ASTM D3274-09(2017)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Surface Disfigurement of Paint Films by Fungal or Algal Growth, or Soil and Dirt Accumulation
Standard Test Method for Evaluating Degree of Surface Disfigurement of Paint Films by Fungal or Algal Growth, or Soil and Dirt Accumulation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The growth of fungi in and on the surface of paint films represents a major cause of discoloration or disfigurement of painted surfaces. Because of their dark pigmentation, it is frequently difficult to distinguish fungi from dirt or soil particles.
4.2 Use of Pictorial Standards:
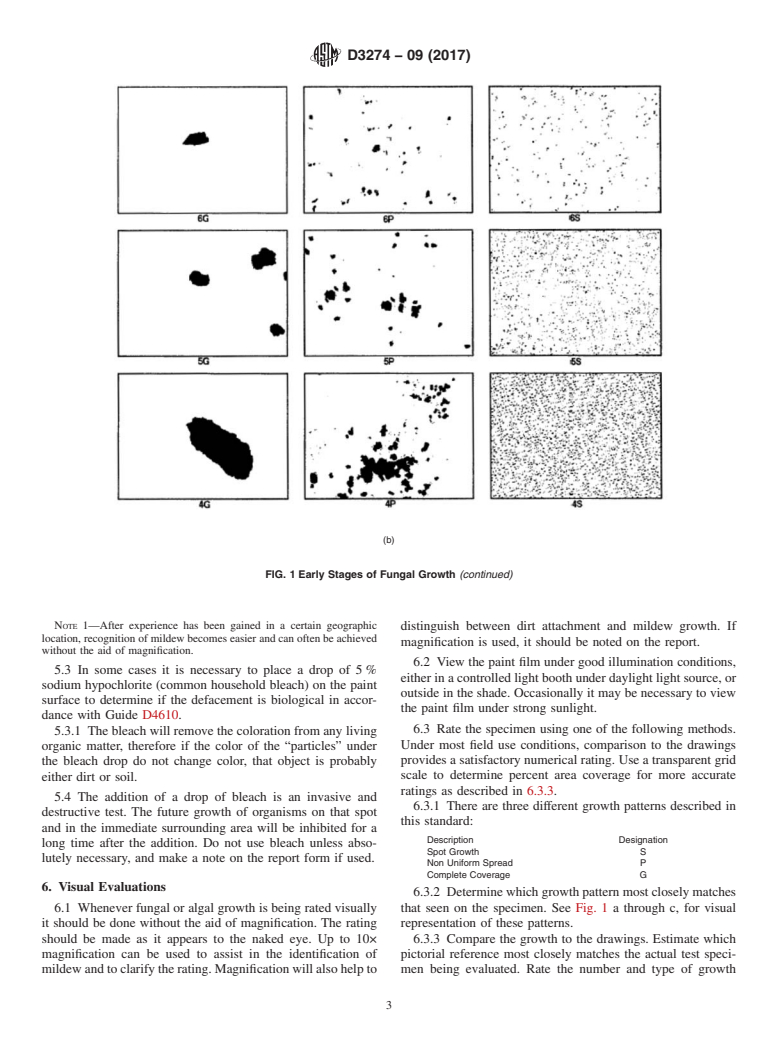
4.2.1 The pictorial references that are part of this test method are for illustration purposes and may be used for visual comparisons.
4.2.2 The diagrams represent an idealized schematic of various growth levels on paint films. they are intended as a representation only, but will serve as a useful guideline to establish amount and type of growth.
4.2.3 The diagrams represented in Fig. 1 are not derived from a linear scale. The scale is intended to provide for more discrimination at the earlier stages of fungal or algal growth. It is at these levels that greater discernment is necessary.
4.2.4 Comparisons made on dark colored substrates will be much more difficult, and will therefore require much more care and attention. It must be noted that because it is difficult to distinguish mild fungal or algal growth on the very dark substrates, there may be a tendency to under-rate those specimens.
SCOPE
1.1 Fungal growth, frequently referred to as mildew in the paint industry, causes defacement of paint film exposed outdoors. The visual rating of paint surface disfigurement due to fungal or algal attack is required in order to compare the performance of different coatings.
1.2 This method of rating mildew evaluation is intended to be used on exterior exposed paint films. This method may be used to rate interior fungal or algal growth, but it should be noted that the growth patterns on interior surfaces are different than exterior due to the lack of weathering influences. It is primarily intended for test specimens, but can also be sued for rating mildew growth on larger structures such as entire houses. If this is used for large areas, the project should be broken down into smaller sections.
1.3 This method is intended for field use for the macro rating of surface disfigurement only. The visual scales are meant to be used by the unaided eye to rate algal, fungal, or dirt disfigurement on larger surface areas such as test panels, siding boards, or entire buildings. Techniques are included for the differentiation of soil and dirt.
1.4 Fungi will grow on most paint films exposed outdoors that are located in conditions favorable to growth. Test procedures such as Practices D1006, D3456, and G7 are available describing natural exposure tests that can be used to expose paint films, in order to create fungal or algal growth.
1.5 The pictorial references available for use with this test method provide a numerical basis for rating the degree of fungal or algal growth on paint films.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D3274 −09 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Evaluating Degree of Surface Disfigurement of Paint Films
1
by Fungal or Algal Growth, or Soil and Dirt Accumulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3274; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 Fungal growth, frequently referred to as mildew in the
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
paint industry, causes defacement of paint film exposed out-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
doors. The visual rating of paint surface disfigurement due to
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
fungal or algal attack is required in order to compare the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
performance of different coatings.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.2 This method of rating mildew evaluation is intended to
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
be used on exterior exposed paint films. This method may be
used to rate interior fungal or algal growth, but it should be
2. Referenced Documents
noted that the growth patterns on interior surfaces are different
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
than exterior due to the lack of weathering influences. It is
D1006Practice for Conducting Exterior Exposure Tests of
primarily intended for test specimens, but can also be sued for
Paints on Wood
rating mildew growth on larger structures such as entire
D3456Practice for Determining by Exterior Exposure Tests
houses. If this is used for large areas, the project should be
theSusceptibilityofPaintFilmstoMicrobiologicalAttack
broken down into smaller sections.
D4610Guide for Determining the Presence of and Remov-
1.3 This method is intended for field use for the macro ing Microbial (Fungal or Algal) Growth on Paint and
rating of surface disfigurement only. The visual scales are
Related Coatings
meanttobeusedbytheunaidedeyetoratealgal,fungal,ordirt G7Practice for Atmospheric Environmental Exposure Test-
disfigurementonlargersurfaceareassuchastestpanels,siding
ing of Nonmetallic Materials
boards, or entire buildings. Techniques are included for the
differentiation of soil and dirt. 3. Terminology
3.1 Types of Fungal Growth—Duringexaminationofapaint
1.4 Fungi will grow on most paint films exposed outdoors
film, it may be possible to distinguish between the several
that are located in conditions favorable to growth. Test proce-
typesoffungaloralgalgrowth.Ifrequired,itmaybenecessary
dures such as Practices D1006, D3456, and G7 are available
to note the type of fungal or algal growth found. Under
describing natural exposure tests that can be used to expose
magnification, and with some identification training, it is
paint films, in order to create fungal or algal growth.
possible to be able to distinguish growth types. The following
1.5 The pictorial references available for use with this test
definitions are some growth types that may be found.
method provide a numerical basis for rating the degree of
3.2 hyphae, n—thread-like, tubular fungal filaments that
fungal or algal growth on paint films.
compose the mycelium.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.3 mildew, n—a popular term for the conglomerations of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
fungi that grow on and disfigure paint films.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.4 mycelium, n—vegetative mass of hyphae forming the
body of a fungus.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D01.28 on Biodeterioration. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2017. Published December 2017. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D3274–09 (2013). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D3274-09R17. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3274−09 (2017)
3.5 spore—an asexual reproductive cell capable of develop- representation only,
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3274 − 09 (Reapproved 2013) D3274 − 09 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Evaluating Degree of Surface Disfigurement of Paint Films
1
by Fungal or Algal Growth, or Soil and Dirt Accumulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3274; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 Fungal growth, frequently referred to as mildew in the paint industry, causes defacement of paint film exposed outdoors.
The visual rating of paint surface disfigurement due to fungal or algal attack is required in order to compare the performance of
different coatings.
1.2 This method of rating mildew evaluation is intended to be used on exterior exposed paint films. This method may be used
to rate interior fungal or algal growth, but it should be noted that the growth patterns on interior surfaces are different than exterior
due to the lack of weathering influences. It is primarily intended for test specimens, but can also be sued for rating mildew growth
on larger structures such as entire houses. If this is used for large areas, the project should be broken down into smaller sections.
1.3 This method is intended for field use for the macro rating of surface disfigurement only. The visual scales are meant to be
used by the unaided eye to rate algal, fungal, or dirt disfigurement on larger surface areas such as test panels, siding boards, or
entire buildings. Techniques are included for the differentiation of soil and dirt.
1.4 Fungi will grow on most paint films exposed outdoors that are located in conditions favorable to growth. Test procedures
such as Practices D1006, D3456, and G7 are available describing natural exposure tests that can be used to expose paint films, in
order to create fungal or algal growth.
1.5 The pictorial references available for use with this test method provide a numerical basis for rating the degree of fungal or
algal growth on paint films.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1006 Practice for Conducting Exterior Exposure Tests of Paints on Wood
D3456 Practice for Determining by Exterior Exposure Tests the Susceptibility of Paint Films to Microbiological Attack
D4610 Guide for Determining the Presence of and Removing Microbial (Fungal or Algal) Growth on Paint and Related Coatings
G7 Practice for Atmospheric Environmental Exposure Testing of Nonmetallic Materials
3. Terminology
3.1 Types of Fungal Growth—During examination of a paint film, it may be possible to distinguish between the several types
of fungal or algal growth. If required, it may be necessary to note the type of fungal or algal growth found. Under magnification,
and with some identification training, it is possible to be able to distinguish growth types. The following definitions are some
growth types that may be found.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.28 on Biodeterioration.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2013Dec. 1, 2017. Published October 2013December 2017. Originally approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 20092013
ε1
as D3274 – 09 (2013). . DOI: 10.1520/D3274-09R13.10.1520/D3274-09R17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-295
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.