ASTM D3802-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Ball-Pan Hardness of Activated Carbon
Standard Test Method for Ball-Pan Hardness of Activated Carbon
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Several methods have been employed in the past for determining the resistance of activated carbons to particle size degradation under service conditions, including the ball-pan method, the stirring bar method, and the dust elutriation method. None of these have proven completely satisfactory for all applications, and all have been questioned by ASTM Committee D28 on Activated Carbon as tests for establishing degradation resistance. However, the ball-pan method has been used widely in the past and has a broad history in the activated carbon industry for measuring the property loosely described as “hardness.” In this context the test is useful in establishing a measurable characteristic of a carbon. Conceding the fact that the test does not actually measure in-service resistance to degradation, it can be used to establish the comparability of lots ostensibly of the same grade of carbon.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the ball-pan hardness number of granular activated carbons. For the purpose of this test, granular activated carbons are those having particles 90 % of which are larger than 80 mesh (180 μm) as determined by Test Method D2862.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3802 − 23
Standard Test Method for
1
Ball-Pan Hardness of Activated Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3802; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test
Sieves
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the
E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
ball-pan hardness number of granular activated carbons. For
the purpose of this test, granular activated carbons are those
3. Terminology
having particles 90 % of which are larger than 80 mesh
3.1 General—Terms applicable to this standard are defined
(180 μm) as determined by Test Method D2862.
in Terminology D2652.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.2.1 nominal particle size: natural, granular, and irregu-
standard.
larly shaped particle carbons, n—that particle size range,
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
expressed in terms of Specification E11 sieve sizes, whose
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
small end excludes not more than 5 % of the particle size
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
distribution, and whose large end excludes not more than 5 %
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
of the distribution, on a weight basis.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.2.2 nominal particle size: pelleted carbons, n—that par-
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
ticle size range, expressed in terms of Specification E11 sieve
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
sizes, whose small end excludes not more than 10 % of the
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
particle size distribution, and whose large end excludes not
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
more than 5 % of the distribution, on a weight basis.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.2.3 small end nominal particle size, n—that particle size,
expressed by its equivalent Specification E11 sieve, which
2. Referenced Documents
defines the excluded portion of the particle size distribution at
2
its small particle size end in accordance with 3.2.1 or 3.2.2.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B19 Specification for Cartridge Brass Sheet, Strip, Plate,
4. Summary of Test Method
Bar, and Disks
4.1 A screened and weighed sample of the carbon is placed
B150/B150M Specification for Aluminum Bronze Rod, Bar,
in a brass hardness pan with a specified number of stainless
and Shapes
steel balls, then subjected to a combined rotating and tapping
D2652 Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
D2854 Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated action for 30 min. At the end of this period, the amount of
particle size degradation is determined by measuring the
Carbon
D2862 Test Method for Particle Size Distribution of Granu- quantity of carbon, by weight, which is retained on a sieve
whose openings are closest to one half the openings of the
lar Activated Carbon
D2867 Test Methods for Moisture in Activated Carbon sieve that defines the minimum nominal particle size of the
original sample.
5. Significance and Use
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on
Activated Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28.04 on Gas
5.1 Several methods have been employed in the past for
Phase Evaluation Tests.
determining the resistance of activated carbons to particle size
Current edition approved June 1, 2023. Published July 2023. Originally approved
degradation under service conditions, including the ball-pan
in 1979. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D3802 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/
D3802-23.
method, the stirring bar method, and the dust elutriation
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
method. None of these have proven completely satisfactory for
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
all applications, and all have been questioned by ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. Committee D28 on Activated Carbon as tests for establishing
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West C
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3802 − 16 D3802 − 23
Standard Test Method for
1
Ball-Pan Hardness of Activated Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3802; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determining the ball-pan hardness number of granular activated carbons. For the
purpose of this test, granular activated carbons are those having particles 90 % of which are larger than 80 mesh (180 μm) (180 μm)
as determined by Test Method D2862.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and healthsafety, health, and environmental practices and determine
the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B19 Specification for Cartridge Brass Sheet, Strip, Plate, Bar, and Disks
B150/B150M Specification for Aluminum Bronze Rod, Bar, and Shapes
D2652 Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
D2854 Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated Carbon
D2862 Test Method for Particle Size Distribution of Granular Activated Carbon
D2867 Test Methods for Moisture in Activated Carbon
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test Sieves
E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
3. Terminology
3.1 General—Terms applicable to this standard are defined in Terminology D2652.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 nominal particle size: natural, granular, and irregularly shaped particle carbons—carbons, n—that particle size range,
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on Activated Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28.04 on Gas Phase
Evaluation Tests.
Current edition approved June 1, 2016June 1, 2023. Published July 2016July 2023. Originally approved in 1979. Last previous edition approved in 20102016 as
D3802 – 10.D3802 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/D3802-16.10.1520/D3802-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3802 − 23
TABLE 1 Hardness Test Sieve (HTS) Corresponding to Specification E11 Sieves Defining Small-End Nominal Particle Size (SNPS)
SNPS HTS SNPS HTS
Opening, mm E11 Mesh Opening, μm E11 Mesh Opening, μm E11 Mesh Opening, μm E11 Mesh
1
5.6 3 ⁄2 2800 7 850 20 425 40
4.75 4 2360 8 710 25 355 45
4.00 5 2000 10 600 30 300 50
3.35 6 1700 12 500 35 250 60
2.80 7 1400 14 425 40 212 70
2.36 8 1180 16 355 45 180 80
2.00 10 1000 18 300 50 150 100
1.70 12 850 20 250 60 125 120
1.40 14 710 25 212 70 106 140
1.18 16 600 30 180 80 90 170
1.00 18 500 35
expressed in terms of Specification E11 sieve sizes, whose small end excludes not more than 5 % of the particle size distribution,
and whose large end excludes not more than 5 % of the distribution, on a weight basis.
3.2.2 nominal particle size: pelleted carbons—carbons, n—that particle size range, expressed in terms of Specification E11 sieve
sizes, whose small end excludes not more than 10 % of the particle size distribution, and whose large end excludes not more than
5 % of the distribution, on a weight basis.
3.2.3 small end nominal particle size—size, n—that particle size, expressed by its equivalent Specification E11 sieve, which
defines the excluded portion of the particle size distribution at its small particle size end in accordance with 3.2.1 or 3.2.2.
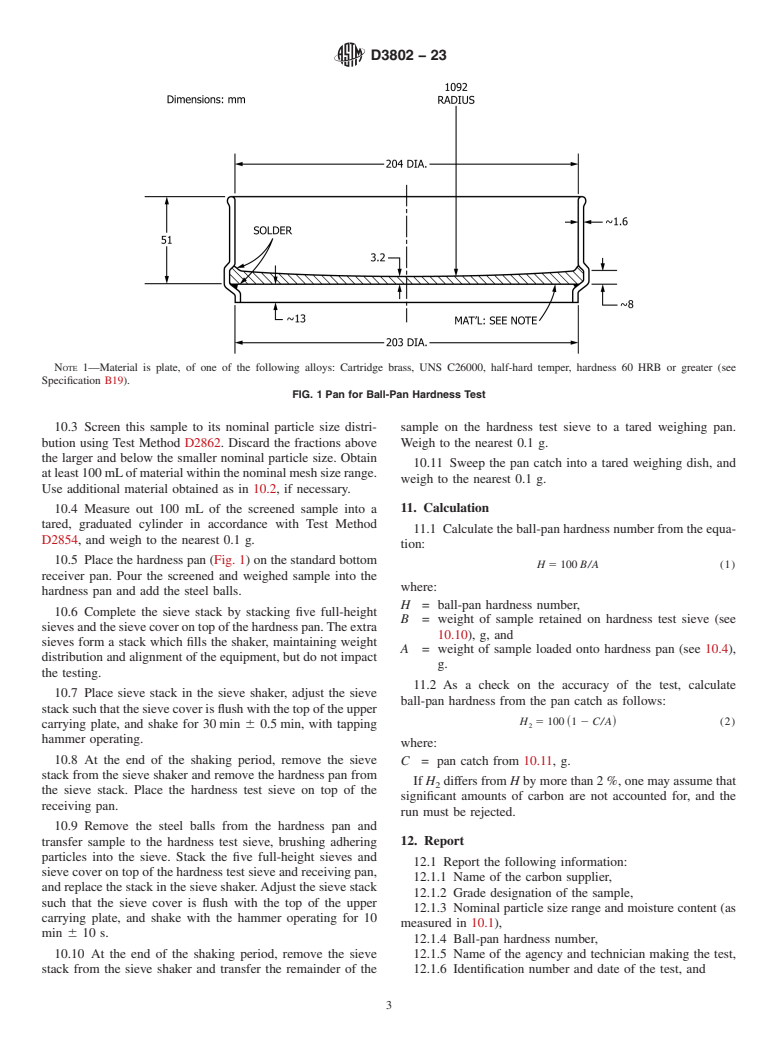
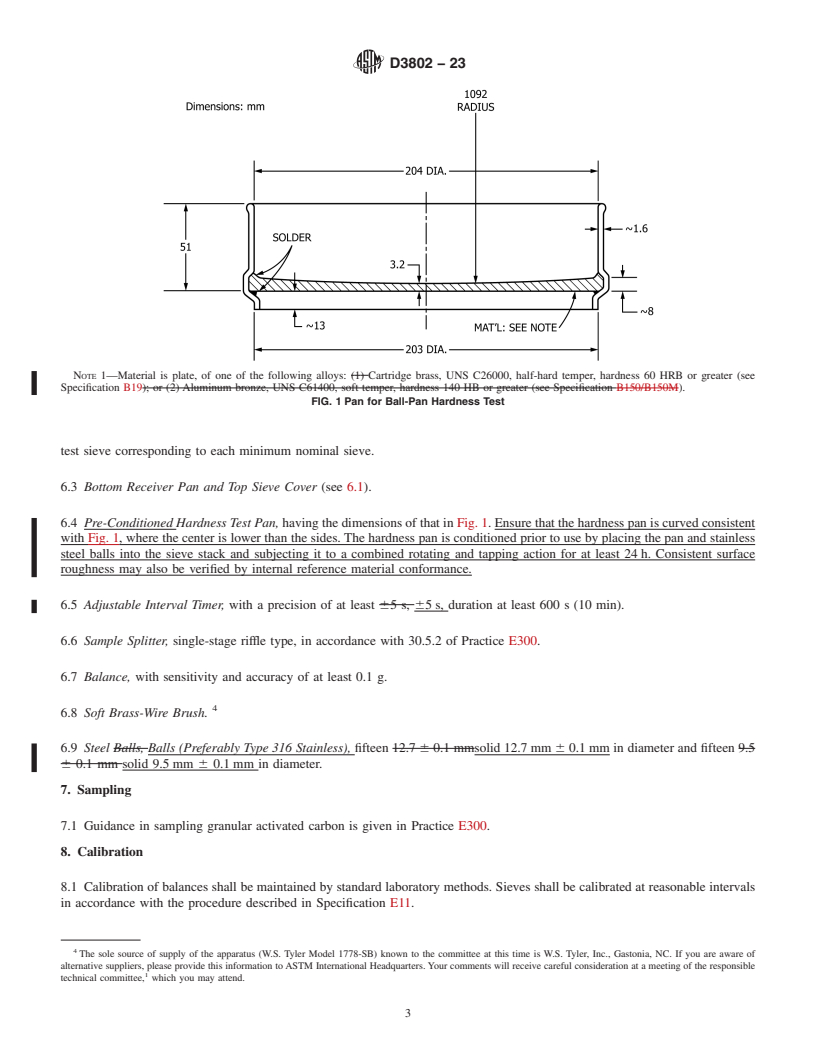
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A screened and weighed sample of the carbon is placed in a speci
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.