ASTM D4266-96(2007)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Precoat Capacity of Powdered Ion-Exchange Resins
Standard Test Methods for Precoat Capacity of Powdered Ion-Exchange Resins
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The salt removal capacity of a powdered resin precoat is limited by the capacity of either the anion-exchange resin or the cation-exchange resin contained in it. Applications include condensate polishing in fossil-fueled electric generating plants, as well as condensate polishing, spent fuel pool water treatment, reactor water treatment, and low-level radioactive liquid waste treatment in nuclear-powered electric generating plants.
By determining the ion-exchange capacity profile of either a cation exchange resin or an anion-exchange resin (capacity expended per unit of time under specific conditions), it is possible to estimate runlength and remaining capacity when treating a liquid of the same makeup. Although they cannot accurately predict performance during condenser leaks, these test methods are useful for determining operating capacities as measured under the test conditions used.
These test methods may be used to monitor the performance of either powdered anion-exchange resin or powdered cation-exchange resin. The total capacity of either resin depends primarily upon the number density of ion-exchange sites within the resin. The operating capacity is a function of the total capacity, degree of conversion to the desired ionic form when received, and properties of the resin and the system that affect ion exchange kinetics.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the operating ion-exchange capacity of both powdered cation-exchange resins (hydrogen form) and powdered anion-exchange resins (hydroxide form). These test methods are intended for use in testing new powdered ion-exchange resins when used for the treatment of water. The following two test methods are included:
Sections Test Method A—Operating Capacity, Anion-Exchange
Resin, Hydroxide Form7 to 15 Test Method B—Operating Capacity, Cation-Exchange
Resin, Hydrogen Form16 to 24
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D 4266–96 (Reapproved 2007)
Standard Test Methods for
Precoat Capacity of Powdered Ion-Exchange Resins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4266; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
operating ion-exchange capacity of both powdered cation- 3.1.1 powdered ion-exchange material, n—anion-exchange
exchange resins (hydrogen form) and powdered anion- resin that has undergone post-manufacturing size reduction to
exchange resins (hydroxide form). These test methods are less than 300 µm.
intended for use in testing new powdered ion-exchange resins 3.1.2 resindosage,n—theweightofmixedresinappliedper
when used for the treatment of water. The following two test unit area of precoatable filter surface. This is expressed as dry
methods are included: pounds per square foot.
3.1.3 resin floc, n—thatvoluminousaggregateformedwhen
Sections
Test Method A—Operating Capacity, Anion-Exchange 7 to 15
powdered anion-exchange resin and powdered cation-
Resin, Hydroxide Form
exchange resin are slurried together in an aqueous suspension.
Test Method B—Operating Capacity, Cation-Exchange 16 to 24
3.1.4 resin ratio, n—the ratio of the weights of powdered
Resin, Hydrogen Form
cation-exchange resin to powdered anion-exchange resin used
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
to prepare a resin slurry. If not otherwise indicated, it is
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
understood to be the ratio of the dry resin weights.
information only.
3.2 Definitions—Fordefinitionsofothertermsusedinthese
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
test methods, refer to Terminology D1129.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Significance and Use
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 Thesaltremovalcapacityofapowderedresinprecoatis
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
limited by the capacity of either the anion-exchange resin or
the cation-exchange resin contained in it.Applications include
2. Referenced Documents
condensatepolishinginfossil-fueledelectricgeneratingplants,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
as well as condensate polishing, spent fuel pool water treat-
D1125 Test Methods for Electrical Conductivity and Re-
ment, reactor water treatment, and low-level radioactive liquid
sistivity of Water
waste treatment in nuclear-powered electric generating plants.
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
4.2 By determining the ion-exchange capacity profile of
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
either a cation exchange resin or an anion-exchange resin
D2687 Practices for Sampling Particulate Ion-Exchange
(capacity expended per unit of time under specific conditions),
Materials
it is possible to estimate runlength and remaining capacity
D4456 Test Methods for Physical and Chemical Properties
when treating a liquid of the same makeup. Although they
of Powdered Ion Exchange Resins
cannot accurately predict performance during condenser leaks,
E200 Practice for Preparation, Standardization, and Stor-
thesetestmethodsareusefulfordeterminingoperatingcapaci-
age of Standard and Reagent Solutions for Chemical
ties as measured under the test conditions used.
Analysis
4.3 These test methods may be used to monitor the perfor-
mance of either powdered anion-exchange resin or powdered
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on
cation-exchange resin. The total capacity of either resin de-
Water and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.08 on Membranes and
pendsprimarilyuponthenumberdensityofion-exchangesites
Ion Exchange Materials.
within the resin. The operating capacity is a function of the
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2007. Published January 2008. Originally
total capacity, degree of conversion to the desired ionic form
approved in 1983. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D4266–96 (2001).
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
when received, and properties of the resin and the system that
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
affect ion exchange kinetics.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 4266–96 (2007)
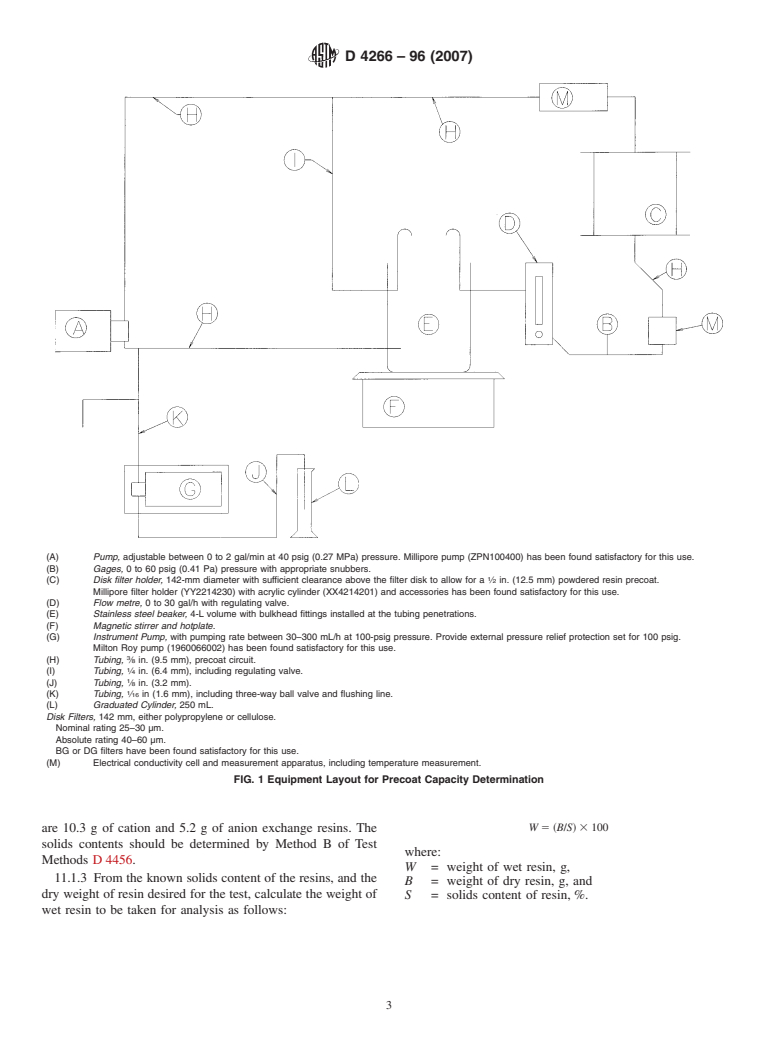
5. Purity of Reagents 9.1.3 Disk Filter Holder, 142-mm diameter with sufficient
clearance above the filter disk to allow for uniform application
5.1 Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests.
of resin precoat.
Unlessotherwiseindicated,itisintendedthatallreagentsshall
9.1.4 Filter-Disk, 142-mm diameter, with nominal retention
conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical
rating of 25 to 30 µm and absolute retention rating of 40 to
Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such
60µm.
specifications are available.
9.1.5 Flow Metre, 0 to 1.89 L/min (0 to 30 gal/h) with
5.2 Purity of Water—Unlessotherwiseindicated,references
regulating valve.
to water shall be understood to mean Type II reagent water,
9.1.6 Beaker, stainless steel, 4 L to volume with bulkhead
Specification D1193.
fittings installed at tubing penetrations.
9.1.7 Chemical Pump, with pumping rate between
6. Sampling
−6 −5
8.33 3 10 and 8.33 3 10 L/s (30 to 300 mL/h) at
6.1 Obtain a representative sample of the powdered ion-
3.45 310 Pa (500 psig) pressure. Suction tubing should be
exchange resin in accordance with Practices D2687 but
3.2-mm ( ⁄8-in.) outside diameter stainless steel and discharge
substituting a 12.5-mm ( ⁄2-in.) inside diameter tube.
tubing should be 1.6-mm ( ⁄16-in.) outside diameter stainless
steel.
TEST METHOD A—OPERATING CAPACITY,
9.2 Electrical Conductivity Measurement Apparatus, con-
ANION-EXCHANGE RESIN, HYDROXIDE FORM
forming to the requirements given in Test Methods D1125,
Method B.
7. Scope
7.1 This test method covers the determination of ion-
10. Reagents
exchange capacity, on a dry weight basis, of new powdered
10.1 Hydrochloric Acid Solution, Standard (0.10 N)—
anion-exchange resins in the hydroxide form.
Prepare and standardize as described in Practice E200.
7.2 The ion-exchange capacity obtainable in commercial
10.2 Polyacrylic Acid Solution, Standard (1+99)—Pipet 1
installations depends not only upon the initial state of the
mL of polyacrylic acid (25 weight% solids, MW<50 000)
powdered resin, but also on how the resin floc is prepared and
into a 100 mL volumetric flask and dilute to 100 mL with
applied, on the condition of the equipment on which it is to be
water. Mix well. Prepare this solution fresh daily.
used, and the pH and general chemistry of the water system
being treated. Thus, this test method has comparative rather
11. Sample Preparation
than predictive value and provides an upper limit on exchange
11.1 Selection of Proper Sample Weight—Use a resin dos-
capacity that may be expected.
2 2
age of 1 kg/m (0.2 lb/ft ) and a resin ratio of 2+1.
11.1.1 If the purpose of the capacity test is to eliminate the
8. Summary of Test Method
resin as a consideration in a situation involving a performance
8.1 The powdered anion-exchange resin to be tested is
problem in a commercial plant, then the capacity test may be
slurried with an appropriate amount of powdered cation-
performed using the same wet resin ratio and the same resin
exchange resin in the hydrogen form, and the resulting floc is
dosage as is used in the commercial equipment.
precoatedontoafilterdisk.Thenadilutestandardizedsolution
2 2
11.1.2 Using a resin dosage of 1 kg/m (0.2 lb/ft ), the
of a strong acid is fed to the precoat while monitoring the
correct dry weight of resin to be used on a 142-mm diameter
effluent stream conductometrically.
filter is 15.5 g. At a resin ratio of 2+1, the dry weights to use
9. Apparatus
9.1 Test apparatus, as shown in Fig. 1, with the following
The sole source of supply of the Millipore filter holder (YY2214230) with
components:
acryliccylinder(XX4214201)andaccessoriesapparatusknowntothecommitteeat
9.1.1 Water Pump—adjustable between 0 to 7.57 L/min (0
this time is the Millipore Corporation, 290 Concord Rd., Billerica, MA 01821. If
you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM
to 2 gal/min) at 2.76 310 Pa (40 psig) pressure.
5 International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a
9.1.2 Pressure Gages (two), 0 to 4.137 310 Pa (0 to 60
meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
psig) with appropriate snubbers.
The sole source of supply of the BG or DG filter apparatus known to the
committee at this time is the Pall Corporation, 30 Sea Cliff Ave., Glen Cove, NY
11542. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to
ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consider-
Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American ation at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not The sole source of supply of the Milton Roy pump (1960066002) apparatus
listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory known to the committee at this time is Milton Roy USA, 201 Ivyland Rd., Ivyland,
Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia PA18974. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information
and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville, to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consid-
MD. erationatameetingoftheresponsibletechnicalcommittee, whichyoumayattend.
4 8
The sole source of supply of the Millipore pump (ZPN100400) apparatus The sole source of supply of the Accumer (1510) apparatus known to the
knowntothecommitteeatthistimeistheMilliporeCorporation,290ConcordRd., committee at this time is the Rohm and Haas Company, 100 Independence Mall
Billerica, MA 01821. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this West, Philadelphia, PA 19106. If you are aware of alternative sup
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.