ASTM E1754-17a
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Low Levels of Water in Liquid Chlorine By Infrared Spectrophotometry
Standard Test Method for Determination of Low Levels of Water in Liquid Chlorine By Infrared Spectrophotometry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Trace amounts of water may be detrimental to the use of chlorine in some applications. The amount of water in the chlorine must be known to prevent problems during its use.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the content of water in liquid chlorine in the concentration range of 0.5 to 15 mg/kg (ppm).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 Review the current Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid procedures, and safety precautions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Section 7 for specific hazards statements.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E1754 − 17a
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Low Levels of Water in Liquid Chlorine By
1
Infrared Spectrophotometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1754; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D6809 Guide for Quality Control and Quality Assurance
Procedures for Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Ma-
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the content
terials
of water in liquid chlorine in the concentration range of 0.5 to
E806 Test Method for Carbon Tetrachloride and Chloroform
15 mg/kg (ppm).
in Liquid Chlorine by Direct Injection (Gas Chromato-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
graphic Procedure)
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information 3
2.2 Federal Standards:
only.
49 CFR 173 Code of Federal Regulations Title 49 Transpor-
1.3 Review the current Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for de- tation: Shippers’General Requirements for Shipments and
Packaging, including Sections:
tailed information concerning toxicity, first aid procedures, and
safety precautions. 173.304 Charging of Cylinders with Liquefied Compressed
Gas
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
173.314 Requirements for Compressed Gases in Tank Cars
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
173.315 Compressed Gases in Cargo Tanks and Portable
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Tank Containers
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3. Summary of Test Method
See Section 7 for specific hazards statements.
3.1 A sample of liquid chlorine is introduced into a special
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
infrared cell and maintained as a liquid under its own pressure.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
A spectrometer scans from 400 to 4400 wavenumbers of the
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
infrared transmission spectrum of liquid chlorine. This spec-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
trum is then ratioed to one obtained of the nitrogen-filled
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
infrared cell previously. The ratioed spectrum is converted to
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
absorbance, and the net absorbance of the water band at 1596
wavenumbers, relative to a reference at 1663 wavenumbers, is
2. Referenced Documents
determined. The amount of water corresponding to this net
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
absorbance is determined from a calibration curve prepared
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
from the infrared absorbances of standards that contain known
concentrations of water in liquid chlorine.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on
4. Significance and Use
Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsi-
4.1 Trace amounts of water may be detrimental to the use of
bility of Subcommittee D16.13 on Chlorine.
Current edition approved July 1, 2017. Published July 2017. Originally approved
chlorine in some applications. The amount of water in the
in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as E1754 – 17. DOI: 10.1520/
chlorine must be known to prevent problems during its use.
E1754-17a.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Documents, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Washington, DC 20401-0001, http://
the ASTM website. www.access.gpo.gov.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1754 − 17a
5. Apparatus
5.1 Infrared Spectrometer, capable of measurements in the
1600 wavenumber region. An FTIR with 4 wavenumber
resolution is the instrument of choice, but dispersive instru-
ments may also be used to achieve similar results.
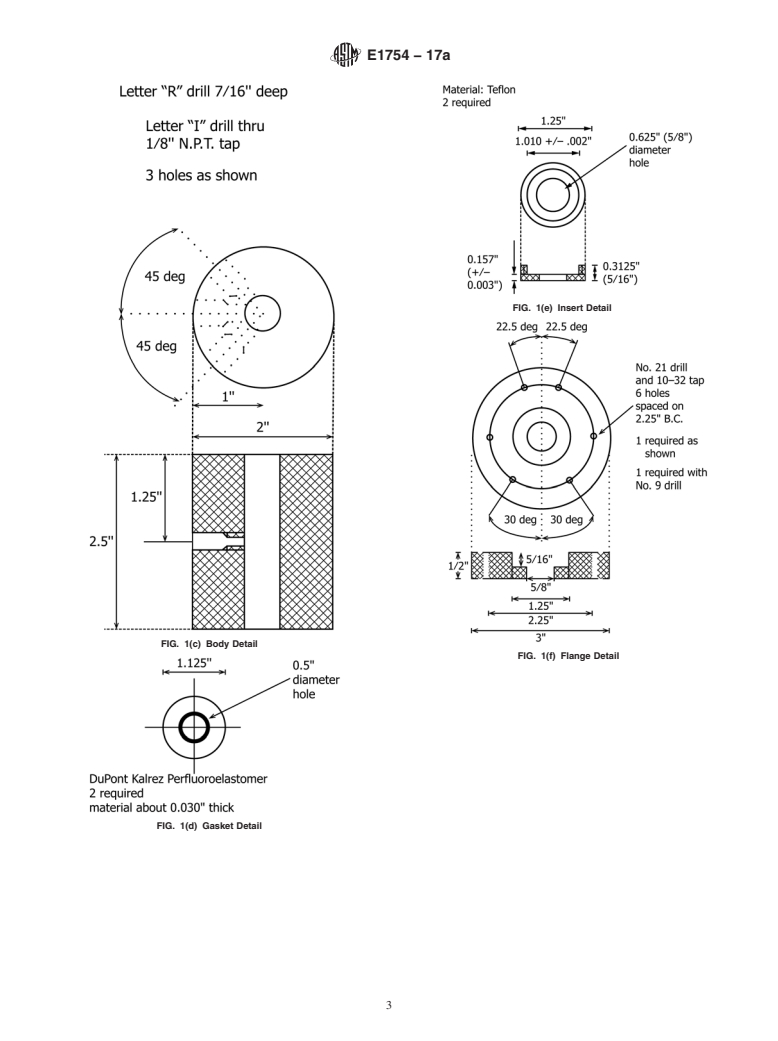
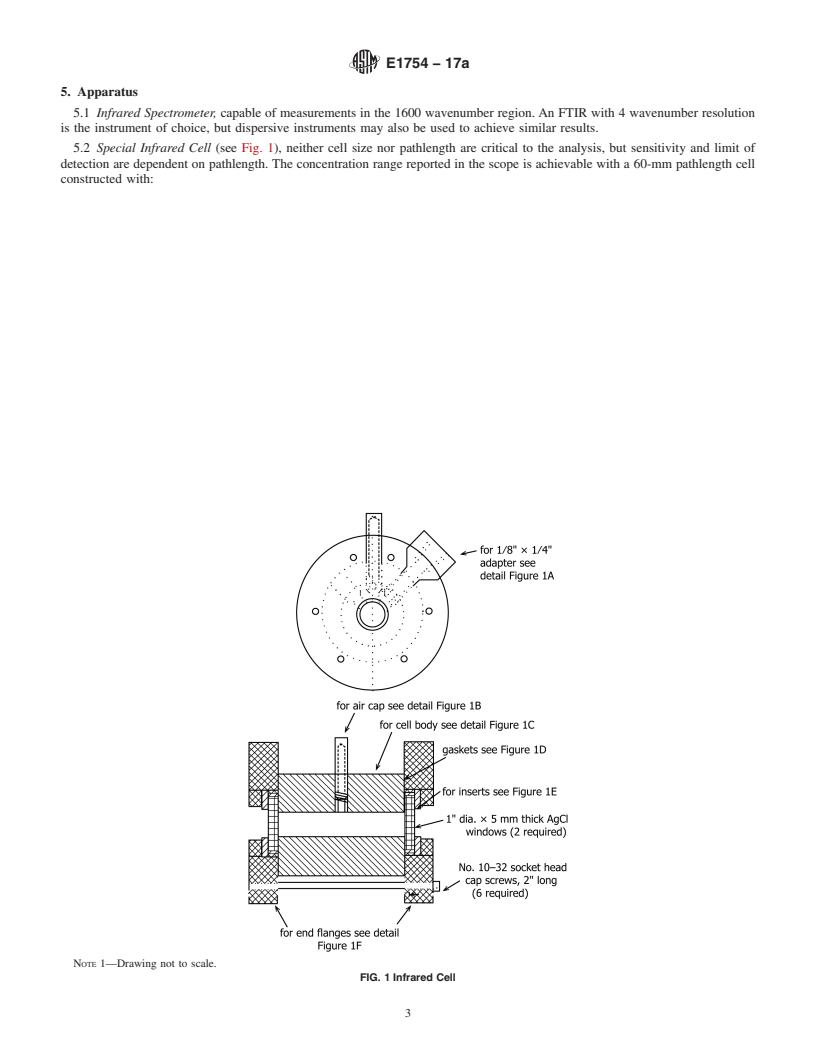
5.2 Special Infrared Cell (see Fig. 1), neither cell size nor
pathlength are critical to the analysis, but sensitivity and limit
of detection are dependent on pathlength. The concentration
range reported in t
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1754 − 17 E1754 − 17a
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Low Levels of Water in Liquid Chlorine By
1
Infrared Spectrophotometry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1754; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the content of water in liquid chlorine in the concentration range of 0.5 to 15
mg/kg (ppm).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 Review the current Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid procedures, and safety
precautions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. See Section 7 for specific hazards statements.
1.4 Review the current Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid procedures, and safety
precautions.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D6809 Guide for Quality Control and Quality Assurance Procedures for Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Materials
E806 Test Method for Carbon Tetrachloride and Chloroform in Liquid Chlorine by Direct Injection (Gas Chromatographic
Procedure)
3
2.2 Federal Standards:
49 CFR 173 Code of Federal Regulations Title 49 Transportation: Shippers’ General Requirements for Shipments and
Packaging, including Sections:
173.304 Charging of Cylinders with Liquefied Compressed Gas
173.314 Requirements for Compressed Gases in Tank Cars
173.315 Compressed Gases in Cargo Tanks and Portable Tank Containers
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A sample of liquid chlorine is introduced into a special infrared cell and maintained as a liquid under its own pressure. A
spectrometer scans from 400 to 4400 wavenumbers of the infrared transmission spectrum of liquid chlorine. This spectrum is then
ratioed to one obtained of the nitrogen-filled infrared cell previously. The ratioed spectrum is converted to absorbance, and the net
absorbance of the water band at 1596 wavenumbers, relative to a reference at 1663 wavenumbers, is determined. The amount of
water corresponding to this net absorbance is determined from a calibration curve prepared from the infrared absorbances of
standards that contain known concentrations of water in liquid chlorine.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on Aromatic Hydrocarbons Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and is the direct
responsibility of Subcommittee D16.16 on Industrial and Specialty Product Standards.
Current edition approved March 1, 2017July 1, 2017. Published March 2017July 2017. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20082017 as E1754
– 08.17. DOI: 10.1520/E1754-17.10.1520/E1754-17a.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from U.S. Government Printing Office, Superintendent of Documents, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Washington, DC 20401-0001, http://www.access.gpo.gov.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1754 − 17a
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Trace amounts of water may be detrimental to the use of chlorine in some applications. The amount of water in the chlorine
must be known to prevent problems during its use.
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
E1754 − 17a
5. Apparatus
5.1 Infrared Spectrome
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.