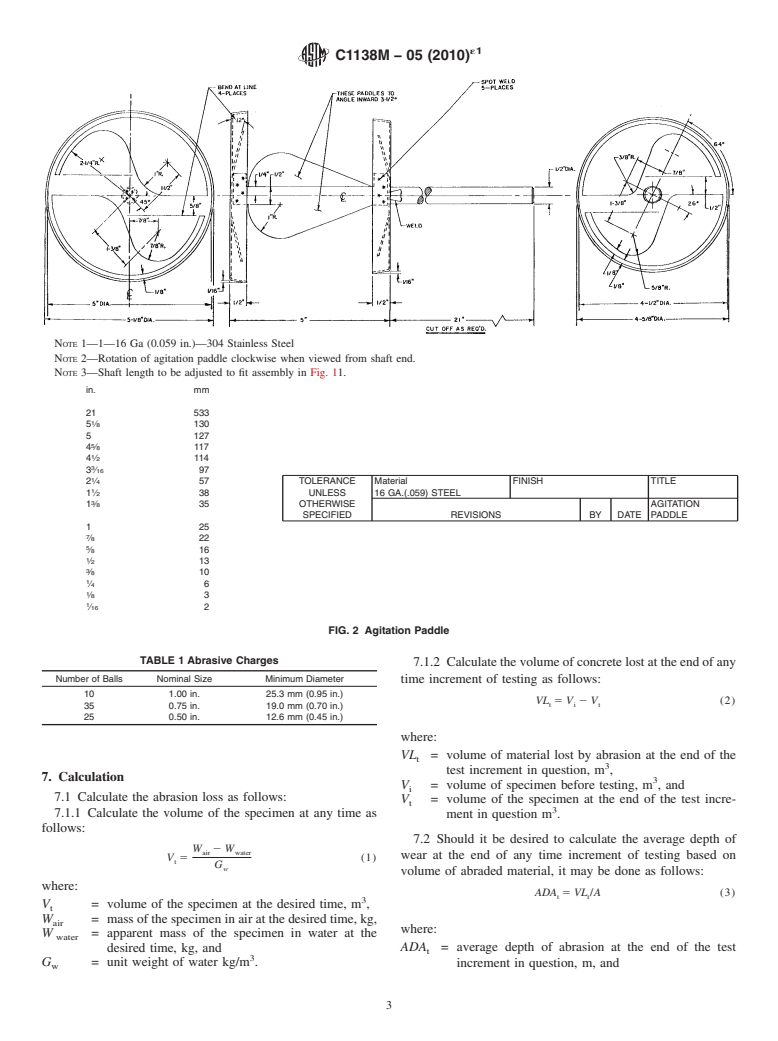
4.3 Agitation Paddle—The agitation paddle shall be as
shown in Fig. 2.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
Concrete and Concrete Aggregatesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
4.4 Abrasive Charges—Seventy grade 1000 chrome steel
C09.62 on Abrasion Testing.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2010. Published December 2010. Originally grinding balls with nominal sizes as specified in Table 1 shall
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as C1138M – 05. DOI:
be used. The steel of which the balls are made shall have a
10.1520/C1138M-05R10e1.
Rockwell C-scale hardness of 65 6 5 as determined by Test
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing,
Methods E18. The balls shall have a smooth texture and no
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 04.02.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
apparent mold seam (see Note 2).
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on NOTE 2—An abrasive charge meeting the requirements of Table 1 will
the ASTM website. have a mass of approximately 1530 to 1900 g (3.8 to 4.2 lb). When the
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
C1138M − 05 (2010)
concrete or cored from hardened concrete (see Note 3). Cores
shall be taken in accordance with Methods C42/C42M.
NOTE 3—Specimens should be tested at an age appropriate for the
material being evaluated. Most testing done to date has been done at 28
days. Concretes containing pozzolans should be tested at an age that
allows development of appropriate strength. Toppings and impregnated
concretes should be tested at an age appropriate for the material and in
compliance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. The appropriate
testing age may also depend upon when the concrete will be put into
service.
5.2 If the specimen has a membrane curing compound on
the surface, remove it completely by steel wire brushing prior
to the soaking period.
5.3 Soak the specimen in lime-saturated water or in the
water to which the concrete shall be subjected in service for a
minimum of 48 h prior to testing.
5.4 Determine the average diameter of the top surface of the
specimen to be tested to the nearest 2 mm ( ⁄16 in.) by
averagingtwodiametersmeasuredatrightanglestoeachother.
This average diameter shall be used in calculating the top
surface area.
5.5 Surface dry the specimen. Determine and record the
mass in air to the nearest 25.0 g (0.05 lb). Determine and
record the apparent mass of the specimen immersed in water to
the nearest 25.0 g (0.05 lb). The procedure of Test Method
C642 shall be followed using water at 23 6 1.7 °C (73.4 6 3
°F) having a density of 997 6 2 kg/m . Remove all entrapped
air by shaking the specimen while it is immersed in the water
for weighing.
FIG. 1 Test Apparatus
6. Procedure
6.1 Place the specimen in the test container with the surface
to be tested facing up and the seating blocks in place.
mass of the charge approaches the lower limit, replace the undersize or
6.2 Position the specimen so that its surface is normal to the
underweight balls not complying with Table 1.
drill shaft and the center of the specimen coincides with the
4.5 Scales—Aplatformscalehavingacapacityofatleast45
drill shaft.
kg (100 lb) or more and accurate to within at least 5.0 g (0.01
lb) at any point within the range used in this test shall be used. 6.3 Mounttheagitationpaddleinthedrillpress.Thebottom
1 1
The scale shall be equipped with a suitable apparatus for oftheagitationpaddleshallbe38 65mm(1 ⁄2 6 ⁄4in.)above
suspending the sample in its container in water from the center the surface of the specimen.
of the weighing platform.
6.4 Dete
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.