ASTM C1088-18
(Specification)Standard Specification for Thin Veneer Brick Units Made From Clay or Shale
Standard Specification for Thin Veneer Brick Units Made From Clay or Shale
ABSTRACT
This specification covers thin veneer brick units made from clay, shale, fire clay, sand, or mixtures thereof, and fired to incipient fusion for use in adhered or fastened veneer applications. The brick units shall be available in both Grades Interior and Exterior of the following types: Type TBS (Standard), which are for general masonry use; Type TBX (Select), which are produced with higher degree of precision; and Type TBA (Architectural), which are selected to produce characteristic architectural effects resulting from nonuniformity in size and texture of the individual units. Materials shall undergo durability, and freezing and thawing tests and should adhere to physical property requirements such as maximum water absorption, maximum saturation coefficient, maximum water loss, breakage, cracking, and weathering index. Bricks should also conform to specified characteristics as to face finish, color and texture, size and dimensions, and warpage.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers thin veneer brick units made from clay, shale, fire clay, sand, or mixtures thereof, and fired to incipient fusion for use in adhered or fastened veneer applications. Three types of thin veneer brick units in each of two grades are covered. In this specification, the term thin veneer brick shall be understood to mean clay masonry unit with a maximum thickness of 13/4 in. (44.45 mm).
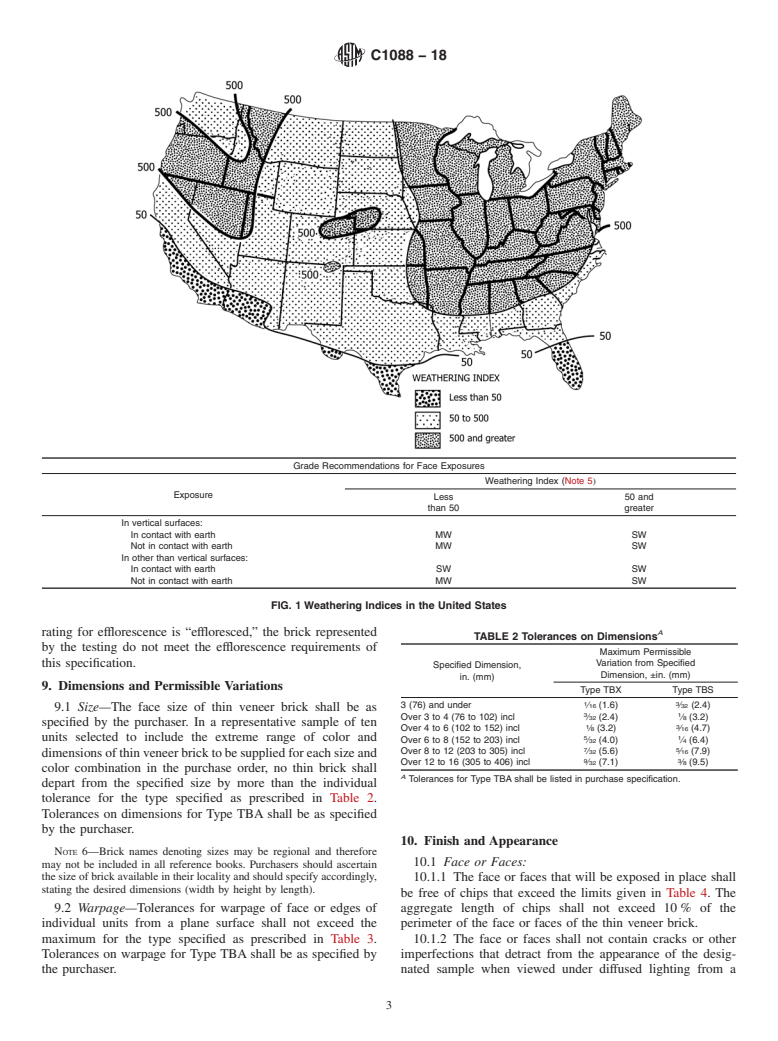
Note 1: Brick intended for paving should be specified under Specification C902.
1.2 The property requirements of this specification apply at the time of purchase. The use of results from testing of brick extracted from masonry structures for determining conformance or nonconformance to the property requirements (Section 7) of this specification is beyond the scope of this specification.
1.3 Brick covered by this specification are manufactured from clay, shale, or similar naturally occurring substances and subjected to a heat treatment at elevated temperatures (firing). The heat treatment must develop sufficient fired bond between the particulate constituents to provide the strength and durability requirements of the specification. (See “firing” and “fired bond” in Terminology C1232.)
1.4 Thin brick are shaped during manufacture by molding, pressing, or extrusion. The shaping method is a way to describe the thin brick. Thin brick may also be cut from thicker masonry units.
1.4.1 This standard and its individual requirements shall not be used to qualify or corroborate the performance of a masonry unit made from other materials, or made with other forming methods, or other means of binding the materials.
1.5 The text of this specification references notes and footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the standard.
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:C1088 −18
Standard Specification for
1
Thin Veneer Brick Units Made From Clay or Shale
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1088; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
1.1 This specification covers thin veneer brick units made
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
from clay, shale, fire clay, sand, or mixtures thereof, and fired
and are not considered standard.
to incipient fusion for use in adhered or fastened veneer
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
applications. Three types of thin veneer brick units in each of
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
two grades are covered. In this specification, the term thin
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
veneer brick shall be understood to mean clay masonry unit
3
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
with a maximum thickness of 1 ⁄4 in. (44.45 mm).
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
NOTE 1—Brick intended for paving should be specified under Specifi-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
cation C902.
1.2 The property requirements of this specification apply at
2. Referenced Documents
the time of purchase. The use of results from testing of brick
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
extracted from masonry structures for determining confor-
C67 Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Brick and
mance or nonconformance to the property requirements (Sec-
Structural Clay Tile
tion 7) of this specification is beyond the scope of this
C902 Specification for Pedestrian and Light Traffic Paving
specification.
Brick
1.3 Brick covered by this specification are manufactured
C1232 Terminology for Masonry
from clay, shale, or similar naturally occurring substances and
subjected to a heat treatment at elevated temperatures (firing).
3. Terminology
The heat treatment must develop sufficient fired bond between
3.1 Definitions—For definitions relating to thin veneer
the particulate constituents to provide the strength and dura-
brick, refer to Terminology C1232.
bility requirements of the specification. (See “firing” and “fired
bond” in Terminology C1232.)
4. Classification
1.4 Thin brick are shaped during manufacture by molding,
4.1 Grades—Grades classify brick according to their resis-
pressing,orextrusion.Theshapingmethodisawaytodescribe
tance to damage by freezing and thawing when saturated at a
thethinbrick.Thinbrickmayalsobecutfromthickermasonry
moisture content not exceeding the 24-h cold water absorption.
units.
Two grades of thin veneer brick units are covered and the
1.4.1 This standard and its individual requirements shall not
requirements are given in Section 7.
be used to qualify or corroborate the performance of a masonry
4.1.1 Grade Exterior—Brick intended for use where high
unit made from other materials, or made with other forming
resistance to damage caused by cyclic freezing and thawing is
methods, or other means of binding the materials.
desired.
1.5 The text of this specification references notes and
4.1.2 Grade Interior—Brick intended for use where moder-
footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and
ate resistance to cyclic freezing and thawing damage is
footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be
permissible.
considered as requirements of the standard.
4.2 Three types of thin veneer brick units are covered as
follows:
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C15 on
Manufactured Masonry Units and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
2
C15.02 on Brick and Structural Clay Tile. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2018. Published October 2018. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as C1088 – 17. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/C1088-18. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1088−18
TABLE 1 Physical Requirements
4.2.1 Type TBS (Standard)—Thin veneer brick for general
use in masonry. Maximum Water Maximum
Absorption by 5-h Saturation
4.2.2 Type TBX (Select)—Thin veneer brick for ge
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1088 − 17 C1088 − 18
Standard Specification for
1
Thin Veneer Brick Units Made From Clay or Shale
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1088; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers thin veneer brick units made from clay, shale, fire clay, sand, or mixtures thereof, and fired to
incipient fusion for use in adhered or fastened veneer applications. Three types of thin veneer brick units in each of two grades
are covered. In this specification, the term thin veneer brick shall be understood to mean clay masonry unit with a maximum
3
thickness of 1 ⁄4 in. (44.45 mm).
NOTE 1—Brick intended for paving should be specified under Specification C902.
1.2 The property requirements of this specification apply at the time of purchase. The use of results from testing of brick
extracted from masonry structures for determining conformance or nonconformance to the property requirements (Section 67) of
this specification is beyond the scope of this specification.
1.3 Brick covered by this specification are manufactured from clay, shale, or similar naturally occurring substances and
subjected to a heat treatment at elevated temperatures (firing). The heat treatment must develop sufficient fired bond between the
particulate constituents to provide the strength and durability requirements of the specification. (See “firing” and “fired bond” in
Terminology C1232.)
1.4 Thin brick are shaped during manufacture by molding, pressing, or extrusion. The shaping method is a way to describe the
thin brick. Thin brick may also be cut from thicker masonry units.
1.4.1 This standard and its individual requirements shall not be used to qualify or corroborate the performance of a masonry
unit made from other materials, or made with other forming methods, or other means of binding the materials.
1.5 The text of this specification references notes and footnotes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes
(excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the standard.
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C67 Test Methods for Sampling and Testing Brick and Structural Clay Tile
C902 Specification for Pedestrian and Light Traffic Paving Brick
C1232 Terminology for Masonry
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions relating to thin veneer brick, refer to Terminology C1232.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C15 on Manufactured Masonry Units and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C15.02 on Brick
and Structural Clay Tile.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2017Sept. 1, 2018. Published October 2017October 2018. Originally approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 20142017 as
C1088 – 14.C1088 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/C1088-17.10.1520/C1088-18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1088 − 18
4. Classification
4.1 Grades—Grades classify brick according to their resistance to damage by freezing and thawing when saturated at a moisture
content not exceeding the 24-h cold water absorption. Two grades of thin veneer brick units are covered and the requirements are
given in Section 67.
4.1.1 Grade Exterior—Brick intended for use where high resistance to damage caused by cyclic freezing and thawing is desired.
4.1.2 Grade Interior—Brick intended f
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.