ASTM E2021-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Hot-Surface Ignition Temperature of Dust Layers
Standard Test Method for Hot-Surface Ignition Temperature of Dust Layers
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is applicable to dusts and powders, and provides a procedure for performing laboratory tests to evaluate hot-surface ignition temperatures of dust layers.
5.2 The test data can be of value in determining safe operating conditions in industrial plants, mines, manufacturing processes, and locations of material usage and storage.
5.3 Due to variation of ignition temperature with layer thickness, the test data at one thickness may not be applicable to all industrial situations (see Appendix X1). Tests at various layer thicknesses may provide a means for extrapolation to thicker layers, as listed in the following for pulverized Pittsburgh bituminous coal dust (2). Mathematical modeling of layer ignition at various layer thicknesses is described in Ref. (3).
Layer Thickness, mm
Hot-Surface Ignition Temperature, °C
6.4
300
9.4
260
12.7
240
25.4
210
5.4 This hot plate test method allows for loss of heat from the top surface of the dust layer, and therefore generally gives a higher ignition temperature for a material than Test Method E771, which is a more adiabatic system.
5.5 This test method for dust layers generally will give a lower ignition temperature than Test Method E1491, which is for dust clouds. The layer ignition temperature is determined while monitoring for periods of minutes to hours, while the dust cloud is only exposed to the furnace for a period of seconds.
Note 1: Much of the literature data for layer ignition is actually from a basket in a heated furnace (4), known as the modified Godbert-Greenwald furnace test. Other data are from nonstandardized hot plates (5-9).
5.6 Additional information on the significance and use of this test method may be found in Ref. (10).
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure to determine the hot-surface ignition temperature of dust layers, that is, measuring the minimum temperature at which a dust layer will self-heat. The test consists of a dust layer heated on a hot plate.2,3
1.2 Data obtained from this test method provide a relative measure of the hot-surface ignition temperature of a dust layer.
1.3 This test method should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials in response to heat and flame under controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire hazard risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test method may be used as elements of a fire risk assessment that takes into account all of the factors that are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard risk of a particular end use product.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 8.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E2021 − 15
Standard Test Method for
1
Hot-Surface Ignition Temperature of Dust Layers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2021; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
4
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure to 2.1 ASTM Standards:
E771 Test Method for Spontaneous Heating Tendency of
determine the hot-surface ignition temperature of dust layers,
5
that is, measuring the minimum temperature at which a dust Materials (Withdrawn 2001)
E1445 Terminology Relating to Hazard Potential of Chemi-
layer will self-heat. The test consists of a dust layer heated on
2,3
a hot plate. cals
E1491 Test Method for Minimum Autoignition Temperature
1.2 Data obtained from this test method provide a relative
of Dust Clouds
measure of the hot-surface ignition temperature of a dust layer.
6
2.2 IEC Standard:
1.3 This test method should be used to measure and describe
IEC 1241-2-1 Electrical Apparatus for Use in the Presence
the properties of materials in response to heat and flame under
of Combustible Dust; Part 2: Test Methods—Section 1:
controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to
Methods for Determining the Minimum Ignition Tempera-
describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire hazard risk of
tures of Dusts, Method A
materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
However, results of this test method may be used as elements
3. Terminology
of a fire risk assessment that takes into account all of the factors
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of other terms used in this
that are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard risk of a
standard, see Terminology E1445.
particular end use product.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.2.1 hot-surface ignition temperature of a dust layer,
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
n—lowest set temperature of the hot plate that causes ignition
standard.
of the dust layer.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.2 ignition of a dust layer, n—initiation of self-heating or
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
combustion in a material under test.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.3 ignition time, n—time between the start of heating and
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau- the point at which the maximum temperature or flaming
combustion is reached.
tionary statements are given in Section 8.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.2.4 temperature rise, ΔT, n—the difference between T
max
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
and the initial set temperature of the hot plate.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.2.5 T , n—maximum temperature measured during test.
max
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4. Summary of Test Method
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.1 The test material is placed within a metal ring on top of
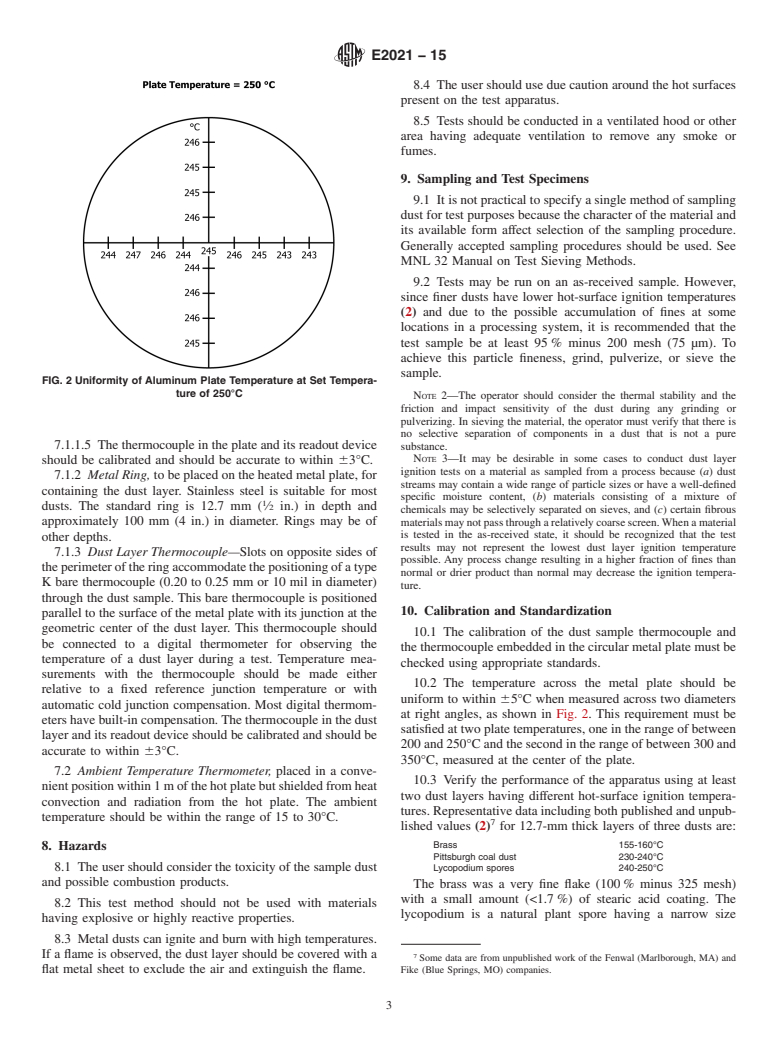
a hot plate, that is at a preset constant temperature.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E27 on Hazard
Potential of Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E27.04 on
4
the Flammability and Ignitability of Chemicals. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved July 1, 2015. Published July 2015. Originally approved contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as E2021 – 09 (2013). DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/E2021-15. the ASTM website.
2 5
This test method is based on recommendations of the National Materials The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
3
Advisory Board of the National Academy of Sciences (1). www.astm.org.
3 6
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
this standard. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2021 − 15
NOTE 1—Much of the literature data for layer ignition is actually fro
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2021 − 09 (Reapproved 2013) E2021 − 15
Standard Test Method for
1
Hot-Surface Ignition Temperature of Dust Layers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2021; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure to determine the hot-surface ignition temperature of dust layers, that is,
2,3
measuring the minimum temperature at which a dust layer will self-heat. The test consists of a dust layer heated on a hot plate.
1.2 Data obtained from this test method provide a relative measure of the hot-surface ignition temperature of a dust layer.
1.3 This test method should be used to measure and describe the properties of materials in response to heat and flame under
controlled laboratory conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire hazard or fire hazard risk of materials,
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of this test method may be used as elements of a fire risk
assessment that takes into account all of the factors that are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard risk of a particular end
use product.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 8.
2. Referenced Documents
4
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5
E771 Test Method for Spontaneous Heating Tendency of Materials (Withdrawn 2001)
E1445 Terminology Relating to Hazard Potential of Chemicals
E1491 Test Method for Minimum Autoignition Temperature of Dust Clouds
6
2.2 IEC Standard:
IEC 1241-2-1 Electrical Apparatus for Use in the Presence of Combustible Dust; Part 2: Test Methods—Section 1: Methods for
Determining the Minimum Ignition Temperatures of Dusts, Method A
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of other terms used in this standard, see Terminology E1445.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 hot-surface ignition temperature of a dust layer, n—lowest set temperature of the hot plate that causes ignition of the dust
layer.
3.2.2 ignition of a dust layer, n—initiation of self-heating or combustion in a material under test.
3.2.3 ignition time, n—time between the start of heating and the point at which the maximum temperature or flaming combustion
is reached.
3.2.4 temperature rise, ΔT, n—the difference between T and the initial set temperature of the hot plate.
max
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E27 on Hazard Potential of Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E27.04 on the
Flammability and Ignitability of Chemicals.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2013July 1, 2015. Published October 2013July 2015. Originally approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 20092013 as
E2021 – 09.E2021 – 09 (2013). DOI: 10.1520/E2021-09R13.10.1520/E2021-15.
3
2
This test method is based on recommendations of the National Materials Advisory Board of the National Academy of Sciences (1).
3
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of this standard.
4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
5
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
6
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2021 − 15
3.2.5 T , n—maximum temperature measured during test.
max
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The test material is placed within a metal ring on top of a hot plate, that is at a preset constant temperature.
4.2 The sample temperature is monitored to determine t
...








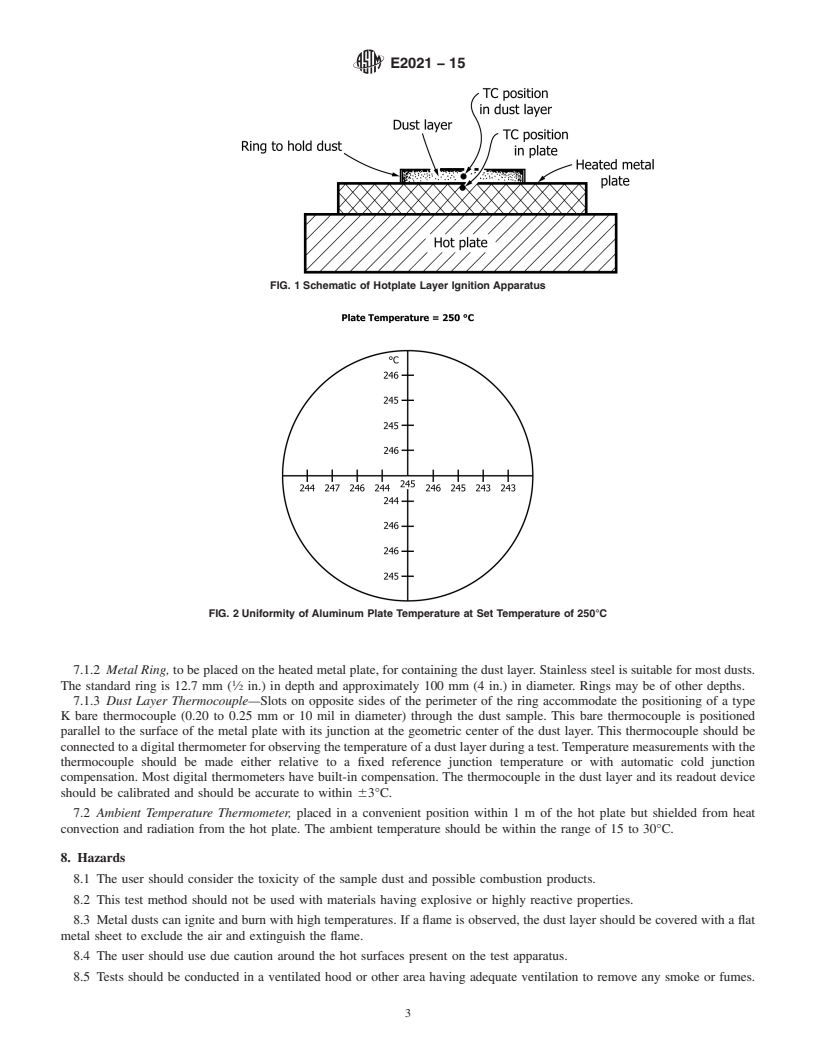
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.