ASTM E806-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Carbon Tetrachloride and Chloroform in Liquid Chlorine by Direct Injection (Gas Chromatographic Procedure)
Standard Test Method for Carbon Tetrachloride and Chloroform in Liquid Chlorine by Direct Injection (Gas Chromatographic Procedure)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 CCl4 and CHCl3 may be present in trace amounts in liquid chlorine. The use of chlorine to purify water would then transfer these compounds to the water. Therefore, when the concentrations of the CCl4 and CHCl3 in the liquid chlorine are known, the maximum amounts contributed to the water by the chlorine can be estimated.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is designed for the determination of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) and chloroform (CHCl3) in liquid chlorine. The lower limit of detection is dependent on the sample size and the instrument used; five ppm (w/w) is achievable.
1.2 Review the current Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid procedures, and safety precautions.
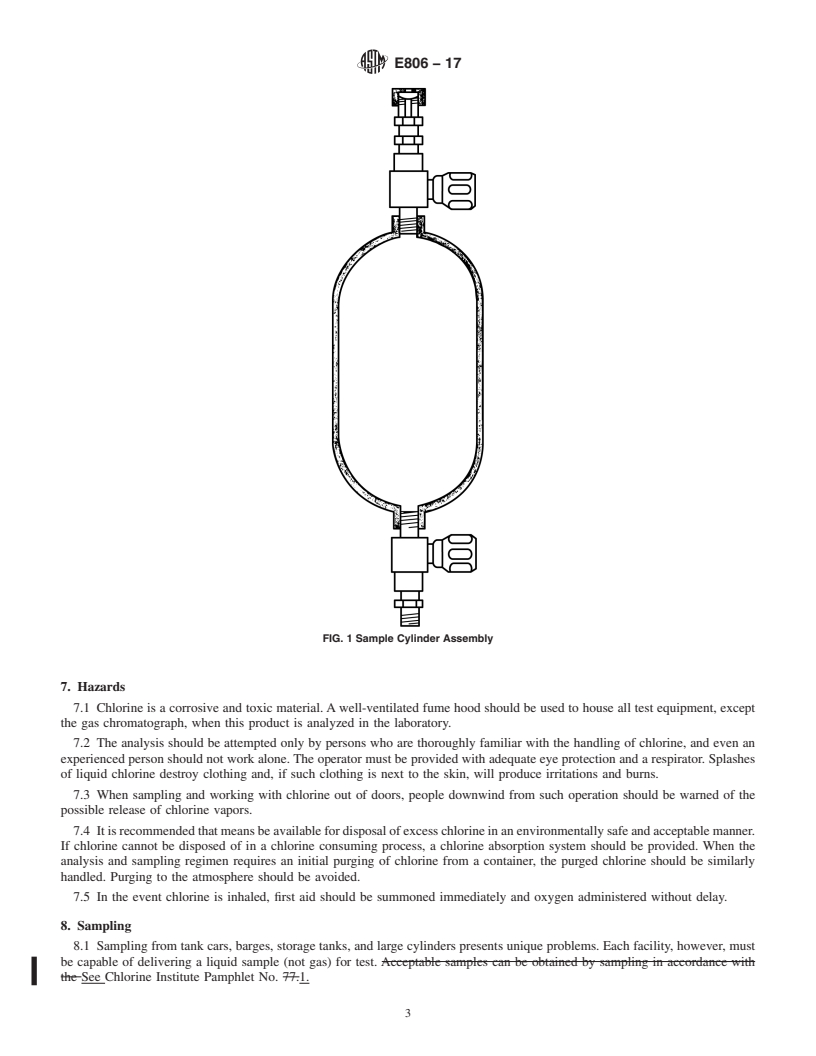
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazards statements are given in Section 7 and in 9.2.3.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E806 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Carbon Tetrachloride and Chloroform in Liquid Chlorine by
1
Direct Injection (Gas Chromatographic Procedure)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E806; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 173.304 Charging of Cylinders with Liquefied Compressed
Gas
1.1 This test method is designed for the determination of
173.314 Requirements for Compressed Gases in Tank Cars
carbon tetrachloride (CCl ) and chloroform (CHCl ) in liquid
4 3
173.315 Compressed Gases in Cargo Tanks and Portable
chlorine. The lower limit of detection is dependent on the
Tank Containers
sample size and the instrument used; five ppm (w/w) is
achievable. 2.3 Other Document:
5
Chlorine Institute Pamphlet No. 1 Chlorine Basics
1.2 ReviewthecurrentSafetyDataSheet(SDS)fordetailed
informationconcerningtoxicity,firstaidprocedures,andsafety
3. Summary of Test Method
precautions.
3.1 A sample of liquid chlorine is injected into a gas
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
chromatograph (GC), equipped with a column capable of
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
separating CCl and CHCl from Cl and other impurities,
4 3 2
standard.
using a suitable syringe. The amounts of CCl and CHCl in
4 3
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the sample are determined by comparison of the areas of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
peaks, obtained with the samples, to areas of peaks obtained
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
with suitable calibration standards, under the same conditions.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazards
4. Significance and Use
statements are given in Section 7 and in 9.2.3.
4.1 CCl and CHCl may be present in trace amounts in
4 3
liquid chlorine. The use of chlorine to purify water would then
2. Referenced Documents
2 transfer these compounds to the water. Therefore, when the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
concentrationsoftheCCl andCHCl intheliquidchlorineare
4 3
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
known, the maximum amounts contributed to the water by the
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
chlorine can be estimated.
3
cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
4
2.2 Federal Standard:
5. Apparatus
49 CFR 173 Code of Federal Regulations Title 49 Transpor-
5.1 Gas Chromatograph, equipped with:
tation; Shippers’General Requirements for Shipments and
6
5.1.1 Injection Port, must be lined with glass, Monel, or
Packagings, including Sections:
nickel; or column must be installed for on-column injection.
7
5.1.2 Septa, from Viton. Silicone septa may produce arti-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on
facts that may interfere with the analysis.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of
5.1.3 Column, Column Materials, and Packing, must be
Subcommittee D16.16 on Industrial and Specialty Product Standards.
Current edition approved March 1, 2017. Published March 2017. Originally compatible with chlorine. Silanized supports and silanized
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as E806 – 08. DOI:
glass wool must be avoided. Column must be able to separate
10.1520/E0806-17.
Cl , CCl , and CHCl . Columns that have been found to be
2
2 4 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
suitable are:
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
5
www.astm.org. Available from The Chlorine Institute Inc., 1300 Wilson Blvd., Suite 525,
4
Available from U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Arlington, VA 22209, https://www.chlorineinstitute.org.
6
Documents, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Washington, DC 20401-0001, http:// Monel is a registered trademark of Special Metals Corporation.
7
www.access.gpo.gov. Viton is a registered trademark of The Chemours Company.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E806 − 17
5.1.3.1 Nickel Tubing, 3.05 m by 3.175 mm outside
diameter, packed with 10 % sodium chloride solution on
8
Porasil C (see Appendix X1 for packing pr
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E806 − 08 E806 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Carbon Tetrachloride and Chloroform in Liquid Chlorine by
1
Direct Injection (Gas Chromatographic Procedure)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E806; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method is designed for the determination of carbon tetrachloride (CCl ) and chloroform (CHCl ) in liquid chlorine.
4 3
The lower limit of detection is dependent on the sample size and the instrument used; five ppm (w/w) is achievable.
1.2 Review the current material safety data sheet (MSDS) Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity,
first aid procedures, and safety precautions.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific hazards statements are given in Section 7 and in 9.2.3.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
3
(Withdrawn 2009)
4
2.2 Federal Standard:
49 CFR 173 Code of Federal Regulations Title 49 Transportation; Shippers’ General Requirements for Shipments and
Packagings, including Sections:
173.304 Charging of Cylinders with LiquifiedLiquefied Compressed Gas
173.314 Requirements for Compressed Gases in Tank Cars
173.315 Compressed Gases in Cargo Tanks and Portable Tank Containers
2.3 Other Document:
5
Chlorine Institute Pamphlet No. 77 Sampling1 Liquid ChlorineChlorine Basics
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A sample of liquid chlorine is injected into a gas chromatograph (GC), equipped with a column capable of separating CCl
4
and CHCl from Cl and other impurities, using a suitable syringe. The amounts of CCl and CHCl in the sample are determined
3 2 4 3
by comparison of the areas of the peaks, obtained with the samples, to areas of peaks obtained with suitable calibration standards,
under the same conditions.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 CCl and CHCl may be present in trace amounts in liquid chlorine. The use of chlorine to purify water would then transfer
4 3
these compounds to the water. Therefore, when the concentrations of the CCl and CHCl in the liquid chlorine are known, the
4 3
maximum amounts contributed to the water by the chlorine can be estimated.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D16.16 on Industrial and Specialty Product Standards.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2008March 1, 2017. Published January 2009March 2017. Originally approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 20032008
as E806 – 99 (2003).E806 – 08. DOI: 10.1520/E0806-08.10.1520/E0806-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Documents, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Washington, DC 20402.20401-0001, http://
www.access.gpo.gov.
5
Available from The Chlorine Institute Inc., 70 W. 40th St., New York, NY 10018.1300 Wilson Blvd., Suite 525, Arlington, VA 22209, https://www.chlorineinstitute.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E806 − 17
5. Apparatus
5.1 Gas Chromatograph, equipped with:
6
5.1.1 Injection Port, must be lined with glass, Monel,®Monel, or nickel; or column must be installed for on-column injection.
7
5.1.2 Septa, from Viton.®Viton. Silicone septa may produce artifacts that may interfere with the analysis.
5.1.3 Column, Column Materia
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.